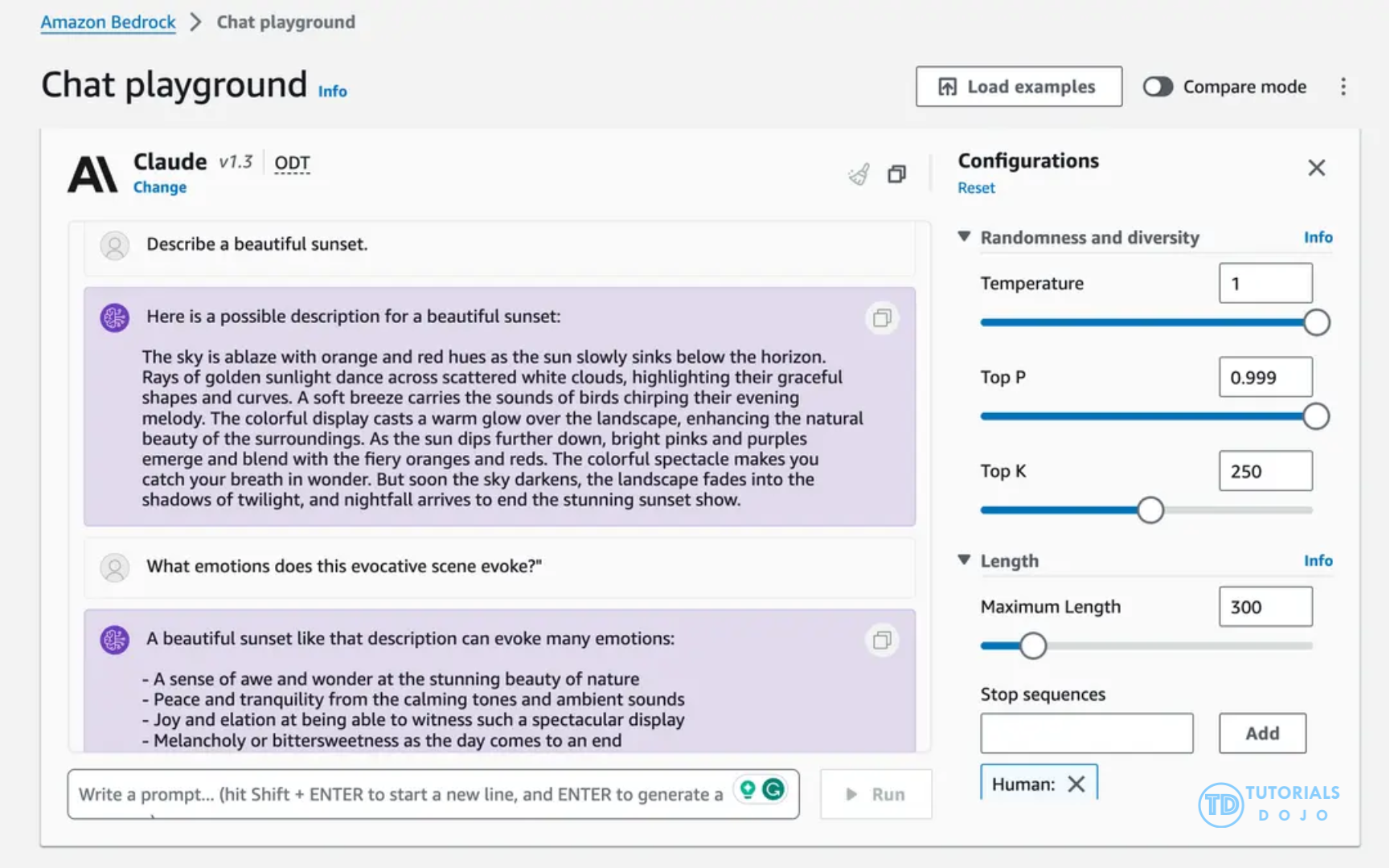
Prompt Engineering
Prompt Engineering
- developing, designing, and optimizing prompts to enhance the output of FMs for your needs
- Improved Prompting technique consists of:
- Instructions – a task for the model to do (description, how the model should perform)
- Context – external information to guide the model
- Input data – the input for which you want a response
- Output Indicator – the output type or format
- Negative Prompting
- A technique where you explicitly instruct the model on what not to include or do in its response
- Negative Prompting helps to:
- Avoid Unwanted Content
- Maintain Focus
- Enhance Clarity – prevents the use of complex terminology or detailed data, making
the output clearer and more accessible

Prompt Performance Optimization
- System Prompts – how the model should behave and reply
- Temperature (0 to 1) – creativity of the model’s output
- Low (ex: 0.2) – outputs are more conser vative, repetitive, focused on most likely response
- High (ex: 1.0) – outputs are more diverse, creative, and unpredictable, maybe less coherent
- Top P (0 to 1)
- You set a value for “p” (e.g., 0.9). The model considers the most probable tokens in order until their probabilities add up to or exceed ‘p’.
- Low P (ex: 0.25) – consider the 25% most likely words, will make a more coherent response
- High P (ex: 0.99) – consider a broad range of possible words, possibly more creative and diverse output
- You set a value for “p” (e.g., 0.9). The model considers the most probable tokens in order until their probabilities add up to or exceed ‘p’.
- Top K – limits the number of probable words
- The model selects the next word from a fixed number of the most probable options
- During generation, the model predicts a probability distribution over the vocabulary for the next token. Instead of sampling from the entire vocabulary, Top K sampling only considers the top K most probable tokens. For instance, if K = 50, only the 50 most probable tokens are considered, and the rest are discarded. The model then randomly selects one of these tokens based on their probabilities.
