AWS Lambda
- Synchronous Invocations
- Results is returned right away
- This is default (RequestResponse) if the Lambda function is invokes by manually or custom application without modify the invocation type
- Client need to handle Errors with actions (debug, retries, exponential backoff, etc)
- Users Invoked
- Elastic Load Balancing (Application Load Balancer)
- Amazon API Gateway
- Amazon CloudFront (Lambda@Edge)
- Amazon S3 Batch
- Service Invoked
- Amazon Cognito
- AWS Step Functions
- Others
- Amazon Lex
- Amazon Alexa
- Amazon Kinesis Data Firehose
- Asynchronous Invocations
- S3, SNS, CloudWatch Events (ie EventBridge)
- Or Invocation type set to “Event“
- Put the invocations into Events Queue
- Retry on errors for 3 times, init Run – 1min wait – 1st retry – 2 mins wait – 2nd retry – 2mins wait – final retry; duplicate logs entries in CloudWatch Logs as retried
- the processing is idempotent
- Can define a DLQ (dead-letter queue) – SNS or SQS – for failed processing (need correct IAM permissions)
- Invoked by
- Amazon Simple Storage Service (S3), with S3 Events Notifications
- Amazon Simple Notification Service (SNS)
- Amazon CloudWatch Events / EventBridge
- AWS CodeCommit (CodeCommit Trigger : new branch, new tag, new push)
- AWS CodePipeline (invoke a Lambda function during the pipeline, Lambda must callback)
- Amazon CloudWatch Logs (log processing)
- Amazon Simple Email Service
- AWS CloudFormation
- AWS Config
- AWS IoT
- AWS IoT Events
- By configuring the application to asynchronously process requests by changing the invocation type of the Lambda function to “Event,” the function can run in the background without blocking the main application. When the processing is complete, Lambda can store it back to S3 and trigger another event, such as a notification to the user that the image is ready.
- To expose Lambda as an HTTP(S) endpoint
- ALB, registered Lambda in a target group; also QueryParameters and Headers needed to be Key/Value paired
- support multi-value headers, auto-convert multiple values with same key into arrays to Lambda
- API Gateway
- ALB, registered Lambda in a target group; also QueryParameters and Headers needed to be Key/Value paired
- Event Source Mapping (synchronous invoked)
- Streams
- Kinesis Data Streams or DynamoDB Streams
- One Lambda invocation per stream shard
- Processed items aren’t removed from the stream
- process multiple batches in parallel (up to 10 batches per shard)
- By default, if your function returns an error, the entire batch is reprocessed until the function succeeds, or the items in the batch expire
- Queue
- SQS (standard) queue & SQS FIFO queue
- Long Polling with batch size (1-10 messages)
- the DLQ have to set on SQS, not on Lambda
- items would be deleted from queue once successfully processed by Lambda
- For SQS (standard) queue Lambda adds 60 more instances per minute to scale up, up to 1000 batches
- For SQS FIFO queue Lambda scales to the number of active message groups (defined in GroupID), and messages under same GroupID would be processed in order
- Streams
- Event Object – original sources prepared for application codes
- JSON, contains information from the invoking service (e.g., EventBridge, custom, …)
- Lambda runtime converts the event to an object (e.g., dict type in Python)
- Example: input arguments, invoking service arguments, …
- Context Object – details about the Lambda resources described
- Provides methods and properties that provide information about the invocation, function, and runtime environment
- Passed to your function by Lambda at runtime
- Example: aws_request_id, function_name, memory_limit_in_mb, …
- Destinations
- Asynchronous invocations – can define destinations for successful and failed event to
- Amazon SQS
- Amazon SNS
- AWS Lambda
- Amazon EventBridge bus
- Event Source mapping – only for discarded event batches, send to
- Amazon SQS
- Amazon SNS
- Asynchronous invocations – can define destinations for successful and failed event to
- Environment variables enable you to dynamically pass settings to your function code and libraries without making changes to your code. Environment variables are key-value pairs that you create and modify as part of your function configuration
- Lambda Execution (not Resource-Based) Role (IAM Role), to grant the Lambda function permissions to AWS services/resources
- AWSLambdaBasicExecutionRole – Upload logs to CloudWatch
- AWSLambdaKinesisExecutionRole – Read from Kinesis
