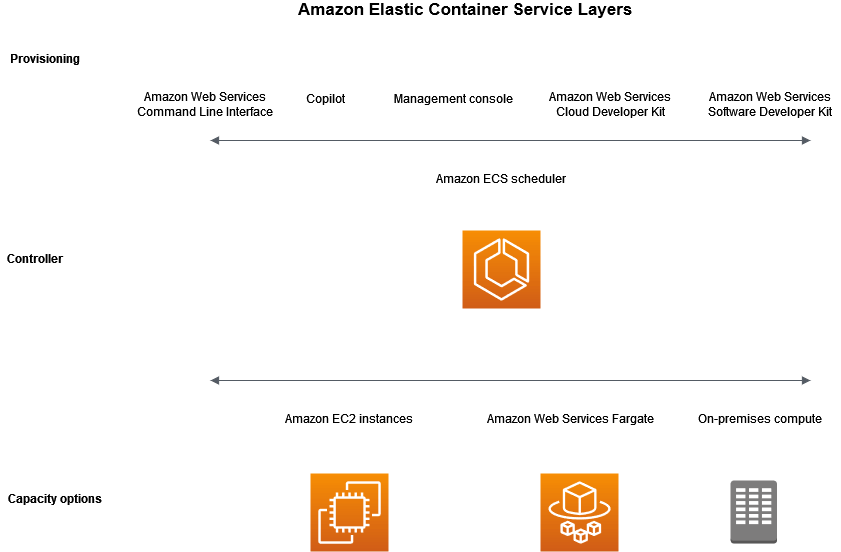
Amazon Elastic Container Service (ECS)
- Container management service for Docker containers (ECS Task)
- Highly scalable / high performance, lets you run applications on an EC2 cluster
- Amazon Elastic Container Registry (ECR) is private repository for Docker images, the public version is Amazon ECR Public Gallery; backed by Amazon S3, access controlled through IAM
- ECS Launch Types
- Fargate Launch Type is serverless, managed by AWS
- EC2 Launch Type gives you direct access to the instances, but you have to manage them, with ECS Agent
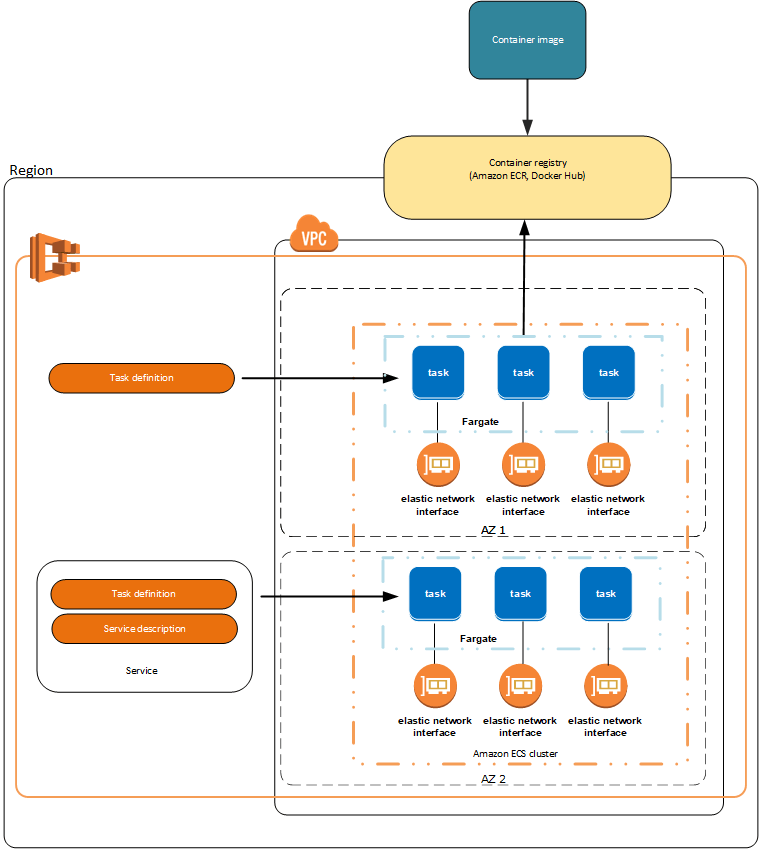
- Launch Docker containers on AWS = Launch ECS Tasks on ECS Clusters
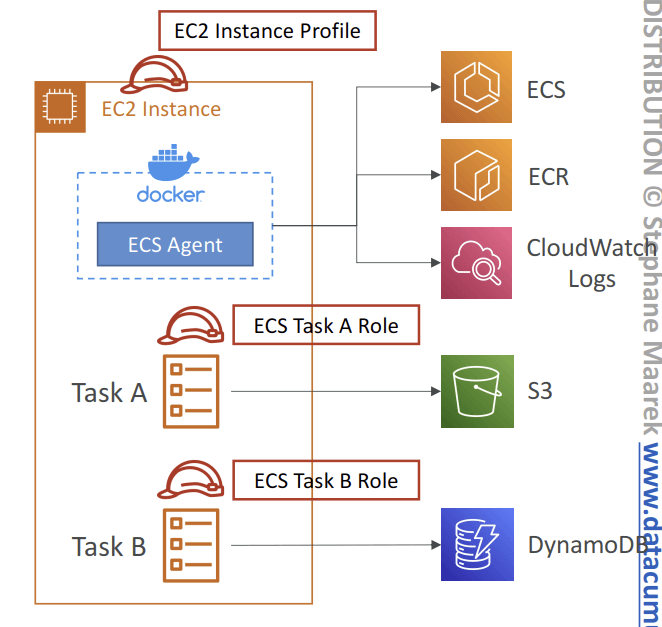
- ECS Agent would use EC2 Instance Profile
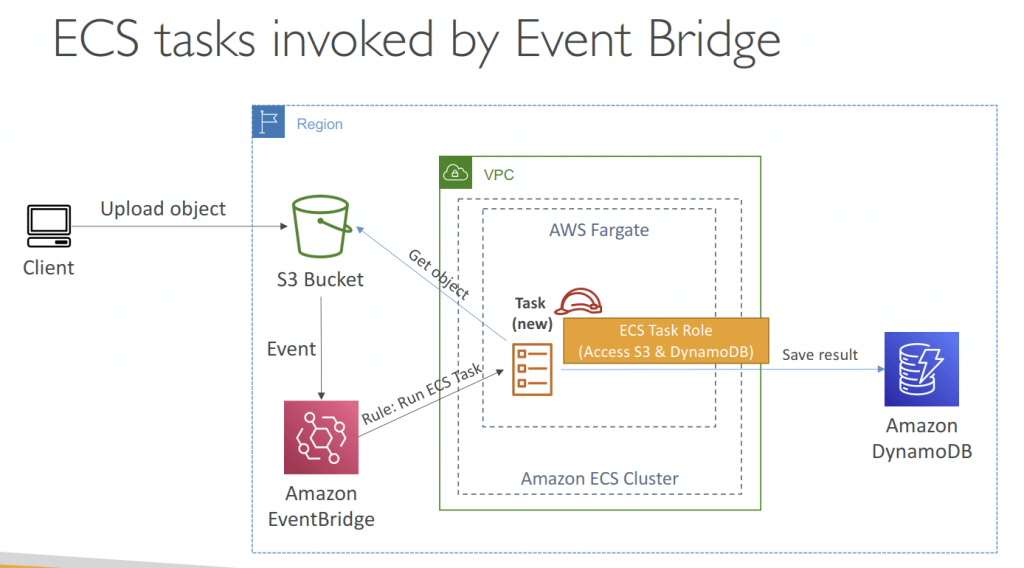
- ESC Tasks use each individual ESC Task Role, which is defined in the task definition
- ECS Task definition is metadata in JSON, up to 10 containers in one file