- Low K (ex: 10) – more coherent response, less probable words
- High K (ex: 500) – more probable words, more diverse and creative
- Length – maximum length of the answer
- Stop Sequences – tokens that signal the model to stop generating output
- Temperature (higher) increases variety, while Top-P (lower) and Top-K (lower) reduce variety and focus samples on the model’s top predictions.
- [ 🧐QUESTION🧐 ] produce responses that are more consistent, deterministic, and less random Storage
- Lower temperature
- controls the randomness of the model’s output
- Lower top_k
- limits the number of most probable tokens the model considers at each step, leading to more focused outputs.
- Higher top_p
- works similarly but dynamically selects tokens based on cumulative probability, allowing more flexibility in response generation
- adjusts the model’s options based on the probability threshold, resulting in slightly different behavior.
- Lower temperature
Latency
- how fast the model responds
- impacted by a few parameters:
- The model size
- The model type itself (Llama has a different performance than Claude)
- The number of tokens in the input (the bigger the slower)
- The number of tokens in the output (the bigger the slower)
- Latency is not impacted by Top P, Top K, Temperature
Zero-Shot Prompting
- Present a task to the model without providing examples or explicit training for that specific task
- fully rely on the model’s general knowledge
- The larger and more capable the FM, the more likely you’ll get good results
Few-Shots Prompting
- Provide examples of a task to the model to guide its output
- We provide a “few shots” to the model to perform the task
- If you provide one example only, this is also called “one-shot” or “single-shot”
Chain of Thought Prompting
- Divide the task into a sequence of reasoning steps, leading to more structure and coherence
- Using a sentence like “Think step by step” helps
- Helpful when solving a problem as a human usually requires several steps
- Can be combined with Zero-Shot or Few-Shots Prompting
- Guides the model to reason step by step before providing a final answer. Instead of directly asking for a conclusion, the prompt encourages the model to explicitly articulate intermediate steps, which improves accuracy and transparency, particularly for multi-step or logical tasks. In the context of financial reasoning, this ensures that each calculation or decision point is visible, making outputs verifiable by auditors or clients and reducing the risk of errors in critical decision-making.
Structured reasoning techniques, such as chain-of-thought instruction patterns, help guide a foundation model through step-by-step analysis and ensure the model forms conclusions in a clear and logically connected manner. By directing the model to reveal or follow intermediate reasoning steps, assessments become more consistent and easier to validate. Amazon Bedrock supports this prompting approach by allowing detailed instructions within the prompt that encourage deeper reasoning instead of shallow pattern matching. This approach helps stabilize the model’s interpretation when working with dense financial disclosures or complex regulatory structures, which naturally require multi-step understanding.
A structured prompt workflow further strengthens model performance by presenting information in a well-organized and predictable format. Separating context, metadata, document sections, constraints, and output expectations allows the model to understand how different pieces of input relate to one another. Amazon Bedrock provides support for this design through prompt templates and structured formatting patterns that help teams build clear and repeatable input pipelines. By giving the model a stable structure, ambiguity is reduced and the likelihood of inconsistent or disjointed assessments is minimized, especially when handling multi-section filings or layered disclosure narratives.
When combined, these two methods offer a cohesive way to resolve the integration challenges described in the scenario. Chain of thought instruction patterns improve the quality of the model’s reasoning across intricate financial content, while structured prompt workflows introduce the clarity and organization needed for predictable output generation. Together, they create a more reliable and explainable interaction between the reporting engine and the foundation model in Amazon Bedrock, ultimately resulting in more consistent, high-quality regulatory assessments.
Agentic AI
Agents in Bedrock
- Giving tools to your LLM!
- The LLM is given discretion on which tools to use for what purpose
- The agent has a memory, an ability to plan how to answer a request, and tools it can use in the process.
- In practice, the “memory” is just the chat history and external data stores, and the “planning module” is guidance given to the LLM on how to break down a question into sub-questions that the tools might be able to help with.
- Prompts associated with each tool are used to guide it on how to use its tools.
- “Tools” are just functions provided to a tools API.
- In Bedrock, this can be a Lambda function.
- Prompts guide the LLM on how to use them.
- Tools may access outside information, retrievers, other Python modules, services, etc.
- How
- Start with a foundational model to work with
- In Bedrock, “Action Groups” define a tool
- A prompt informs the FM when to use it
- “Use this function to determine the current weather in a city”
- You must define the parameters your tool (Lambda function) expects
- Define name, description, type, and if it’s required or not
- The description is actually important and will be used by the LLM to extract the
required info from the user prompt - You can also allow the FM to go back and ask the user for missing information it needs for a tool
- This can be done using OpenAI-style schemas, or visually with a table in the Bedrock
UI
- A prompt informs the FM when to use it
- Agents may also have knowledge bases associated with them
- Again, a prompt tells the LLM when it should use it
- “Use this for answering questions about X”
- This is “agentic RAG” – RAG is just another tool
- Again, a prompt tells the LLM when it should use it
- Optional “Code Interpreter” allows the agent to write its own code to answer questions or produce charts.
- Deploying
- Create an “alias” for an agent
- This creates a deployed snapshot
- On-Demand throughput (ODT)
- Allows agent to run at quotas set at the account level
- Provisioned throughput (PT)
- Allows you to purchase an increased rate and number of tokens for your agent
- Your application can use the InvokeAgent request using your alias ID and an Agents
for Amazon Bedrock Runtime Endpoint.