- AWSLambdaDynamoDBExecutionRole – Read from DynamoDB Streams
- AWSLambdaSQSQueueExecutionRole – Read from SQS
- AWSLambdaVPCAccessExecutionRole – Deploy Lambda function in VPC
- AWSXRayDaemonWriteAccess – Upload trace data to X-Ray
- EventBridge
- Lambda Resources Based Policy, to allow resources to call Lambda functions
- Lambda Event Variables, as key / value pair in “String” form
- Can embrace X-Ray for tracing, by enabling “Active Tracing” in configuration, with IAM Execution Role (AWSXRayDaemonWriteAccess)
- _X_AMZN_TRACE_ID: contains the tracing header
- AWS_XRAY_CONTEXT_MISSING: by default, LOG_ERROR (The X-Ray SDK uses this variable to determine its behavior in the event that your function tries to record X-Ray data, but a tracing header is not available)
- AWS_XRAY_DAEMON_ADDRESS: the X-Ray Daemon IP_ADDRESS:PORT
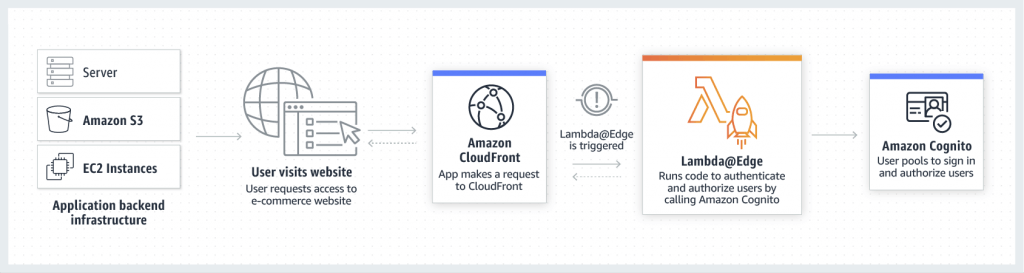
- Edge functions attached on CloudFront with
- CloudFront Functions, as lightweight functions written in JavaScript, can be millions requests per second
- change viewer requests (after CloudFront received) and viewer responses (before forwarding to clients)
- managed in CloudFront
- Lambda@Edge
- Lambda functions written in NodeJS or Python, only support up to 1K request per second
- change CloudFront requests and responses:
- Viewer Request – after CloudFront receives a request from a viewer
- Origin Request – before CloudFront forwards the request to the origin
- Origin Response – after CloudFront receives the response from the origin
- Viewer Response – before CloudFront forwards the response to the viewer
- Authoring in one AWS Region (us-east-1)
- CloudFront Functions, as lightweight functions written in JavaScript, can be millions requests per second
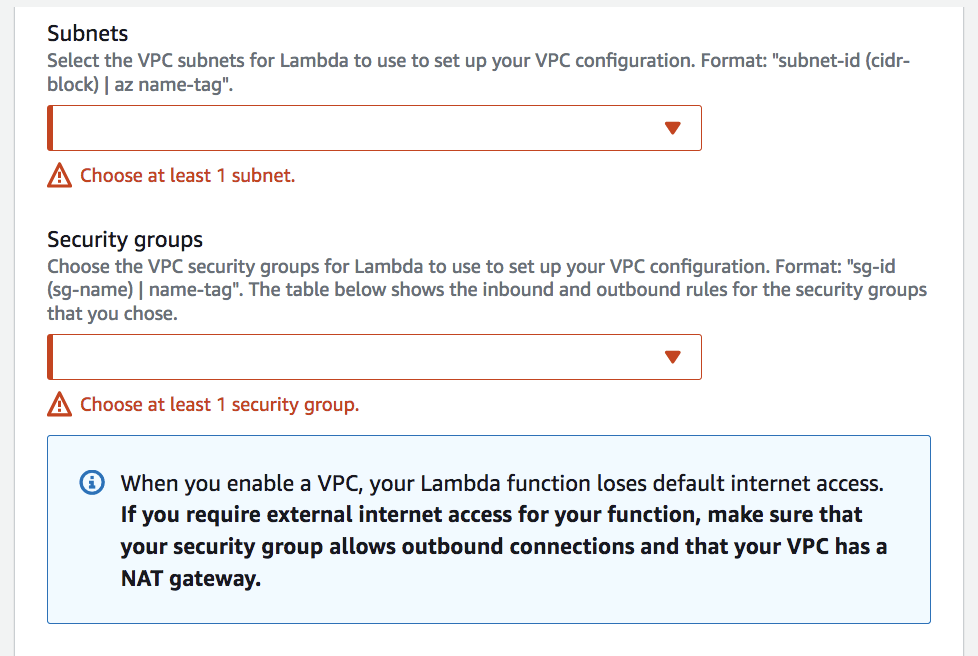
- to allow Lambda to access VPC resources (RDS, ElasticCache, internal ELB, etc.), an Elastic Network Interface (ENI) created by Lambda
- with VPC ID, subnets, and security groups
- using AWSLambdaVPCAccessExecutionRole permission
- no internet access, unless the deployed in a private subnet has setup NAT Gateway or NAT instance
- without NAT, can access AWS resources via VPC Endpoints
- Lambda Function Configuration and Performance
- RAM: 128MB to 10GB
- vCPU would be assigned more if RAM > 1792MB; also need to enable multi-threading in code
- Timeout is 3(default) – 900 seconds
- Execution Context is a temporary runtime environment that initializes any external dependencies
- re-use by other function invoke would boost performance (like DB/HTTP connect)
- does included the /tmp directory, allowing max 10GB file for temporary; generating KMS Data Keys to encrypt if needed
- for permanent objects, using S3
- Lambda Layers – ZIP archive
- Custom Runtimes Library (C++ & Rust)
- split/package dependencies as externalised for re-use
- A function can use up to 5 layers at a time.
- File System Mounting
- EFS with EFS Access Points if Lambda deployed within same VPC
- Watch out the EFS connection (and burst) limits, as each Lambda instance use its own non-shared connection
- Concurrency and Throttling
- Lambda Throttling refers to the rejection of the Lambda function to invocation requests. At this event, the Lambda will return a throttling error exception which you need to handle. This happens because your current concurrency execution count is greater than your concurrency limit.
- Configure reserved concurrency
- Use exponential backoff in your app – uses progressively longer waits between retries for consecutive error responses
- Use a dead-letter queue – to catch any events that are discarded due to constant throttles. This can protect your data if you’re seeing significant throttling
- Request a service quota increase
- The concurrent executions refers to the number of executions of your function code that are happening at any given time.
- concurrent executions = (invocations per second) x (average execution duration in seconds)
- Max 1000 concurrent executions as default, with 100+ in “unreserved pool”; so the max capacity to assigned to all Lambda functions would be no more than 900
- to evenly shared in two functions, that would be 450 concurrent executions
- For Lambda functions that process Kinesis or DynamoDB streams, the number of shards is the unit of concurrency. If your stream has 100 active shards, there will be at most 100 Lambda function invocations running concurrently. This is because Lambda processes each shard’s events in sequence.