- Image name
- Port Binding for Container and Host
- on EC2 Launch type, if only define container port, then the ALB would use Dynamic Host Port Mapping, then on EC2 instance’s Security Group should set allow on any port from ALB security group
- each task has its unique private IP on Fargate Launch, so only define the container port
- Memory and CPU required
- Environment variables (Hardcoded ,SSM Parameter Store, Secrets Manager, or files stored in S3)
- Networking
- IAM Role (One IAM Role per Task Definition)
- Logging configuration (CloudWatch)
- Data Volume to share data among multiple containers (Applications and Metrics/Logs, aka sidecar)
- EC2 Launch Type – using EC2 instance storage
- Fargate Launch Type – using ephemeral storage (20-200 GB), data deleted when containers demolished
- ECS Task Placement strategy & Task Placement constraints – Only for EC2 Launch Type
- find instances meet CPU/Memory/Port requirements
- find those satisfy task placement constraints
- distinctInstance – place each task on different container instance
- memberOf – using Cluster Query Language, placing on certain instances (like t2.*)
- find those satisfy task placement strategies
- Binpack – cost-saving by using least available amount of CPU or Memory as minimum instances
- Random
- Spread (can be AZ or instance ID)
- Mount EFS for ECS tasks; in comparison, S3 cannot be mounted as File System
- Works for both EC2 and Fargate launch types
- tasks in any AZ will share the same data
- Use cases: persistent multi-AZ shared storage for your containers
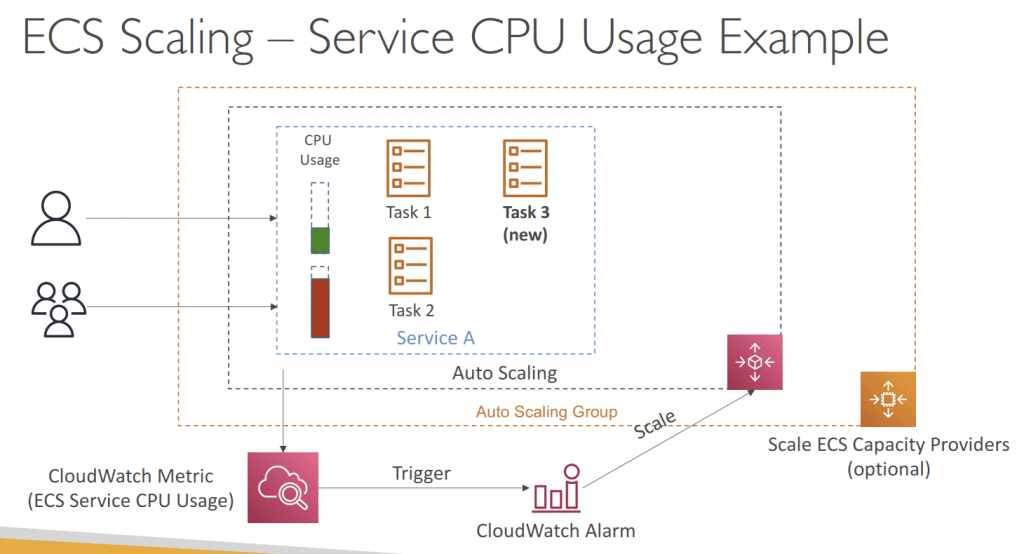
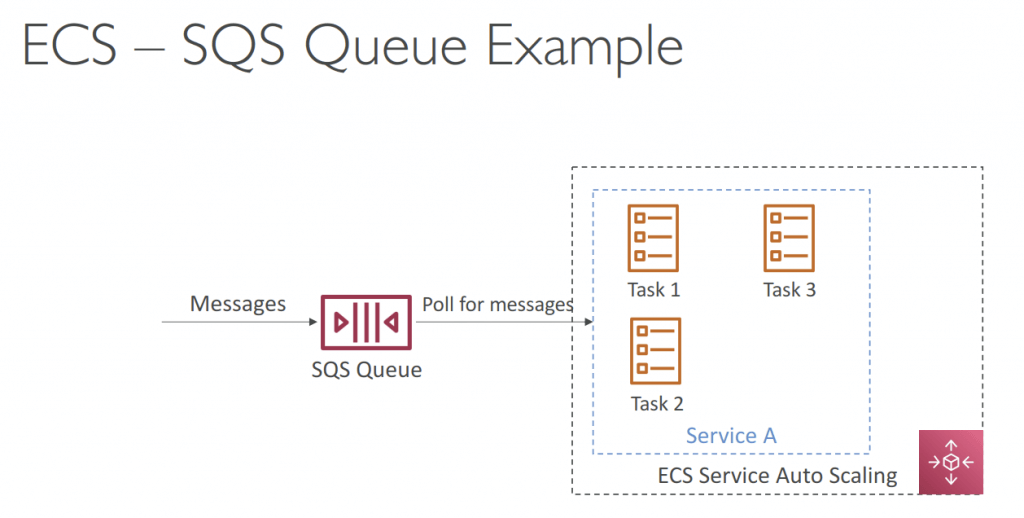
- ECS does not use EC2 Auto Scaling, instead, uses the AWS Application Auto Scaling based on
- Average CPU Utilization
- Average Memory Utilization – Scale on RAM
- ALB Request Count Per Target
- AWS Application Auto Scaling policy can be