- Create an “alias” for an agent
Multi-agent workflows
- Similar to just giving tools to a single agent
- But many tools may be used at once
- For example, coding agents may need to operate on multiple files in different ways to achieve a larger task
- Workflows that require complex decision making can benefit from these agents (otherwise, keep it simple with deterministic workflows.)
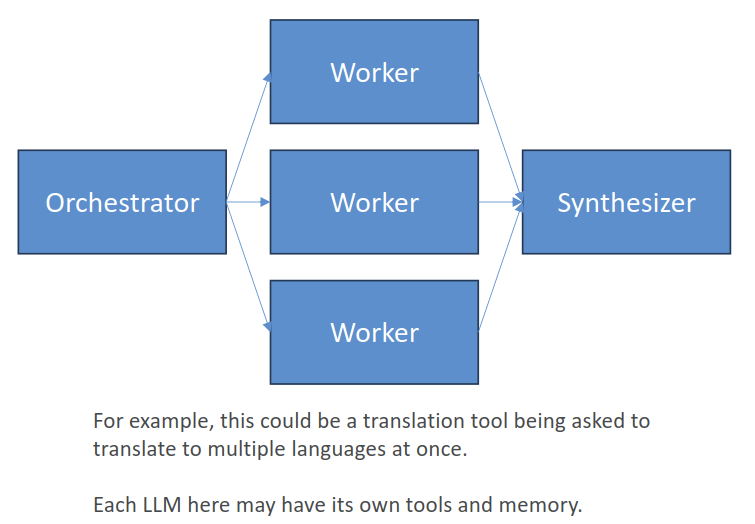
- The Orchestrator breaks down tasks and delegates them to worker LLM’s
- A Synthesizer can then combine their results
- When to use
- Too many tools
- If one agent has trouble choosing the appropriate tool, multiple specialized agents with specific tools might work better
- Complex logic
- Prompts get too complicated with conditional statements, better to define the flow with specialized agents
- Too many tools
- Routing
- A “router” LLM chooses just one of many specialized agents to call in turn
- Use for complex tasks where a single classification is needed
- i.e., how large of a model is needed for the task
- What kind of customer service query is being received
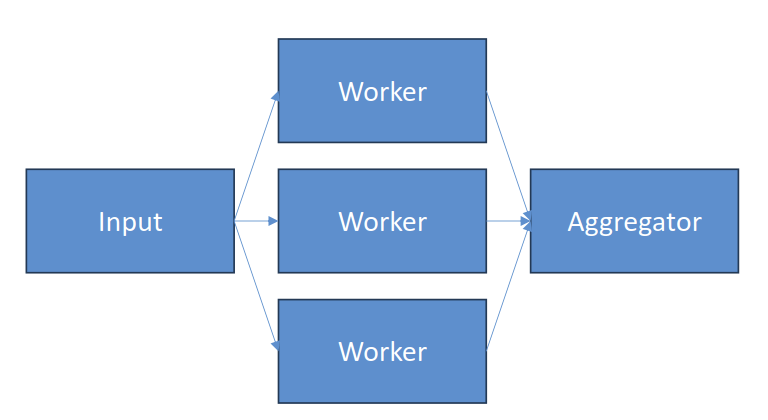
- Parallelization
- A lot like the orchestrator
- But without complex orchestration
- Sectioning: independent subtasks run in parallel
- Running multiple guardrails at once
- Running multiple evaluations at once
- Voting
- Do the same thing with different models or prompts
- Let them vote on the right result
- A lot like the orchestrator
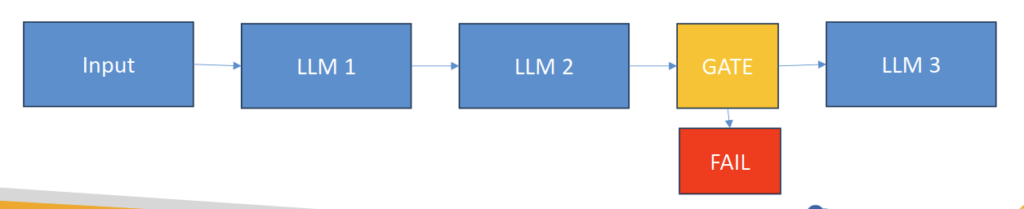
- Prompt Chaining
- Use when a task has a discrete sequence of known steps
- Each LLM processes the output of the previous one
- Can add “gates” to keep things on track as you go, or exit early
- Examples
- Write a document, then translate it to different languages
- Write an outline, then make slides
- Evaluator – Optimizer
- One LLM generates a response
- Another evaluates that response
- If it’s not good enough, provide feedback and try again
- Examples
- Code reviewing code and incorporating those recommendations
- Complex search that requires multiple rounds
- Adding Memory
- Short-term
- Chat history within a session / immediate context
- Enables conversations
- Events within sessions
- This could be in-memory or in a big distributed cache
- Elasticache, MemoryDB, even DynamoDB is OK
- Long-term
- Stores “extracted insights”
- Summaries of past sessions
- Preferences (your coding style and favorite tools, for example)
- Facts you gave it in the past
- “Memory Records” that store structured information derived from agent interactions
- “Strategies” for user preferences, semantic facts, session summaries
- This all needs to be stored somewhere!
- Long-term: DynamoDB, SQLLite, RDS, Aurora, etc.
- AgentCore Memory
- Mem0 (Strands uses this)
- You could frame Knowledge Bases as a form of long-term memory too.