- Can set “reserved concurrency” at function lv; the exceeds of execution amount, would trigger “throttle”
- Synchronous Invoke: ThrottleError -429
- Asynchronous Invoke: retry and then go to DLQ
- Cold Start – processing for first request of new instance would be slower
- Provisioned Concurrency would ensure instances would be allocated before function invoked; so no cold start occurrs
- Lambda Throttling refers to the rejection of the Lambda function to invocation requests. At this event, the Lambda will return a throttling error exception which you need to handle. This happens because your current concurrency execution count is greater than your concurrency limit.
- Upload the zip (code + dependency libaries) straight to Lambda if less than 50MB, else to S3 first
- Using CloudFormation to deployment:
- inline – use Code.ZipFile property; could not include dependencies
- Local Lambda folder path (declared in the CodeUri property)
- The aws cloudformation package command packages the local artifacts (local paths) that your AWS CloudFormation template references.
- After you package your template’s artifacts, run the aws cloudformation deploy command to deploy the returned template.
- S3 – with S3Bucket + S3Key + S3ObjectVersion; however, anytime to update Lambda, more than one of three properties needs change as well as the codes (zip file)
- Lambda Container Images with max-size of 10GB in ECR, with Lambda Runtime API
- Versions – default is $LATEST, each version (immutable) has their own ARNs
- Alias – a pointer to Lambda version, as mutable; alias enable canary deployment with weight assign; most time aliases can be used as staging, with also their own ARNs
- with “routing-config”, can allows you to point to two different versions of the Lambda function and dictate what percentage of incoming traffic is sent to each version.
- Function URL, for public access on internet with unique URL
- Can be $LATEST or Alias, no Versions
- Throttle by Reserved Concurrency
- Secured by Resource-based Policy or Cross-Origin Resources Sharing (CORS)
- AuthType NONE: allow public with unauthenticiated, but need Resource-based Policy grant public access
- AuthType AWS_IAM
- Code Profiling – use CodeGuru Profiler can gain insight of runtime performance
- Java and Python
- AmazonCodeGuruProfilerAgentAccess
- Errors
- The InvalidParameterValueException will be returned if one of the parameters in the request is invalid. For example, if you provided an IAM role in the CreateFunction API which AWS Lambda is unable to assume.
- exceeded your maximum total code size per account, the CodeStorageExceededException will be returned
- the resource already exists, the ResourceConflictException will be returned
- encountered an internal error, the ServiceException will be returned
Step Functions
- Workflow in JSON
- Start with SDK, API Gateway call, or Event Bridge
- Task: Invoke 1 AWS service or Run 1 Activity
- States: Choice, Fail-or-Succeed, Pass, Wait, Map, Parallel
- Fail state could not trigger “Retry”
- Error Handling should be in Step Functions, not in Task; using Retry and Catch, running from top to bottom but not sequentially (“OR”)
- Wait for Task token: append .waitForTaskToken in Resource, pause the running until receiving a SendTaskSuccess or SendTaskFailure API call. (PUSH mechanism)
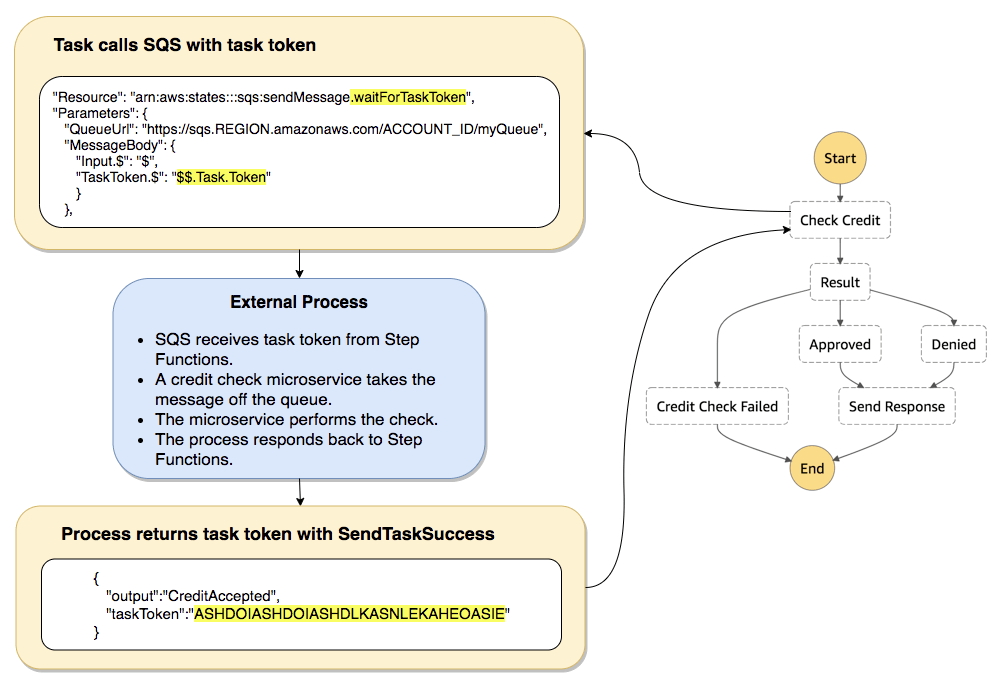
- Activity Task: Activity Worker on EC2/Lambda/.., using GetTaskActivity API call for poll, sending response with SendTaskSuccess or SendTaskFailure API call (PULL mechanism), with SendTaskHeartBeat + HeartBeatSeconds
- Standard vs Express (asynchronous and synchronous)
- Developers can target specific errors, such as timeouts or exceptions thrown by AWS Lambda functions, by defining a Retry field in the state’s configuration. This ensures that transient issues or expected problems do not immediately cause the workflow to fail. Instead, the system can attempt to resolve the issue through retries based on the parameters provided. This mechanism is handy for handling spikes in data volume or temporary resource constraints, ensuring that workflows are designed to be robust and resilient under varying conditions.