- Target Tracking – scale based on the target specific CloudWatch metric
- Step Scaling – based on a specified CloudWatch Alarm
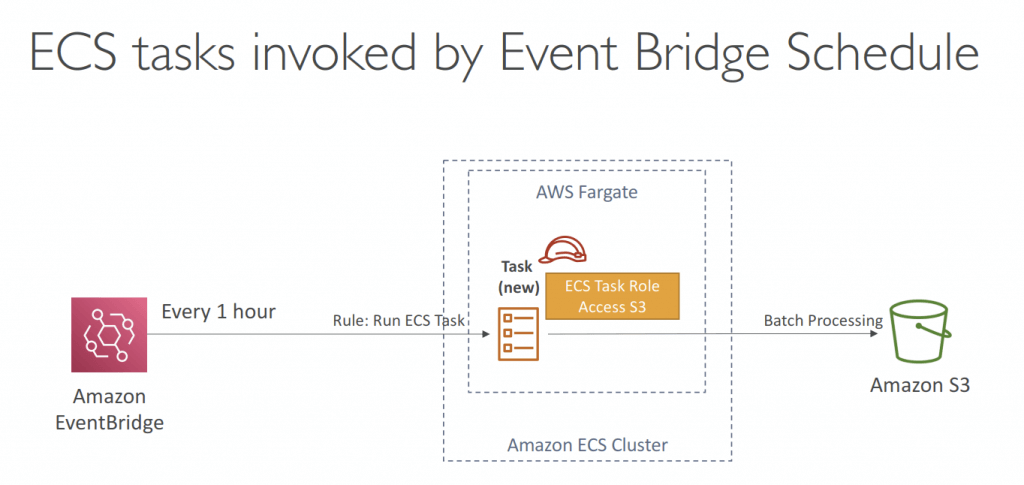
- Scheduled Scaling – scale based on a specified date/time (predictable changes)
- Under EC2 Launch Type, the way to auto-scaling EC2 instances by
- Auto Scaling Group Scaling – use EC2 ASG to check instance loadings (CPU, Memory, etc.)
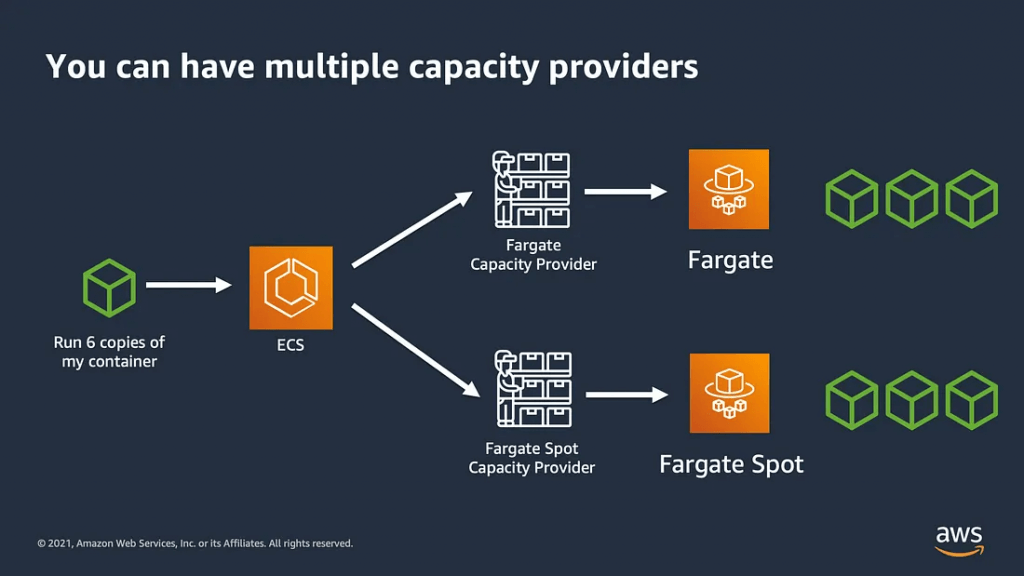
- ECS Cluster Capacity Provider, paired with ASG
- Used to automatically provision and scale the infrastructure for your ECS Tasks
- Imagine you have an e-commerce application running on ECS. You can define a capacity provider strategy that uses an Auto Scaling group for EC2 instances to handle the bulk of your traffic, and then also use Fargate for handling sudden traffic spikes. ECS will then automatically manage the scaling of both your EC2 instances and Fargate resources, ensuring optimal performance and cost efficiency.