- Short-term
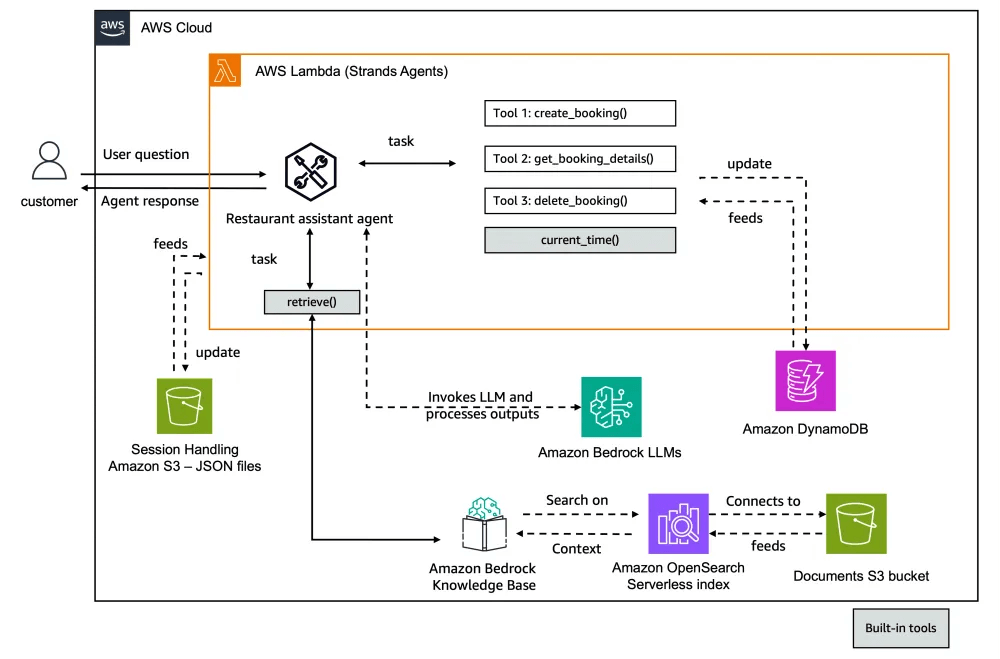
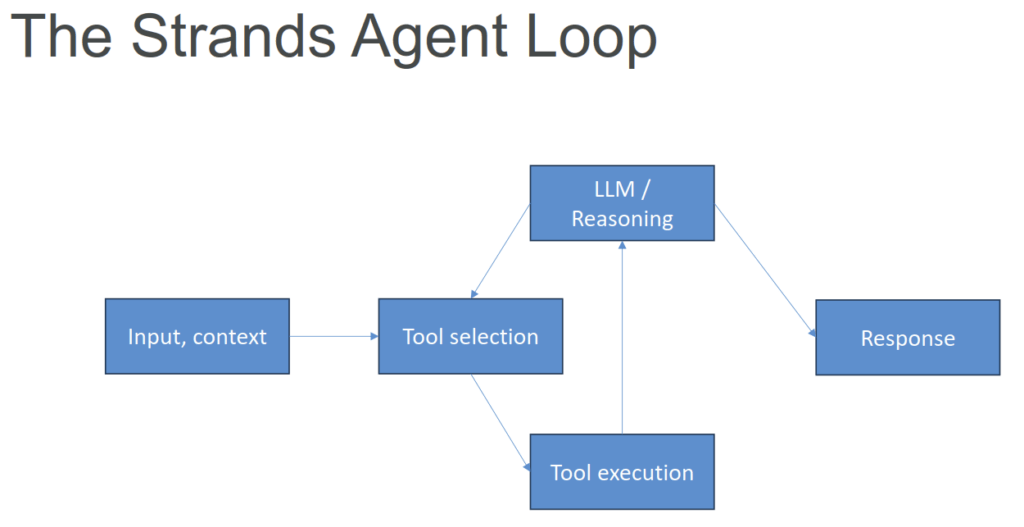
Strands Agents
- Another Agents Python SDK (like OpenAI Agents SDK, CrewAI, LangGraph, Google ADK)
- Released by Amazon as open source
- You can create specialized agents and multi-agent systems
- Complex task decomposition
- Collaborative problem solving
- Of course it has tighter AWS integration
- Bedrock models, Lambda, Step Functions, and more
- But it’s not tied to AWS
- You can use it with OpenAI and others if you want to
- Multimodal support (text, speech, images, video)
- MCP (Model Context Protocol) support
AWS Agent Squad
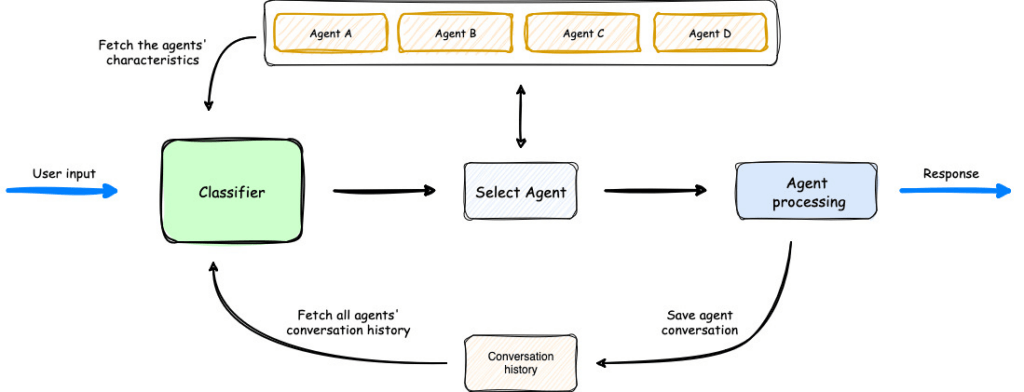
- Another open-sourced framework for multi-agent workflows
- https://github.com/awslabs/agent-squad
- Intelligent intent classification
- Routes queries to the right agent
- Python and TypeScript
- Shares contexts across agents
- Many pre-built agents and classifiers
- Integrates with Bedrock Agents
- Can extend Bedrock Flows
- Conversation memory, orchestration
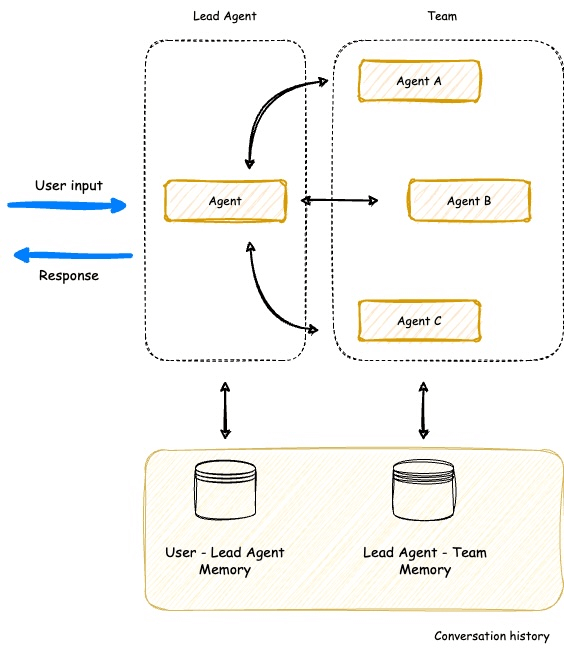
- Supervisor Agent
- Coordinates multiple specialized agents (like Strands!)
- Agent Squad is focused on routing, Strands on tool use in a single agent loop
| Framework | AWS integration | Autonomous multi-agent support | Autonomous workflow complexity | Multimodal capabilities | Foundation model selection | LLM API integration | Production deployment |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| Amazon BedrockAgents | Strongest | Adequate | Adequate | Strong | Strong | Strong | Fully managed |
| AutoGen | Weak | Strong | Strong | Adequate | Adequate | Strong | Do it yourself (DIY) |
| CrewAI | Weak | Strong | Adequate | Weak | Adequate | Adequate | DIY |
| LangChain/LangGraph | Adequate | Strong | Strongest | Strongest | Strongest | Strongest | Platform or DIY |
| Strands Agents | Strongest | Strong | Strongest | Strong | Strong | Strongest | DIY |
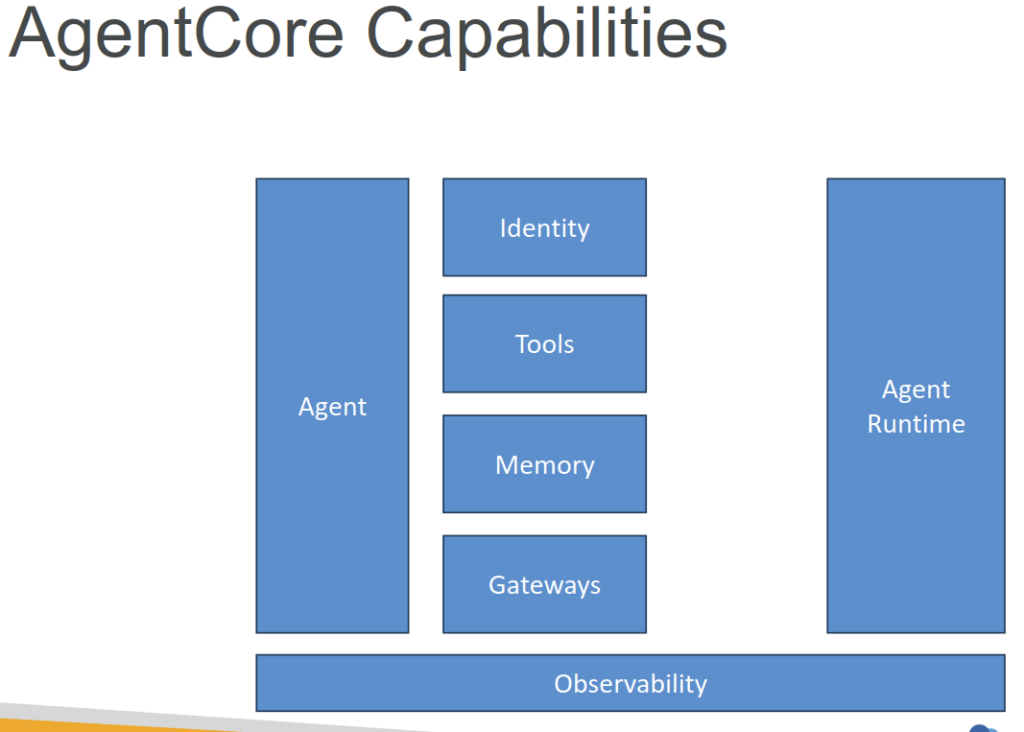
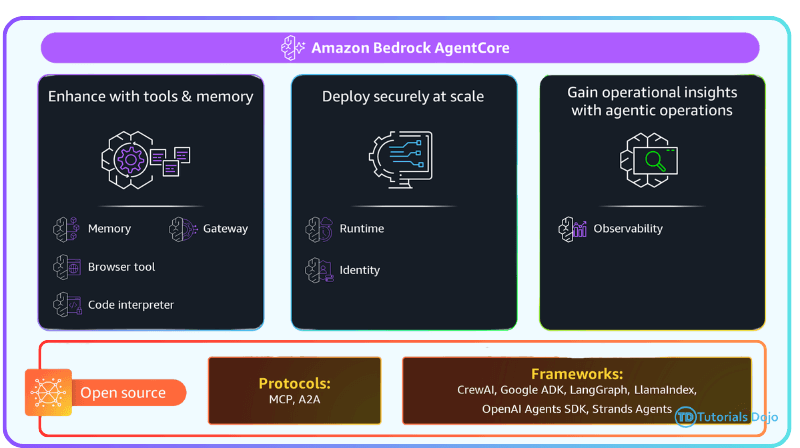
Bedrock AgentCore
- Hands deployment and operation of AI agents at scale
- No fussing with Docker, ECR, ECS, etc
- Serverless
- And it works with ANY agent framework
- You aren’t tied to Bedrock agents
- You aren’t even tied to AWS’s Strands framework
- OpenAI Agent SDK, LangGraph / LangChain, CrewAI, whatever
- (although… Strands does get better support…)
- Includes a “starter toolkit” to make deployment of agents to AWS super easy
