== AUTHORISATION ==
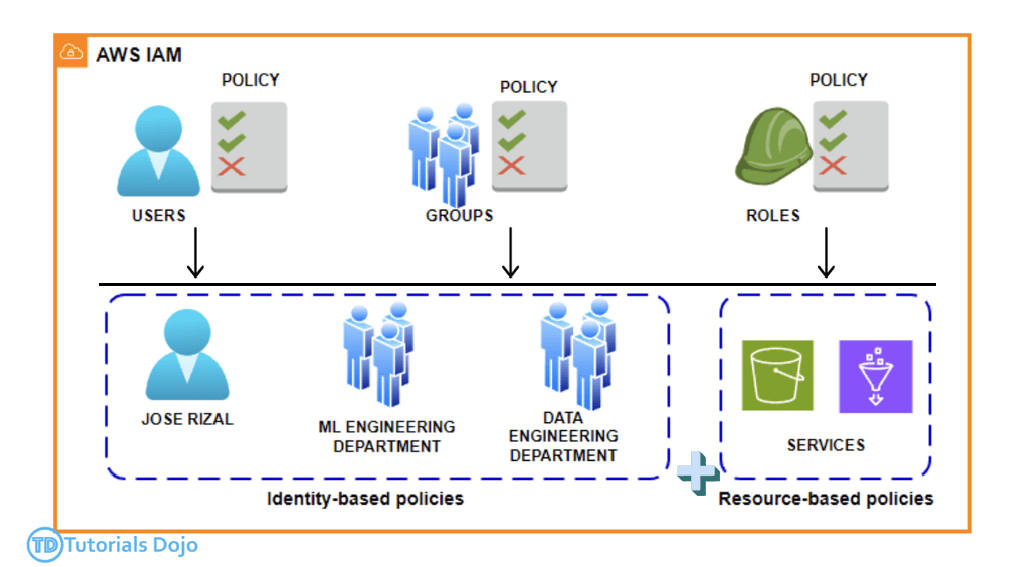
Identity and Access Management (IAM)
- Users (one physical user = one AWS user) and Groups (groups contain only users, no subgroups)
- The permissions boundary for an IAM entity (user or role) sets the max permissions that the entity can have
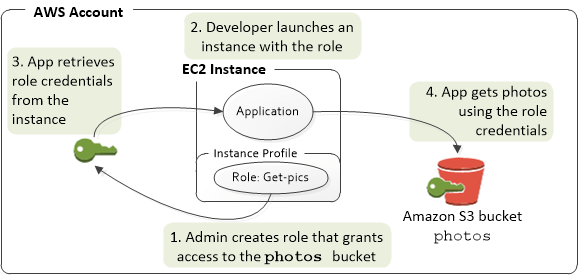
- IAM Role
- Roles hand out automatic credentials and permissions
- Giving permissions to non-humans, such as services / applications
- Giving permissions to federated / outside users & groups
- Authorisations from identity providers (like AWS Cognito) are mapped to your IAM role(s), NOT users or groups
- to pass the role to service, the users need to have iam:PassRole permission; to see, using iam:GetRole
- Roles can only passed to what their trust allows, using “Trust Relationships”
- Roles hand out automatic credentials and permissions
- IAM Policies
- assign permissions, using JSON documents
- using “least privilege principle”
- consist of
- version
- id (optional)
- statement
- Sid (optional)
- Effect: Allow or Deny
- Principal: account/user/group/role
- Action: list of action, like S3:GetObject, S3:PutObject, iam:PassRole, iam:GetRole
- Resource: AWS resource
- Condition (optional)
- Permission Evaluation Flow
- If there’s explicit DENY, end flow with DENY
- Else, if there is an ALLOW, end flow with ALLOW
- Else, DENY
- Dynamic Policy, with variable as ${aws:username}
- Policy Management
- AWS Managed Policy
- Customer Managed Policy, has version control + rollback
- Inline Policy, strict 1-to-1 relationship with principal; would be also deleted while delete principal
- IAM Password Policy, set minimum length, require specific character types (number, upper/lower-case letters, non-alphabetic), expiration, and re-use forbidden
- Multi Factor Authentication (MFA)
AWS IAM Identity Center (AWS Single Sign-On)
- centralizes access management across AWS accounts and applications
- issues temporary security credentials for users to access AWS resources
IAM Security/Audit Tools
- IAM Credentials Report (account-lv)
- IAM Access Advisor (user-lv), for check/revise the permissions granted with usage
- IAM Policy Simulator evaluates the policies that you choose and determines the effective permissions for each of the actions that you specify
AWS STS (Security Token Service)
- request temporary limited-privilege (15mins to 1 hour) credentials for IAM users, or for users that you authenticate such as federated users from an on-prem directory
- APIs
- AssumeRole
- AssumeRoleWithSAML
- AssumeRoleWithWebIdentity -> using Cognito Identity Pools instead
- GetSessionToken, for MFA (returns “Access ID”, “Secret Key”, “Session Token”, and “Expiration Date”)