- AWS Coplit is the CLI tool, running apps on AppRunner, ECS and Fargate; with CodePipeline for deployment <— Deprecated in Feb 2025.
- Load Balancer Integrations
- Application Load Balancer supported and works for most use cases
- Network Load Balancer recommended only for high throughput / high performance use cases, or to pair it with AWS Private Link
- Classic Load Balancer supported but not recommended (no advanced features – no Fargate)
- IAM roles for ECS
- EC2 Instance Profile (EC2 Launch Type only):
- Used by the ECS agent
- Makes API calls to ECS service
- Send container logs to CloudWatch Logs
- Pull Docker image from ECR
- Reference sensitive data in Secrets Manager or SSM Parameter Store
- ECS Task Role:
- Allows each task to have a specific role
- Use different roles for the different ECS Services you run
- Task Role is defined in the task definition
- EC2 Instance Profile (EC2 Launch Type only):
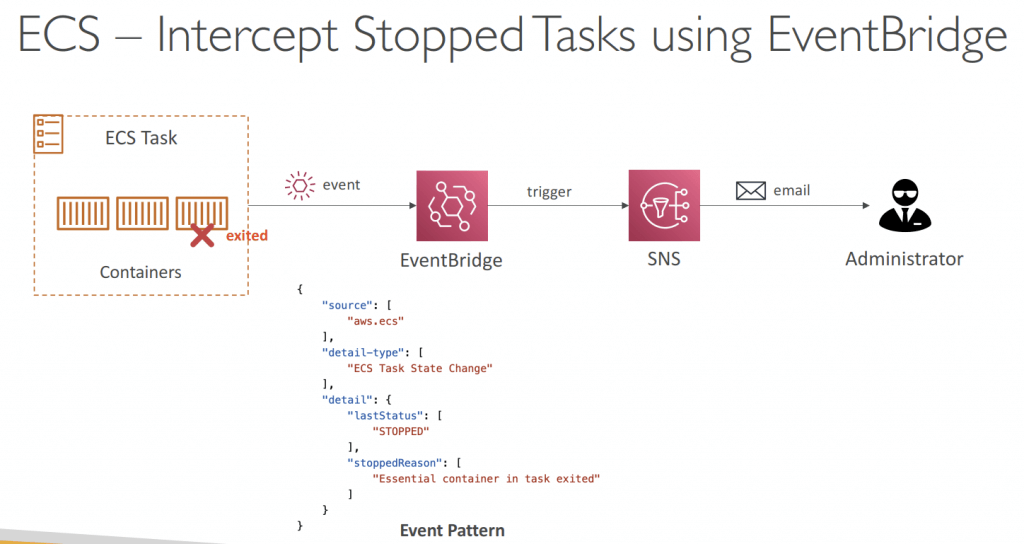
- Logging with “awslogs” driver
- Containers can send application logs directly to CloudWatch Logs
- You need to turn on awslogs log driver (for CW Logs)
- Configure logConfiguration parameters in your Task Definition
- Fargate Launch Type
- Task Execution Role must have the required permissions
- Supports awslogs, splunk, awsfirelens log drivers
- EC2 Launch Type
- Prevents logs from taking up disk space on your container EC2 instances
- Uses CloudWatch Unified Agent & ECS Container Agent
- Enable logging using ECS_AVAILABLE_LOGGING_DRIVERS in /etc/ecs/ecs.config
- Container EC2 instances must have permissions
- Create the required IAM Policy and attach it to the
ecsInstanceRole. Install the Amazon CloudWatch Logs agent on the Amazon ECS instances. Use theawslogsLog Driver in the Amazon ECS task definition. - The type of information that is logged by the containers in your task depends mostly on their
ENTRYPOINTcommand. By default, the logs that are captured show the command output that you would normally see in an interactive terminal if you ran the container locally, which are theSTDOUTandSTDERRI/O streams. Theawslogslog driver simply passes these logs from Docker to CloudWatch Logs. - You can use subscriptions to get access to a real-time feed of log events from CloudWatch Logs and have it delivered to other services such as a Amazon Kinesis stream, Amazon Kinesis Data Firehose stream, or AWS Lambda for custom processing, analysis, or loading to other systems. To begin subscribing to log events, create the receiving source, such as a Kinesis stream, where the events will be delivered. A subscription filter defines the filter pattern to use for filtering which log events get delivered to your AWS resource, as well as information about where to send matching log events to.