- Includes several tools and capabilities you can include in your agents
- Agent Runtime
- Serverless endpoints
- Deploy your agent to ECR, enhanced with AgentCore capabilities
- “Starter toolkit” manages it all for you, using CodeBuild
- But you can build your own Docker containers if you want
- Can have multiple endpoints
- Observability dashboard lets you track usage and performance
- Through “GenAI Observability” feature in CloudWatch
- Adding Memory
- Short-term
- Chat history within a session / immediate context
- Enables conversations
- API centered around Session objects that contain Events
- Long-term
- Stores “extracted insights”
- Summaries of past sessions
- Preferences (your coding style and favorite tools, for example)
- Facts you gave it in the past
- API involves “Memory Records” that store structured information derived from agent interactions
- “Strategies” for user preferences, semantic facts, session summaries
- This all needs to be stored somewhere!
- The OpenAI Agents SDK gives you a SQLLite implementation
- But maybe you need something that scales better, and is serverless
- Enter AgentCore Memory
- Short-term
- Built-In Tools
- Browser Tool, Allows control of your browser to interact with the web
- Code Interpreter, Lets you run code (in an isolated container) Python, JavaScript, TypeScript
- Importing Bedrock Agents
- Bedrock has its own system for endpoints…
- Importing is just a matter of running agentcore import-agent
- This generates Strands code (or LangChain / LangGraph) in an output directory
- From there you can test or deploy it like any other AgentCore agent
- Gateway
- Addresses the problem of using external tools at scale
- Convert APIs, Lambda functions, or other services into MCP tools
- Targets can be OpenAPI (REST), Smithy models (that’s an AWS thing),
or Lambda
- Targets can be OpenAPI (REST), Smithy models (that’s an AWS thing),
- Agents can then access them through Gateway endpoints
- Manages OAuth security / credentials
- Semantic tool selection
- Identity
- This is different from OAuth identity for users and connecting to services
- This is about your agent’s identity / identities
- Secure access to external tools and AWS services
- Central repository for all of your agent identities
- Similar to a Cognito user pool
- Secure credential storage
- OAuth 2.0 support
- Built-in support for Google, GitHub, Slack, Salesforce, Atlassian