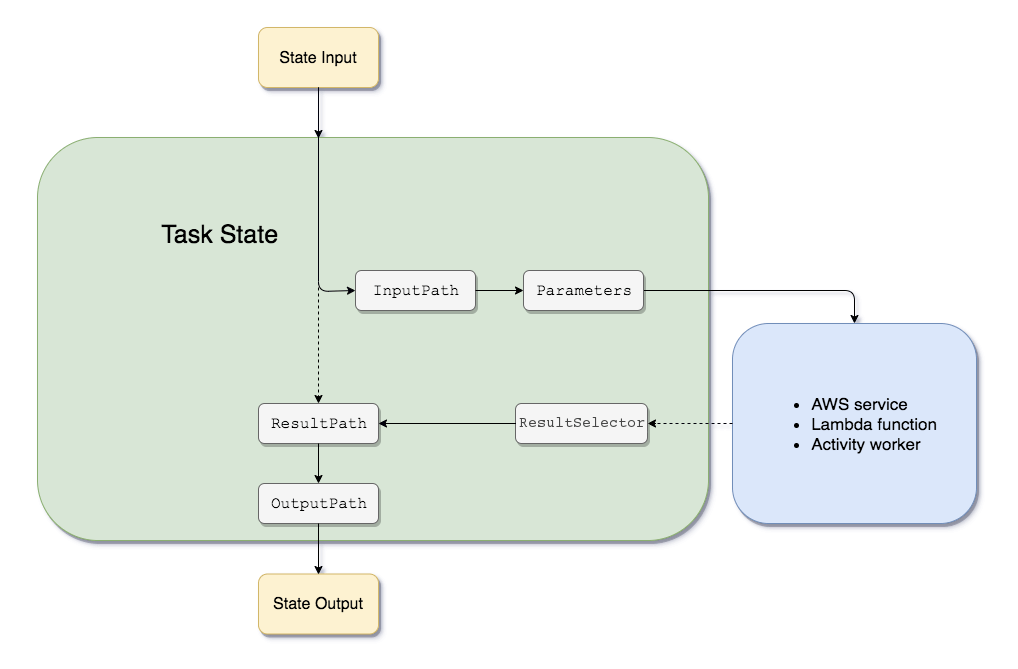
- Amazon States Language filters/control the flow
- InputPath – filtering the JSON notation by using a path
- Parameters – can only be used on the input level of a state
- ResultPath – the only one that can control input values and its previous results to be passed to the state output
- OutputPath – filter out unwanted information and pass only the portion of JSON
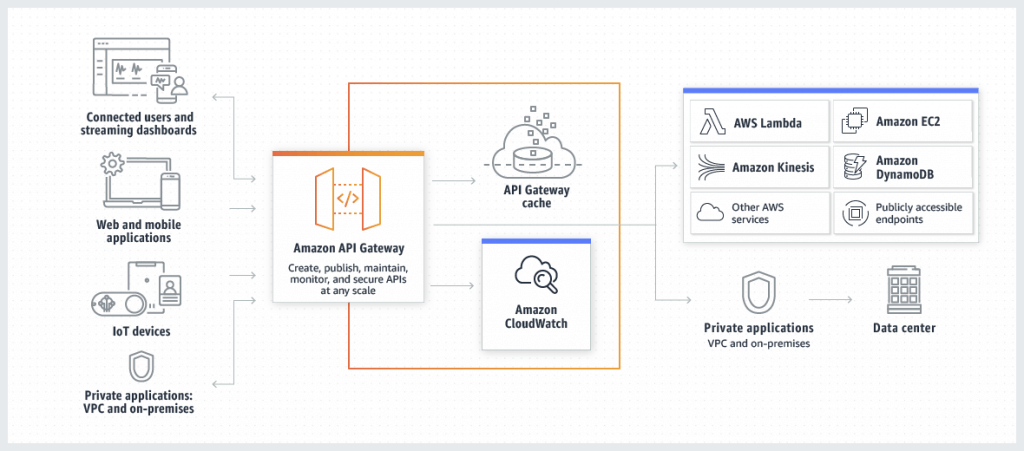
Amazon API Gateway
- Endpoints
- Edge-Optimized (default):
- For global clients, the requests are routed through the CloudFront Edge locations (improves latency)
- The API Gateway still lives in only one region
- Regional:
- For clients within the same region
- Could manually combine with CloudFront (more control over the caching
strategies and the distribution)
- Private:
- Can only be accessed from your VPC using an interface VPC endpoint (ENI)
- Use a resource policy to define access
- Edge-Optimized (default):
- Security
- IAM Role – Authentication; IAM Policy & Resources Policy – Authorization
- Attaching a resource policy to the API that grants permission to the specified IAM role to invoke the execute-api:Invoke action allows the specified IAM role to make authorized requests to the API while denying access to any other unauthorized users or roles.