- Elastic Load Balancing provides access logs that capture detailed information about requests sent to your load balancer. Each log contains information such as the time the request was received, the client’s IP address, latencies, request paths, and server responses. You can use these access logs to analyze traffic patterns and troubleshoot issues.
- Access logging is an optional feature of Elastic Load Balancing that is disabled by default. After you enable access logging for your load balancer, Elastic Load Balancing captures the logs and stores them in the Amazon S3 bucket that you specify as compressed files. You can disable access logging at any time.
- Each access log file is automatically encrypted before it is stored in your S3 bucket and decrypted when you access it. You do not need to take any action; the encryption and decryption is performed transparently. Each log file is encrypted with a unique key, which is itself encrypted with a master key that is regularly rotated.
- Logging with Sidecar Container
- Using a sidecar container which is responsible for collecting logs from all other containers and files on the file system and send the logs to a log storage (e.g., CloudWatch Logs)
| awslog | splunk | awsfirelens | |
|---|---|---|---|
| Purpose | This is the default and simplest driver, designed to send container logs directly to Amazon CloudWatch Logs. | This driver is specifically designed to send container logs to a Splunk instance. | This driver acts as a log router, leveraging Fluentd or Fluent Bit as a sidecar container to provide highly customizable log routing and processing. |
| Configuration | Requires minimal configuration, primarily specifying the CloudWatch log group. | Requires specifying the Splunk endpoint and potentially other Splunk-specific configurations. | More complex setup involving a sidecar container and detailed Fluentd/Fluent Bit configurations to define log destinations (e.g., CloudWatch, Splunk, S3, Elasticsearch, Kinesis), filtering, and enrichment. |
| Use Case | Ideal for basic logging needs where CloudWatch Logs is the sole or primary log destination. | Suitable for organizations already utilizing Splunk as their central log management and analysis platform. | Best for advanced logging scenarios requiring routing to multiple destinations, complex log transformations, or integration with diverse logging tools beyond CloudWatch or Splunk directly. It offers flexibility to send logs to Splunk, CloudWatch, or other custom destinations based on the Fluent Bit/Fluentd configuration. |
- You can update a running service to change the number of tasks that are maintained by a service, which task definition is used by the tasks, or if your tasks are using the Fargate launch type, you can change the platform version your service uses. If you have an application that needs more capacity, you can scale up your service. If you have unused capacity to scale down, you can reduce the number of desired tasks in your service and free up resources. If you have updated the Docker image of your application, you can create a new task definition with that image and deploy it to your service.
- If your updated Docker image uses the same tag as what is in the existing task definition for your service (for example,
my_image:latest), you do not need to create a new revision of your task definition. You can update the service using the procedure below, keep the current settings for your service, and select Force new deployment. The new tasks launched by the deployment pull the current image/tag combination from your repository when they start. - The service scheduler uses the minimum healthy percent and maximum percent parameters (in the deployment configuration for the service) to determine the deployment strategy. When a new task starts, the Amazon ECS container agent pulls the latest version of the specified image and tag for the container to use. However, subsequent updates to a repository image are not propagated to already running tasks.
- To have your service use a newly updated Docker image with the same tag as in the existing task definition (for example,
my_image:latest) or keep the current settings for your service, select Force new deployment. The new tasks launched by the deployment pull the current image/tag combination from your repository when they start. The Force new deployment option is also used when updating a Fargate task to use a more current platform version when you specifyLATEST. For example, if you specifiedLATESTand your running tasks are using the1.0.0platform version and you want them to relaunch using a newer platform version. - It is mentioned in the scenario that the new tasks are occasionally running the old image of the application. The ECS cluster is also using Service Auto Scaling that automatically launches new tasks based on demand. We can conclude that the root cause is not in the task definition since this issue only occurs occasionally, and the other tasks were properly updated. If the ECS task is still running an old image, then it is possible that the ECS agent is not running properly.