- allows inbound authentication via OpenID Connect (OIDC).
- By configuring AgentCore Identity as an inbound provider, the system validates JWT tokens issued by an external corporate identity provider (IdP) before the AI agent can process any request. The “allowed audiences” configuration ensures that only tokens for the specified application ID are accepted, providing fine-grained access control and reducing the risk of unauthorized use.
- It ensures that only authenticated and authorized users can access the AI agent, without relying solely on AWS IAM credentials. AgentCore Identity also integrates seamlessly with outbound OAuth flows, enabling agents to securely access other AWS services and APIs while keeping user access tightly controlled.
- Agent Core memory in Amazon Bedrock refers to the system’s RAM to process and manage data while executing these generative AI models. It stores active data such as input queries, model parameters, and intermediate results. Memory is essential for handling multiple requests simultaneously, particularly in high-demand applications like customer support chatbots.
- To resolve memory-related performance degradation in Amazon Bedrock, the solution is to expand the memory capacity of the Amazon Bedrock AgentCore agent. Increasing memory allows the system to handle larger datasets, more complex queries, and higher volumes of requests without degrading performance, ensuring better stability and responsiveness during peak usage.
- [ NOT ] Increase the number of Bedrock AgentCore agent instances is only a scaling solution, which may distribute the load.
- [ NOT ] Add more processing power to the Bedrock AgentCore agent is primarily a solution for improving the speed of computations.
- [ NOT ] Upgrade the storage capacity of the Bedrock AgentCore agent focuses on expanding storage.
- [ 🧐QUESTION🧐 ] AgentCore with Context and Session Storage
- Bedrock AgentCore serves as the reasoning and orchestration layer, enabling the assistant to interpret natural language requests, make decisions, and perform structured operations against backend systems. Instead of hardcoding workflows or intent trees, the agent can dynamically plan steps, invoke services, and return meaningful results to customers through natural conversation. This approach significantly improves automation accuracy, scalability, and user experience while reducing the need for manual rule creation.