- GetFederationToken
- GetCallerIdentity
- DecodeAuthorizationMessage
- STS for MFA, needs
- using GetSessionToke api
- in IAM Policy, need set in Conditions (in statement), as “aws:MultiFactorAuthPresent:true”
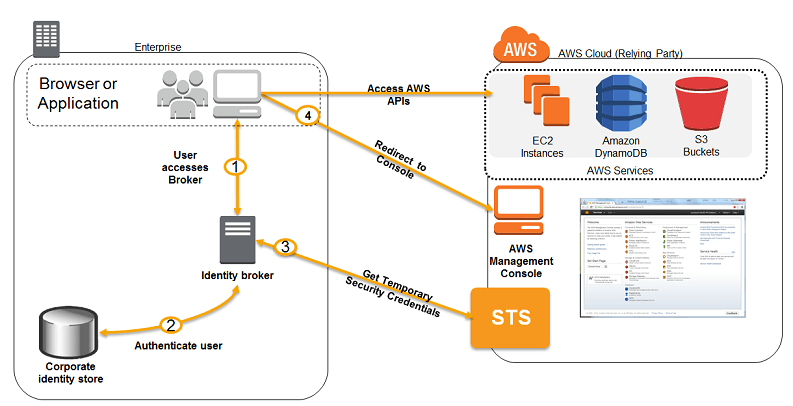
- Federation: STS can be used Federation (typically with Azure AD). It uses SAML 2.0 for authentication to grant temporary access based on the AD creds
- Single Sign-On: STS can be used to develop a custom identity broker for SSO to a service such as the AWS management console:
- Verify that the user is authenticated on the local IDP (AD)
- Call STS AssumeRole or GetFederationToken API to get temp credentials
- Pass the temp creds to AWS federation endpoint to request a sign-in token
- Construct a URL to the service that includes the token which can be provided to the user
For On-Premier applications
- Applications running outside of an AWS environment will need access keys for programmatic access to AWS resources. For example, monitoring tools running on-premises and third-party automation tools will need access keys.
- However, if the resources that need programmatic access are running inside AWS, the best practice is to use IAM roles instead. An IAM role is a defined set of permissions—it’s not associated with a specific user or group. Instead, any trusted entity can assume the role to perform a specific business task.
- Access keys are long-term credentials for an IAM user or the AWS account root user. You can use access keys to sign programmatic requests to the AWS CLI or AWS API (directly or using the AWS SDK).
- In order to use the AWS SDK for your application, you have to create your credentials file first at ~/.aws/credentials for Linux servers or at C:\Users\USER_NAME\.aws\credentials for Windows users and then save your access keys.
== CERTIFICATE & KEYS ==
AWS Certificate Manager (ACM)
- manage SSL/TLS certificates, for in-flight encryption of websites (HTTPS)
- SSL refers to Secure Sockets Layer, used to encrypt connections
- TLS refers to Transport Layer Security, which is a newer version
- automatically renewal
- Elastic Load Balancers(Application Load Balancer & Network Load Balancer), CloudFront Distributions, API Gateway Calls
- Public and Private
AWS Private Certificate Authority (CA)
- including root and subordinaries certificates (X.509), trusted by only private Organisation
Encryption
- Best practice is to lock away or delete the root user access keys. Never store in an S3 bucket, even if encrypted
- Never ever store your secrets in plaintext, especially in your code!
- Encryption in flight
- SSL/TLS is for encrypting data in transit, not data at rest.
- SSL/TLS is synonymous with HTTPS traffic. It goes over port 443.