- Cognito User Pool – Authentication; API Gateway Methods – Authorization, or Custom Authorizer
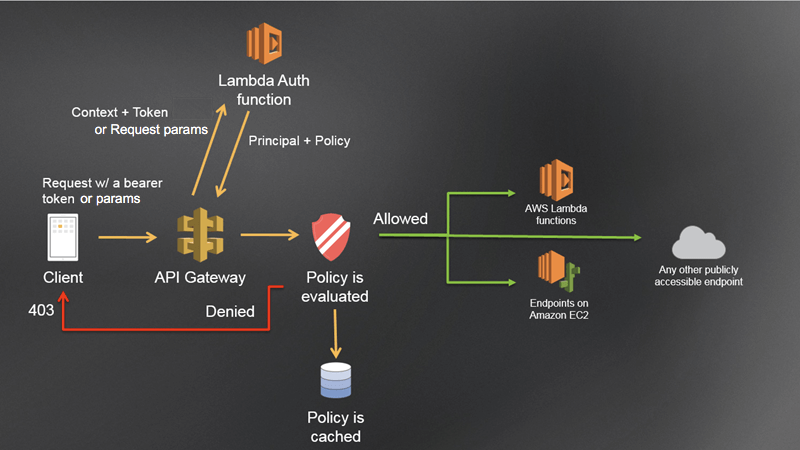
- Custom Authorizer / Lambda Authorizer (External)
- A token-based Lambda authorizer (also called a TOKEN authorizer) receives the caller’s identity in a bearer token, such as a JSON Web Token (JWT) or an OAuth token. <- most aligned with OAuth/SAML.
- A request parameter-based Lambda authorizer (also called a REQUEST authorizer) receives the caller’s identity in a combination of headers, query string parameters, stageVariables, and $context variables.
- Custom Domain Name HTTPS security through integration with AWS Certificate Manager (ACM)
- for Edge-Optimized endpoint, then the certificate must be in us-east-1
- for Regional endpoint, the certificate must be in the API Gateway region
- Must setup CNAME or A-alias record in Route 53
- IAM Role – Authentication; IAM Policy & Resources Policy – Authorization
- Deployment Stages/Environments
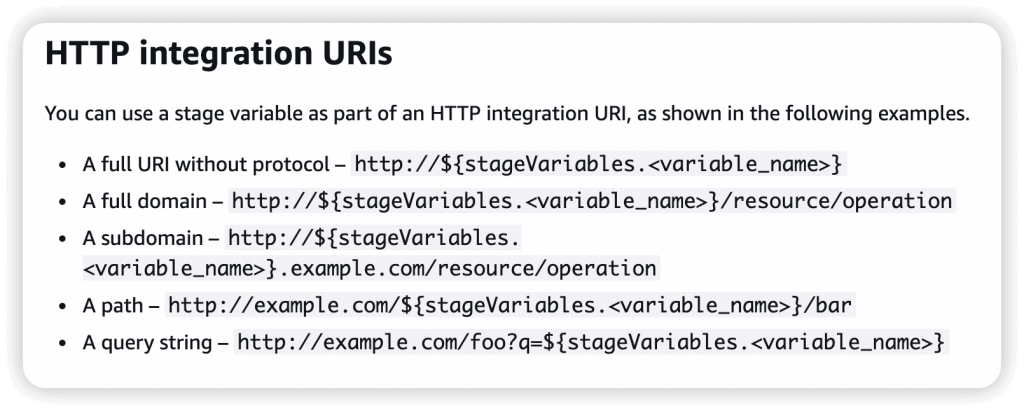
- Stage variables are (like environment variables) for API Gateway, passed to the ”context” object in AWS Lambda, with Format: ${stageVariables.variableName}
- Canary deployments, choose the % of traffic the canary channel, suitable for Green/Blue Deployment
- Integration Types
- MOCK: API Gateway returns a response directly
- HTTP / AWS (Lambda & AWS Services): for example, call SQS. Setup data mapping using mapping templates for the request & response
- Mapping templates can be used to modify request / responses
- Rename / Modify query string parameters
- Modify body content
- Add headers
- Uses Velocity Template Language (VTL): for loop, if etc…
- Filter output results (remove unnecessary data)