- Amazon DynamoDB works alongside AgentCore as the context persistence and session storage layer. It provides a secure, low-latency database for storing user sessions, conversation history, and transaction data. With its serverless architecture, DynamoDB can scale automatically to handle thousands concurrent users while maintaining millisecond performance. Its encryption, access control, and built-in backup features ensure that sensitive customer data is stored in compliance with privacy and corporate policies. This makes DynamoDB ideal for storing agent memory and real-time state information needed in multi-turn conversations.
- [ NOT ] Use Amazon Kendra to search for answers to product manuals and FAQs. Combined with AWS Lambda to manage refund requests and data updates is incorrect.
- This approach uses Amazon Kendra and AWS Lambda, primarily focusing on information retrieval and lightweight automation. While Kendra excels at semantic search across product manuals, FAQs, and internal documents, it cannot manage multi-turn conversational context or execute reasoning-based workflows.
- [ NOT ] Use Amazon Titan Text G1 for conversation handling and maintain customer session states in a Python dictionary within the application memory for short-term interactions is incorrect.
- Using Amazon Titan Text G1 alone for conversation handling would provide natural language understanding and generation without the ability to plan, reason, or interact with backend systems. Storing session data in a Python dictionary is only suitable for temporary, in-memory processing during a single session and cannot handle multi-user or persistent conversations. This setup would break when scaled, as it lacks secure data management and enterprise-grade reliability.
- [ NOT ] Use Amazon Lex V2 to build a conversational chatbot for customer interactions and store conversation transcripts in Amazon S3 for historical analysis is incorrect.
- Amazon Lex V2 is primarily designed to build rule-based conversational bots that use predefined intents and slot-filling to respond to user inputs. While it can automate simple interactions, it lacks the generative reasoning and multi-step planning required for complex workflows such as personalized product recommendations or refund processing. Lex also does not natively manage context beyond basic session attributes, and storing transcripts in Amazon S3 would only support historical record-keeping, not active memory or dynamic context management.
- [🧐QUESTION🧐 ] Bedrock AgentCore Capabilities
- Gateway
- establishes a decision layer that evaluates incoming requests and applies predefined routing logic to determine which model, tool, or agent component should process the workload.
- plays a central role in request governance by acting as a decision point that evaluates inbound requests and selects the proper processing path. This design allows organizations to enforce routing policies, integrate business rules, and maintain consistency across multiple models or agent components. For large-scale or regulated environments, having a centralized routing mechanism helps ensure predictable execution, improved maintainability, and better control over how workloads move through the system.
- Observability
- provides visibility into agent execution, trace data, and operational behavior. While observability tools are valuable for debugging and performance analysis, they do not determine routing logic, maintain interaction context, or enforce user-level access boundaries. It is typically used for monitoring and troubleshooting rather than orchestrating functional behavior within an AI workflow.
- Memory
- provides a mechanism for persisting relevant interaction details so the platform can maintain continuity and refer back to important information in subsequent exchanges.
- introduces a structured way for agents to work with contextual information across interactions. Instead of treating each request as an isolated event, developers can configure memory behaviors that allow agents to recall and incorporate previously observed details into future responses. This is especially valuable in enterprise workflows where continuity—such as recalling user preferences, previous task steps, or prior tool outputs—improves accuracy and reduces repetitive interactions. By managing contextual state at scale, AgentCore Memory enhances the overall intelligence and adaptability of the system.
- Code Interpreter
- a tool that executes code in a controlled environment to help an agent perform tasks such as calculations, data manipulation, or lightweight analysis. It does not evaluate requests, maintain past interaction details, or manage user-specific restrictions. This capability supports tool execution, not foundational operational controls.
- Browser Tool
- enables an agent to perform web browsing tasks, retrieve online data, or gather external information needed for reasoning. While useful for augmenting the agent’s knowledge, it does not influence routing, state retention, or identity handling. This tool is primarily designed for information retrieval and does not manage architectural-level responsibilities in the system.
- Identity
- enforces user-level context by determining which role, permissions, and access boundaries apply before any reasoning or tool use is performed by the system.
- ensures that every interaction occurs within the correct user-access boundary. In multi-tenant or highly regulated environments, the system must confirm which permissions, roles, or policies apply before allowing an agent to perform reasoning or invoke tools. AgentCore Identity provides the mechanism for enforcing these rules, ensuring that AI-driven operations respect organizational security requirements. This capability helps prevent unauthorized access, supports compliance objectives, and gives teams confidence that generative AI components operate with proper isolation
- Gateway
Model Context Protocol (MCP)
- Standardized interface for agent-tool interactions
- “Like a USB-C port for AI Applications” – Anthropic
- Technically the data layer is JSON-RPC 2.0
- Transport is stdio or HTTP streaming
- Access external tools with consistent interaction patterns
- Standardizes how apps provide context to LLM’s
- Pretty much any agent SDK can call external MCP servers (including Strands)
- Servers may expose tools, resources, and prompts
- Some popular MCP servers:
- GitHub, Atlassian, PostgreSQL, Slack, Google Maps… even Udemy!