- Server-side encryption at rest
- Data is encrypted after being received by the server, and decrypted before being sent
- So the data stored is in an encrypted from
- Types
- SSE-C: use customer-provided keys and manage them yourself
- SSE-S3, SSE-SQS, SSE-DDB: Amazon manages the keys
- SSE-KMS: keys are managed in Amazon Key Management Service
- CloudHSM: generate and use your own encryption keys, held in the cloud in Amazon’s HSM
- Client-side encryption
- Data stored is also in an encrypted from
- but the is encrypted before sending to the server, and decrypted in client side after being received
AWS Key Management Service (KMS)
- AWS manages encryption keys for us
- Fully integrated with IAM for authorization
- Able to audit KMS Key usage using CloudTrail
- KMS Keys is the new name of KMS Customer Master Key (KMS CMK)
- Symmetric (AES-256 keys)
- AWS services default
- must call KMS API
- encrypt up to 4 KB of data through KMS
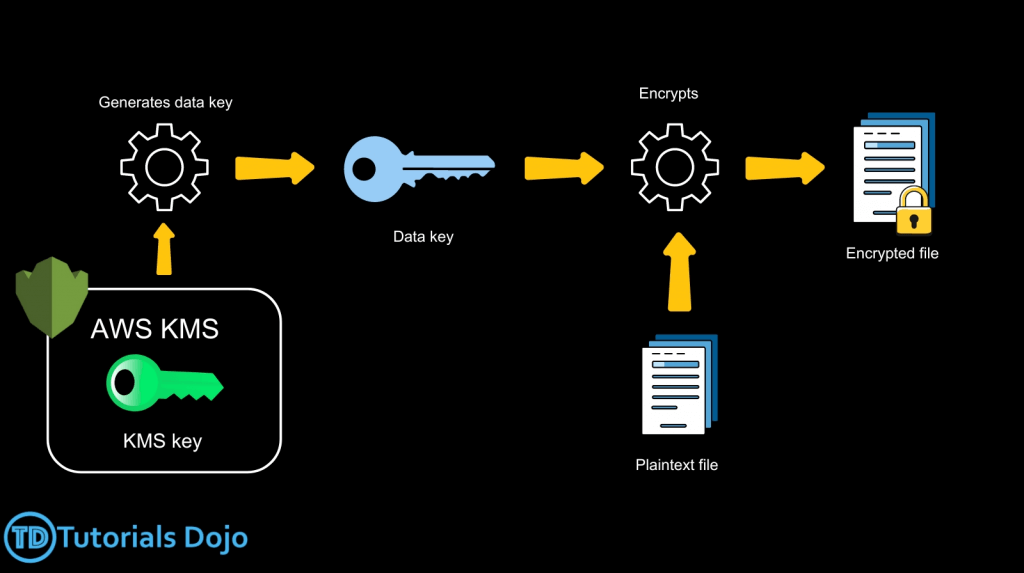
- to encrypt > 4KB with KMS Encrypt API call, need to use Envelope Encryption (aka GenerateDataKey API), let client side to Encrypt/Decrypt with DEK received
- GenerateDataKey: generates a unique symmetric data key (DEK)
- returns a plaintext copy of the data key
- AND a copy that is encrypted under the CMK
- GenerateDataKeyWithoutPlaintext
- Generate a DEK that is encrypted under the CMK
- Decrypt: decrypt up to 4 KB of data (also “Data Encryption Keys”)
- GenerateRandom: Returns a random byte string
- Encrypt data locally in your application (ie, Envelope Encryption) with KMS
- Use the GenerateDataKey operation to get a data encryption key.
- Use the plaintext data key (returned in the Plaintext field of the response) to encrypt data locally, then erase the plaintext data key from memory.
- Store the encrypted data key (returned in the CiphertextBlob field of the response) alongside the locally encrypted data.
- To Decrypt data locally:
- Use the Decrypt operation to decrypt the encrypted data key. The operation returns a plaintext copy of the data key.
- Use the plaintext data key to decrypt data locally, then erase the plaintext data key from memory.
- Envelope encryption is the practice of “encrypting plaintext data with a data key and then encrypting the data key under another key”. But, eventually, one key must remain in plaintext so you can decrypt the keys and your data. This top-level plaintext encryption key is known as the root key.
- GenerateDataKey: generates a unique symmetric data key (DEK)
- Asymmetric (RSA & ECC key pairs)
- Public (Encrypt) and Private Key (Decrypt) pair
- Symmetric (AES-256 keys)
- Types of KMS Keys
- AWS Owned Keys (free): SSE-S3, SSE-SQS, SSE-DDB (DynamoDB)
- AWS Managed Key (free): aws/service-name, automatic renew every 1 year
- Customer managed keys created in KMS: $1 / month, can be renewed automatic & on-demand
- Customer managed keys imported: $1 / month, only manual rotation
- AWS Encryption SDK has already implemented Envelope Encryption
- the feature – Data Key Caching, can reuse the data keys, with LocalCryptoMaterialsCache
- Request Quotas: if got ThrottlingException, use exponential backoff (backoff and retry); and all cryptographic operations (aka Encrypt and Decrypt), they share a quota
- To hugely reduce the cost on S3 encryption, use “S3 Bucket Key”
CloudHSM
- Compared with KMS, AWS provisions encryption with dedicated hardware (HSM = Hardware Security Module)
- Encryption keys are managed on client side
- Good option to use with SSE-C encryption
- CloudHSM clusters are spread across Multi AZ (HA)
AWS System Manager (SSM) Parameter Store
- Secure storage for configuration and secrets
- Version tracking of configurations / secrets
- Allow to assign a TTL to a parameter (expiration date) to force updating or deleting sensitive data such as passwords
- Parameter policies are only available for parameters in the Advanced tier
- Expiration – deletes the parameter at a specific date
- ExpirationNotification – sends an event to Amazon EventBridge (Amazon CloudWatch Events) when the specified expiration time is reached.