- Content-Type can be set to application/json or application/xml
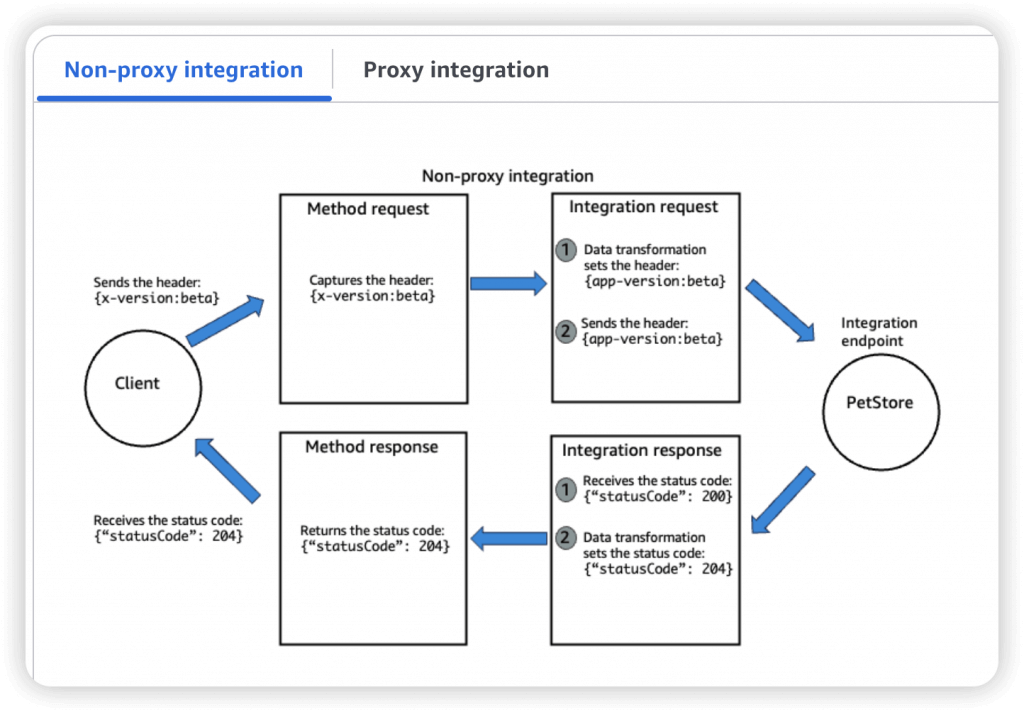
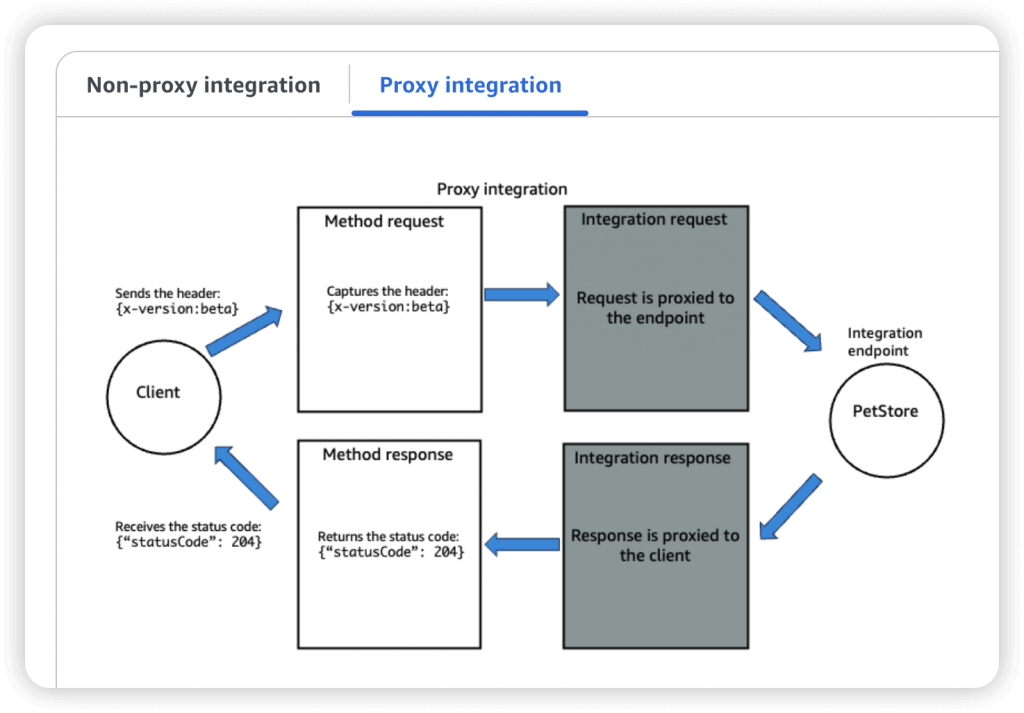
- AWS_PROXY (Lambda Proxy)
- incoming request from the client is the input to Lambda
- No mapping template; headers, query string parameters… are passed as arguments
- HTTP_PROXY
- No mapping template
- Possibility to add HTTP Headers if need be (ex: API key)
- So enforce the request formats (like necessary fields/parameters), please set the checks on Method Request
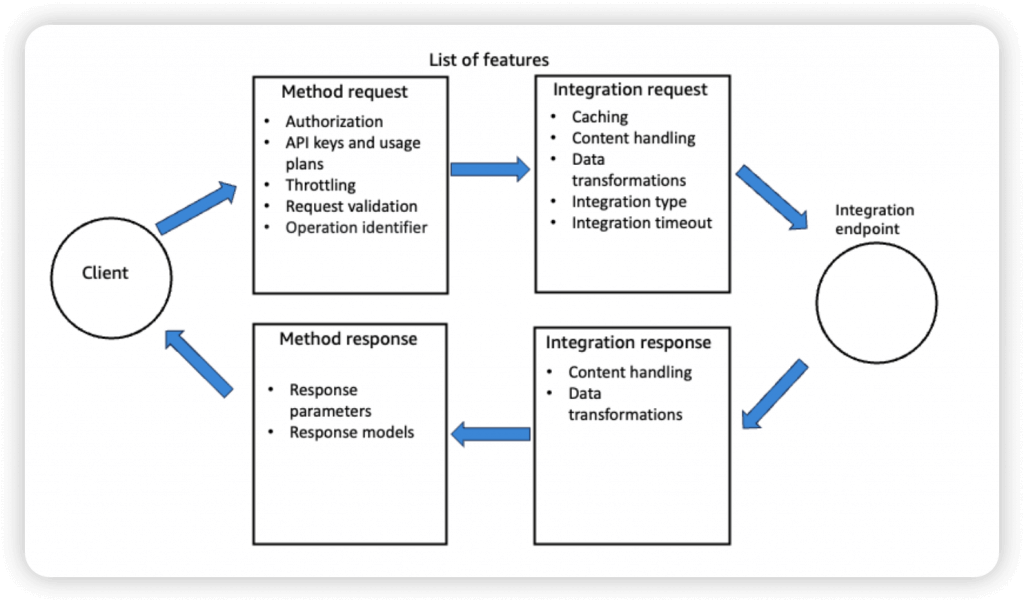
- A Method is an incoming request submitted by the client and can contain the following request parameters: a path parameter, a header, or a query string parameter (, or a body via POST/PUT)
- Swagger / Open API import to quickly define APIs
- OpenAPI specs can be written in YAML or JSON
- Using OpenAPI we can generate SDK for our applications
- Request Validation
- Returns a 400-error response to the caller if validation failed
- Cache API responses
- Default TTL (time to live) is 300 seconds, ranging from 0-3600s
- Caches are defined per stage, possible to override cache settings per method
- Clients can invalidate the cache with header: Cache-Control: max-age=0
- Usage Plan, using API Keys to identify clients and meter access
- API Keys are alphanumeric string values
- Throttling limits
- Quotas limits is the overall number of maximum requests
- Callers must supply an assigned API key in the x-api-key header in requests
- API keys by themselves do not grant access to execute an API. They need to be associated with a usage plan, and that usage plan then determines which API stages and methods the API key can access.