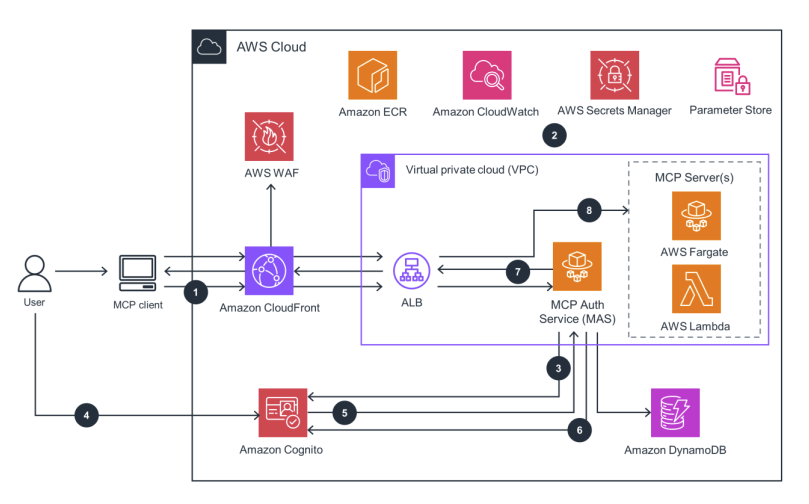
- Deploying your Own MCP Server
- For stateless, lightweight access:
- AWS Lambda
- For complex tools:
- Amazon ECS
- Or Fargate
- Amazon ECS
- API Gateway
- Can also expose MCP endpoints
- Use MCP client libraries
- Abstract away the complexities of the protocol, don’t re-invent the wheel!
- You can also deploy MCP servers with AgentCore
- For stateless, lightweight access:
OpenAPI and GenAI
- Originally Swagger – a spec for defining interfaces for web services
- Can also be used to define interfaces between FM’s and tools
- Helps with reliable tool operations
- Standardize function definitions
- Define input parameters, expected outputs, error conditions per tool
- May be used with Bedrock action groups
- Upload OpenAPI schema to S3, or edit it in the console
- The action group can then refer to it to guide its tool use
Humans in the Loop
Amazon Q
- Fully managed Gen-AI assistant for your employees
- Based on your company’s knowledge and data
- Answer questions, provide summaries, generate content, automate tasks
- Perform routine actions (e.g., submit time-off requests, send meeting invites)
- Built on Amazon Bedrock (but you can’t choose the underlying FM)
- Data Connectors (fully managed RAG) – connects to 40+ popular enterprise data sources
- Amazon S3, RDS, Aurora, WorkDocs…
- Microsoft 365, Salesforce, GDrive, Gmail, Slack, Sharepoint…
- Plugins – allows you to interact with 3rd party services
- Jira, ServiceNow, Zendesk, Salesforce…
- Custom Plugins – connects to any 3rd party application using APIs
- Authenticated through IAM Identity Center
- Users receive responses generated only from the documents they have access to
- IAM Identity Center can be configured with external Identity Providers
- IdP: Google Login, Microsoft Active Directory…
- Admin Controls
- Controls and customize responses to your organizational needs
- Admin controls == Guardrails
- Block specific words or topics
- Respond only with internal information (vs using external knowledge)
- Global controls & topic-level controls (more granular rules)
- Q Apps
- Create Gen AI-powered apps without coding by using natural language
- Leverages your company’s internal data
- Possibility to leverage plugins (Jira, etc…)
- Q Developer
- Answer questions about the AWS documentation and AWS service selection
- Answer questions about resources in your AWS account
- Suggest CLI (Command Line Interface) to run to make changes to your account
- Helps you do bill analysis, resolve errors, troubleshooting…
- AI code companion to help you code new applications (similar to
- GitHub Copilot)
- Supports many languages: Java, JavaScript, Python, TypeScript, C#…
- Real-time code suggestions and security scans
- Software agent to implement features, generate documentation, bootstrapping new projects
- Integrates with IDE (Integrated Development Environment) to help with your software development needs
- Answer questions about AWS development
- Code completions and code generation
- Scan your code for security vulnerabilities
- Debugging, optimizations, improvements
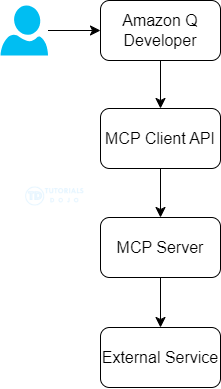
- [ 🧐QUESTION🧐 ] Q Developer uses MCP to connect sources
- The Model Context Protocol (MCP) is an open standard that enables AI assistants to interact with external tools and services. Amazon Q Developer CLI now supports MCP, allowing you to extend Q’s capabilities by connecting it to custom tools and services.
Amazon Q Business
- Fully managed Gen-AI assistant for your employees
- Based on your company’s knowledge and data
- Answer questions, provide summaries, generate content, automate tasks
- Perform routine actions (e.g., submit time-off requests, send meeting invites)
- Built on Amazon Bedrock (but you can’t choose the underlying FM)
- Data Connectors (fully managed RAG) – connects to 40+ popular enterprise data sources
- Amazon S3, RDS, Aurora, WorkDocs…
- Microsoft 365, Salesforce, GDrive, Gmail, Slack, Sharepoint…
- Plugins – allows you to interact with 3rd party services
- Jira, ServiceNow, Zendesk, Salesforce…
- Custom Plugins – connects to any 3rd party application using APIs
- IAM Identity Center
- Users can be authenticated through IAM Identity Center
- Users receive responses generated only from the documents they have access to
- IAM Identity Center can be configured with external Identity Providers
- Admin Controls
- Controls and customize responses to your organizational needs
- Admin controls == Guardrails
- Block specific words or topics
- Respond only with internal information (vs using external knowledge)
- Global controls & topic-level controls (more granular rules)