- NoChangeNotification – sends an event to Amazon EventBridge (Amazon CloudWatch Events) when a parameter has not been modified for a specified period of time.
AWS Secrets Manager
- Capability to force rotation of secrets every X days
- Automate generation of secrets on rotation (uses Lambda)
- Integration with Amazon RDS (MySQL, PostgreSQL, Aurora)
- Mostly meant for RDS integration
== AUTHENTICATION ==
Amazon Cognito
- authentication for users with identity for mobile and web application
- Benefit over IAM: “hundreds of users”, “mobile users” and “authenticate with SAML”
- Cognito User Pools (CUP)
- Authentication, Identity Verification
- Provide sign-in functionality for user
- A serverless database of “User”
- Simple Login (User name/email + Password)
- Password Recovery
- Email/Phone verification
- Multi-Factor authentication (MFA)
- Federated identities with 3rd parties, Google/FB/SAML/OpenID, etc.
- JWT(JSON Web Token) for login send backs
- Integrated with API Gateway & Application Load Balancer
- Lambda Triggers
- Authentication Events (Sign-In)
- Sign-Up
- Messages
- Token Creation
- Hosted Authentication UI & Custom Domain
- ACM certificate in “us-east-1”
- must defined in the “App Integration” section
- Adaptive
- using risk score for each attempt; finally block or requires (second) MFA for suspicious logins
- Integrated with CloudWatch Logs
- JSON Web Token
- Base64 encoded
- Header, Payload(contains “sub”-UUID, email, phone, user name, etc.), and Signature
- Authenicate Users on Application Load Balancer
- Offload the authentication from applications to load balancer
- Identity Provider (IdP): OpenID Connect compliant
- AWS Cognito User Pools
- Set up HTTPS listeners with “authenticate-oidc” or “authenticate-cognito” rules
- OnUnauthenticatedRequest – authenticate(default), deny, allow
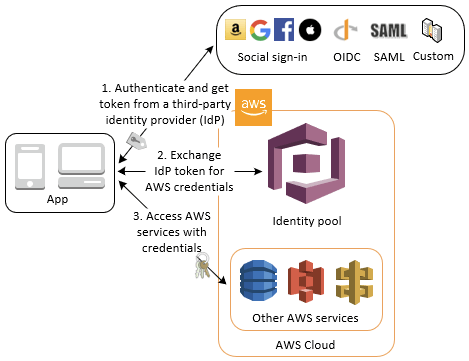
- Cognito Identity Pools (CIP)
- Authorisation, Access Control
- Federated Identities
- Temporary AWS credentials to AWS resources directly (or via API Gateway)
- IAM policies via Security Token Service (STS), at least one “trust” policy
- can be customised based on the user_id
- Identity pool/sources
- Public 3rd Parties (Google, Facebook, Apple, etc.)