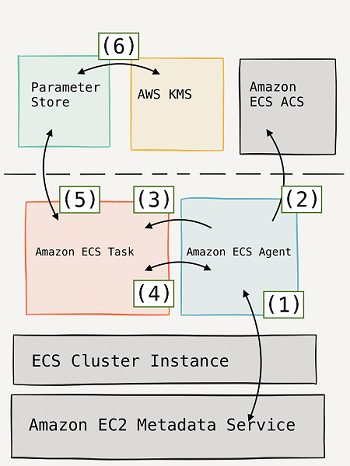
- [ 🧐QUESTION🧐 ] Store secrets out of AMI with lifecycle management
- Within your container definition, specify
secretswith the name of the environment variable to set in the container and the full ARN of either the Secrets Manager secret or Systems Manager Parameter Store parameter containing the sensitive data to present to the container. The parameter that you reference can be from a different Region than the container using it, but must be from within the same account. - AWS Secrets Manager is a secrets management service that helps you protect access to your applications, services, and IT resources. This service enables you to easily rotate, manage, and retrieve database credentials, API keys, and other secrets throughout their lifecycle. Using Secrets Manager, you can secure and manage secrets used to access resources in the AWS Cloud, on third-party services, and on-premises.
- If you want a single store for configuration and secrets, you can use Parameter Store. If you want a dedicated secrets store with lifecycle management, use Secrets Manager.
- Within your container definition, specify
Amazon Elastic Container Registry (ECR)
- Store and manage Docker images on AWS
- Private and Public repository (Amazon ECR Public Gallery https://gallery.ecr.aws)
- Fully integrated with ECS, backed by Amazon S3
- Access is controlled through IAM (permission errors => policy)
- Supports image vulnerability scanning, versioning, image tags, image lifecycle…
- Lifecycle Policies
- Automatically remove old or unused images based on age or count
- Each Lifecycle Policy contains one or more rules
- All rules are evaluated at the same time, then applied based on priority
- Images are expired within 24 hours after they meet the criteria
- Helps you reduce unnecessary storage costs
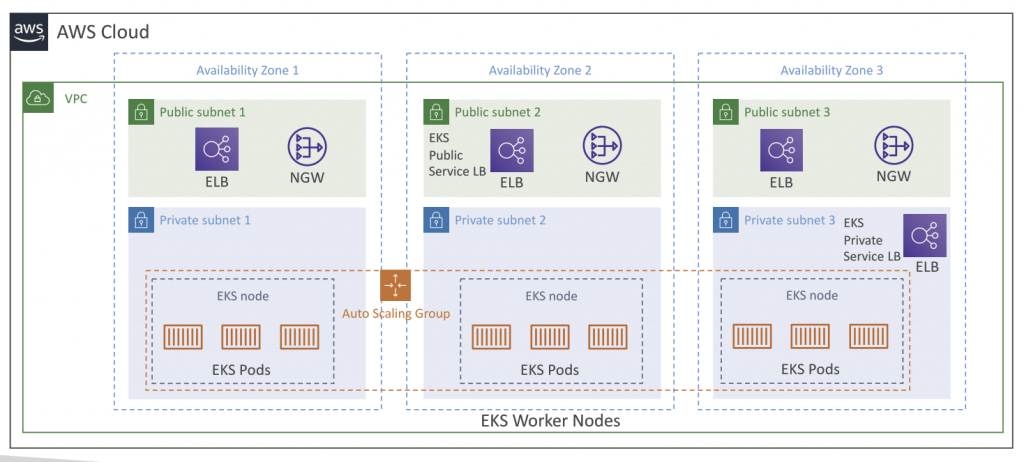
Amazon Elastic Kubernetes Service (EKS)
- EC2 Launch for deploy worker node; Fargate for serverless
- Kubernetes is cloud-agnostic (can be used in any cloud – Azure, GCP…)
- Kubernetes is an open-source system for automatic deployment, scaling and management of containerized (usually Docker) application
- For multiple regions, deploy one EKS cluster per region
- Collect logs and metrics using CloudWatch Container Insights
- Node Types
- Managed Node Groups
- AWS handles EC2 instances with ASG managed by EKS
- On-Demand or Spot instances
- Self-Managed Nodes
- Self create and manage EC2 instance with self-define ASG
- On-Demand or Spot instances
- can use prebuilt AMI – Amazon EKS Optimized AMI
- AWS Fargate
- Managed Node Groups
- Data Volumes
- Can specify StorageClass manifest on EKS cluster, leverage a Container Storage Interface (CSI) compliant driver
- Amazon EBS (EC2)
- Amazon EFS (EC2, Fargate)
- Amazon FSx for Lustre (EC2)
- Amazon FSx for NetApp ONTAP (EC2)
- Persistent storage is a critical component in Kubernetes clusters, especially when applications require data to persist beyond the lifecycle of a pod.