- If the API key is not associated with a usage plan, it will not have permission to access any of the resources, which will result in a “403 Forbidden” error.
- after generating an API key, it must be added to a usage plan by calling the CreateUsagePlanKey method
- CloudWatch Metrics
- CacheHitCount & CacheMissCount – for cache capacities
- Count
- IntegrationLatency – The time between when API Gateway relays a request to the backend and when it receives a response from the backend.
- Latency – The time between when API Gateway receives a request from a client and when it returns a response to the client. The latency includes the integration latency and other API Gateway overhead.
- Throttling limits
- Account Limit, at 10000 rps across all API
- Also can set Stage limit, Method limits, or define Usage Plans to throttle per customer
- like Lambda Concurrency, one API that is overloaded, if not limited, can cause the other APIs to be throttled
- Errors
- 4xx means Client errors
- 400: Bad Request
- 403: Access Denied, WAF filtered (Authorization Failure)
- 429: Quota exceeded, Throttle (Too Many Requests, aka retriable error)
- 5xx means Server errors
- 502: Bad Gateway Exception
- usually for an incompatible output returned from a
Lambda proxy integration backend (for example, XML, not JSON format) - or occasionally for out-of-order invocations due to
heavy loads.
- usually for an incompatible output returned from a
- 503: Service Unavailable Exception
- 504:
- Integration_Failure – The gateway response for an integration failed error.
- Integration_Timeout – ex Endpoint Request Timed-out Exception; API Gateway requests time out after 29 second maximum
- 502: Bad Gateway Exception
- Connection refused, may be because “API Gateway expose HTTPS endpoints only”
- 4xx means Client errors
- CORS must be enabled when you receive API calls from another domain.
- The OPTIONS pre-flight request must contain the following headers:
- Access-Control-Allow-Methods
- Access-Control-Allow-Headers
- Access-Control-Allow-Origin
- The OPTIONS pre-flight request must contain the following headers:
- REST (apigateway) vs HTTP (apigatewayv2)
- https://dev.to/tinystacks/api-gateway-rest-vs-http-api-what-are-the-differences-2nj
| Feature | HTTP API | REST API |
| Core Protocol | HTTP | HTTP + REST Principles |
| Features | Basic (e.g., limited authentication) | Rich (API keys, request validation, private endpoints) |
| Cost | Generally lower | Generally higher |
| Performance | Often faster | Can have slightly lower performance |
| Flexibility | Less flexible | Highly flexible and scalable |
| Architectural Style | Not strictly bound | Adheres to REST principles (statelessness, client-server) |
| Purpose | Simpler applications, internal use, rapid development | Public-facing APIs, microservices, complex integrations |
| Canary Deployments | Not supported | Supported |
| Programmatic Model | Simplified | Can be more complex |
| Endpoint Types | Limited (e.g., regional) | Supports various types |
| Security Options | Fewer options | More options (authentication, authorization, encryption) |
| Deployments | Automatic deployments | Manual or more involved |
| Authorizers | HTTP API | REST API |
| AWS Lambda | V | V |
| IAM | V | V |
| Resource Policies | V | |
| Amazon Cognito | V | V |
| Native OpenID Connect / OAuth 2.0 / JWT | V |
- WebSocket API
- Server can push information to the client (wss://abcdef.execute-api.us-west-1.amazonaws.com/dev/@connections/connectionId)
- POST: Server send message to the connected Client
- GET: get connection status
- DELETE: disconnect with Client
- This enables stateful application use cases
- WebSocket APIs are often used in real-time applications such as chat applications, collaboration platforms, multiplayer games, and financial trading platforms.
- Works with AWS Services (Lambda, DynamoDB) or HTTP endpoints
- Routing
- https://docs.aws.amazon.com/apigateway/latest/developerguide/websocket-api-develop-routes.html
- Incoming JSON messages are routed to different backend
- If no routes => sent to $default route
- You request a route selection expression to select the field on JSON to route from
- Sample expression: $request.body.action
- The result is evaluated against the route keys available in your API Gateway
- The route is then connected to the backend you’ve setup through API Gateway
- Server can push information to the client (wss://abcdef.execute-api.us-west-1.amazonaws.com/dev/@connections/connectionId)
Amazon SQS
- Queue model as pull-based
- ideal for solutions that must be durable and loosely coupled
- Max message size is 256kb, and max retention time of 14 days; also the message is persisted in SQS until a consumer deletes
- When a consumer picks a message from the queue, the message stays in the queue but is invisible until the job is processed. If the visibility timeout (default: 30s) is over (ie, job is not processed in time), then the message reappears in the queue for another consumer to take.