- OpenID Connect & SAML
- AWS Cognito User Pools
- Developer Authenticated Identities (custom Login server)
- unauthenicate (guess) access
- can partition users with IAM policy “variables”
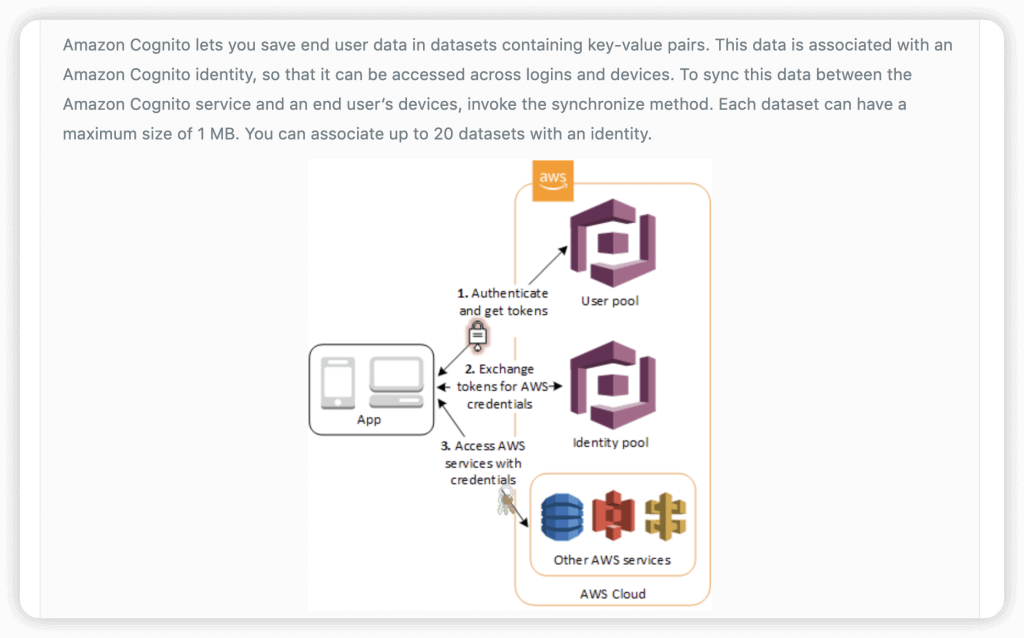
- Amazon Cognito Sync is an AWS service and client library that enables cross-device syncing of application-related user data.
AWS Directory Services
- for MS Active Directory (AD), with AD Domain Services
- AWS Managed Microsoft AD
- an AD instance on AWS, connecting as “trust” with on-premise AD; users are managed on AWS locally; support MFA
- AD Connector
- as (Directory Gateway) proxy only, using on-premise AD to manage; support MFA
- Simple AD
- a seperate AD on AWS, no connection with on-premise AD
- AWS Managed Microsoft AD
== SECURITY ==
AWS Web Application Firewall (WAF)
- Allow all requests except the ones that you specify
- Block all requests except the ones that you specify
- Count the requests that match the properties that you specify
- Prevent SQL-Injection and cross-site scripting attacks
Amazon GuardDuty
- use with CloudWatch+SNS to trigger notifications to services
- GuardDuty is a threat detection service that continuously monitors for malicious activity and unauthorized behavior in your AWS environment.
- Threat Detection – Utilizes machine learning and anomaly detection to identify potentially malicious activity such as unauthorized access, data exfiltration, or compromised instances.
- Security Findings: Provides detailed security findings with severity levels and recommendations for remediation.
- Automated Response: Can be configured to automatically trigger responses or notifications based on detected threats.
AWS Firewall Manager
- simplifies your AWS WAF and AWS Shield Advanced administration and maintenance tasks across multiple accounts and resources.
Amazon Macie
- discover and protect sensitive data (Personal Identifiable Information, PII) by machine learning and pattern matching, on S3 bucket
- Data Discovery – Automatically scans and classifies data stored in Amazon S3 buckets to identify sensitive data such as personally identifiable information (PII) or intellectual property.
- Data Classification – Assigns sensitivity labels to data based on its content and context, helping you understand the level of risk associated with different types of data.
- Security Monitoring – Continuously monitors data access and usage patterns to detect suspicious or unauthorized behavior, such as unusual access patterns or data leaks.
- Compliance Reporting – Provides reports and dashboards to help you demonstrate compliance with data protection regulations such as GDPR, HIPAA, or PCI DSS.
AWS CloudTrail
- Audit API calls made by users / services / AWS console, under AWS account(s)
- history of events / API calls
- Console
- SDK
- CLI
- AWS services
- useful to find AWS resources changes (when and how)
- history of events / API calls
- export logs to CloudWatch Logs or S3
- A trail can be applied to All Regions (default) or a single Region.
- Event Type
- Management Events (default enabled): management operations on resources, can separate as Read and Write
- Data Events (default disabled): resource activities
- Insights Events: to detect unusual activities (by analyze “Write” events)
- Event Retention as 90 days. Can be export to S3 and use Athena for further analysis.

AWS Config
- tracks resource inventory, config history and config change notifications for the purpose of security and compliance. Assess, audit and evaluate the configurations of AWS resources.
Amazon Inspector
- an automated security assessment service that helps improve the security and compliance of applications deployed on AWS.
AWS Accounts
- To apply security restrictions across multiple AWS accounts, use Service Control Policy (SCP). For just a single account, use IAM policies.
- You can migrate an account to another AWS organization, e.g. if you divest a business unit