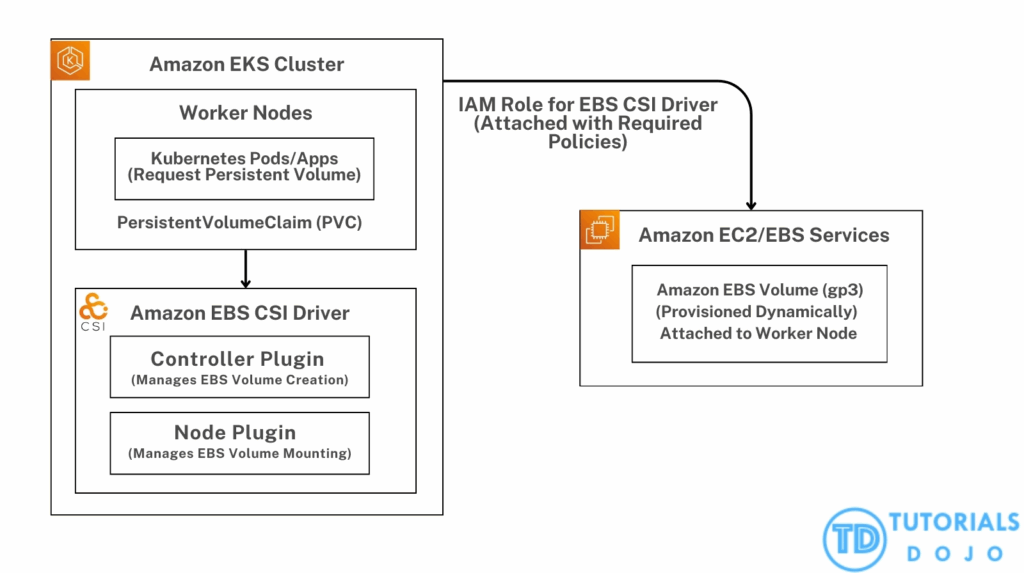
- Persistent storage is often provisioned using Amazon Elastic Block Store (Amazon EBS) volumes.
- The Amazon EBS Container Storage Interface (CSI) driver is responsible for integrating Kubernetes with EBS, enabling dynamic provisioning and management of volumes as per application requirements.
- When integrating the Amazon Elastic Block Store (Amazon EBS) Container Storage Interface (CSI) driver with an Amazon EKS cluster, the EBS CSI driver requires appropriate permissions to dynamically provision and manage EBS volumes.
- These permissions are managed using an IAM role, often attached to the driver itself. The error
<code>EC2:UnauthorizedOperation</code>indicates insufficient permissions for the driver to interact with the Amazon EC2 service, which is required for creating or managing EBS volumes. - AWS recommends assigning an IAM role to the EBS CSI driver with the necessary permissions to provision and manage EBS volumes. This ensures that the driver can perform operations such as creating volumes, attaching them to nodes, and managing lifecycle events.
- Can specify StorageClass manifest on EKS cluster, leverage a Container Storage Interface (CSI) compliant driver
- Control Plane Logging
- Send EKS Control Plane audit and diagnostic logs to CloudWatch Logs
- EKS Control Plane Log Types
- API Server (api)
- Audit (audit)
- Authenticator (authenticator)
- Controller Manager (controllerManager)
- Scheduler (scheduler)
- Ability to select the exact log types to send to CloudWatch Logs
- Nodes & Containers Logging
- You can capture node, pod, and containers logs and send them to CloudWatch Logs
- Use CloudWatch Agent to send metrics to CloudWatch
- Use the Fluent Bit, or Fluentd log drivers to send logs to CloudWatch Logs
- Container logs are stored on a Node directory /var/log/containers
- Use CloudWatch Container Insights to get a dashboarding monitoring solution for nodes, pods, tasks, and services