- Dead Letter Queue (DLQ)
- MaximumReceives is the threshold for message to re-queue in source
- DLQ of a FIFO queue must also be a FIFO queue
- DLQ of a Standard queue must also be a Standard queue
- use “redrive” to put DLQ message to be re-process
- Delay Queue, from 0s (default) to 15mins
- postpone the delivery of new messages to the SQS queue for a number of seconds
- Short polling vs. Long polling = time to wait before polling again
- Short polling is the default. When you poll the SQS, it doesn’t wait for messages to be available in the queue to respond. It checks a subset of servers for messages and may respond that nothing is available yet.
- Long polling waits (with extra time, from 1-20s) for messages to be in the queue before responding, so it uses fewer total requests and reduces cost.
- suitable if the new messages that are being added to the SQS queue arrive less frequently (like the frequency of producer is quite long, several seconds a new message)
- SQS Extended Client (Java Library) for large message (stored in S3 bucket)
- API calls
- CreateQueue (MessageRetentionPeriod), DeleteQueue
- PurgeQueue: delete all the messages in queue
- SendMessage (DelaySeconds), ReceiveMessage, DeleteMessage
- MaxNumberOfMessages: default 1, max 10 (for ReceiveMessage API)
- ReceiveMessageWaitTimeSeconds: Long Polling
- ChangeMessageVisibility: change the message timeout
- Batch APIs for SendMessage, DeleteMessage, ChangeMessageVisibility helps decrease costs
- Standard vs. FIFO: FIFO is very rigorous whereas Standard is best-effort. The trade-off is that Standard has unlimited throughput of transactions per sec.
- FIFO with Message Group ID
- Messages that share a common Message Group ID will be in order within the group
- Each Group ID can have a different consumer (parallel processing!)
- FIFO De-duplication interval is 5 minutes
- Content-based deduplication: will do a SHA-256 hash of the message body
- Explicitly provide a Message Deduplication ID
- FIFO with Message Group ID
- SQS doesn’t prioritize items in the queue. If you need to prioritize use multiple queues, one for each priority type
- ——
- To use industry standards with Apache ActiveMQ, use an Amazon MQ instead of SQS (this is similar to using EKS instead of ECS, the industry-standard version of containers rather than the Amazon proprietary version)
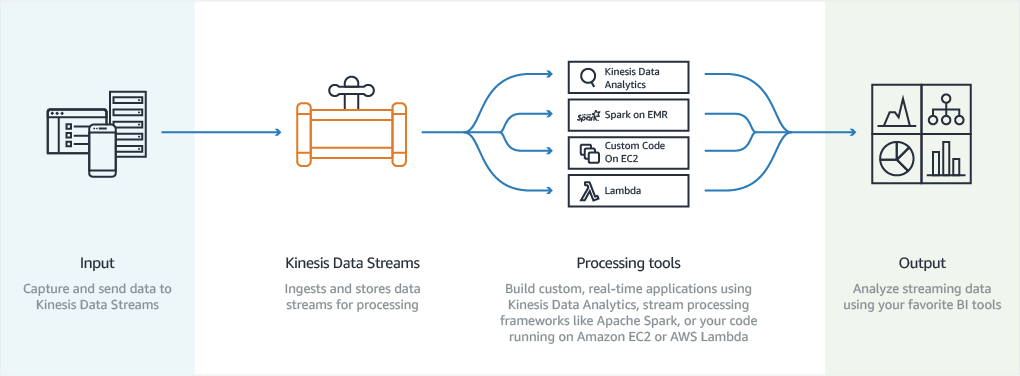
Amazon Kinesis
- Real-time Streaming model, enables the collection, processing, and analysis of real-time data at a massive scale, allowing applications to react to new information almost immediately
- for use cases that require ingestion of real-time data (e.g. IoT sensor data, payment processing application with fraud detection)
- Kinesis data stream is made up of shards, which are made up of data records, which each have a sequence #. Then you map devices to partition keys which group data by shard.
- Resharding
- decrease the stream’s capacity by merging shards
- increase the stream’s capacity by splitting shards
- se metrics to determine which are your “hot” or “cold” shards, that is, shards that are receiving much more data, or much less data, than expected.
- Since the Lambda function is using a poll-based event source mapping for Kinesis, the number of shards is the unit of concurrency for the function.
- embed a primary key within the record to remove duplicates later when processing
- Amazon Kinesis Agent is a lightweight software that helps send log and event data from on-premises servers to Amazon Kinesis Data Streams or Data Firehose
- Kinesis Client Library (KCL)
- ensures that for every shard there is a record processor running and processing that shard. It also tracks the shards in the stream using an Amazon DynamoDB table.
- ensure that the number of instances does not exceed the number of shards
- Each shard is processed by exactly one KCL worker and has exactly one corresponding record processor
- ——-
Amazon SNS
- Pub/Sub model (Publish-Subscribe messaging)
- fully managed messaging service for pushing async notifications, especially used for broadcasting to multiple services
AWS Kinesis Data Firehose
primarily used for loading streaming data into other AWS services (e.g., Amazon S3, Amazon Redshift, Amazon Elasticsearch) for storage or analysis.
optimized for delivering data to storage destinations. It lacks fine-grained control over stream processing, which is necessary for fraud detection, where real-time analysis and immediate action are crucial.