== CODE IMPLEMENTATION ==
AWS Command Line Interface (CLI) & Software Developer Kit (SDK)
- both protected by access keys, generated from AWS Management Console
- CLI can direct access to public APIs of AWS resources
- to use MFA with CLI, which means a temporary session
- run the STS GetSessionToken API call
aws sts get-session-token --serial-number arn-of-the-mfa-device --token-code code-from-token --duration-seconds 3600
- run the STS GetSessionToken API call
- CLI Credentials Provider Chain
- Command line options – –region, –output, and –profile
- Environment variables – AWS_ACCESS_KEY_ID,AWS_SECRET_ACCESS_KEY, and AWS_SESSION_TOKEN
- CLI credentials file – aws configure ~/.aws/credentials
- CLI configuration file – aws configure ~/.aws/config
- Container credentials – for ECS tasks
- Instance profile credentials – for EC2 Instance Profiles
- SDK is set of libraries for programming, as language-specific APIs
- the AWS CLI uses the Python SDK (boto3)
- “us-east-1” would be chosen by default, if no region specified
- SDK Credential Provider Chain
- Java system properties – aws.accessKeyId and aws.secretKey
- Environment variables –
AWS_ACCESS_KEY_ID and AWS_SECRET_ACCESS_KEY - The default credential profiles file – ex at: ~/.aws/credentials, shared by many SDK
- Amazon ECS container credentials – for ECS containers
- Instance profile credentials– used on EC2 instances
- pagination parameters in AWS CLI command could help to solve the Time-Out issue from massive resource item processing
- –page-size
- The CLI still retrieves the entire list, but it makes a greater number of service API calls in the background and retrieves fewer items with each request. This increases the probability that individual calls will succeed in without the use of a timeout.
Cloud Development Kit (CDK)
- CloudFormation using JSON/YAML, but CDK using Javascript/Typescript, Python, Java, .Net
- Contain higher level components, constructs
- encapsulate everything for final CloudFormation stack creation
- AWS Construct Library or Construct Hub
- Layer 1 (L1): CloudFormation(CFN) resources, prefix with “Cfn”, and all resource properties needed to be explicitly configured
- Layer 2 (L2): intent-based API resources, with defaults and boilerplate, also can use methods
- Layer 3 (L3): aka Patterns, represents as multiple related resources (for example, API Gateway + Lambda, or Fargate cluster + Application Load Balancer)
- The codes would be complied to CloudFormation template
- Benefits for Lambda & ECS/EKS as infrastructures and applications runtime codes implemented together
- SAM focus on serverless, good for Lambda, but only JSON/YAML
- Bootstrapping: the process of provisioning before deploying AWS environment (Account+Region)
- CDKToolkit (CloudFormation stack), with S3 Bucket – store files and IAM Roles
- Error: “Policy contains a statement with one or more invalid principal”, due to the lack of new IAM Roles for each new environment
- UnitTest, using CDK Assertion Module for Jest(Javascript) or Pytest(Python)
- Fine-granted Assertions (common): check certain property of certain resource
- Snapshot Test: test against baseline template
AWS CloudFormation
- provision infrastructure using a text-based (JSON/YAML) templates (uploaded to S3) that describes exactly what resources are provisioned and their settings.
- manages the template history similar to how code is managed in source control
- Benefits
- Infrastructure as code (IaC)
- Cost
- Each resources within the stack is tagged with an identifier so you can easily see how much a stack costs you
- Productivity
- Ability to destroy and re-create an infrastructure on the cloud on the fly
- Automated generation of Diagram for your templates!
- Declarative programming (no need to figure out ordering and orchestration)
- Separation of concern: create many stacks for many apps, and many layers.
- Delete the stack would also remove each individual artifact
- Components
- AWSTemplateFormatVersion
- Description
- Resources (mandatory) – aws resources
- Parameters – dynamic inputs (AllowedValues/NoEcho) !Ref
- Pseudo Parameters
- AWS::AccountId
- AWS::Region
- AWS::StackId
- AWS::StackName
- AWS::NotificationARNs
- AWS::NoValue (Doesn’t return a value)
- Pseudo Parameters
- Mappings – static variables !FindInMap [ MapName, TopLevelKey, SecondLevelKey ]
- Outputs – reference about what has been created !ImportValue
- declares optional outputs values that we can import into other stacks (if you export them first)!
- Conditions
- (References / Functions) as Helper
- Transformer- used for Serverless services, especially for AWS SAM.
- 2 methods of updating a stack
- direct update – CloudFormation immediately deploys your changes
- change sets – preview your changes first, then decide if you want to deploy
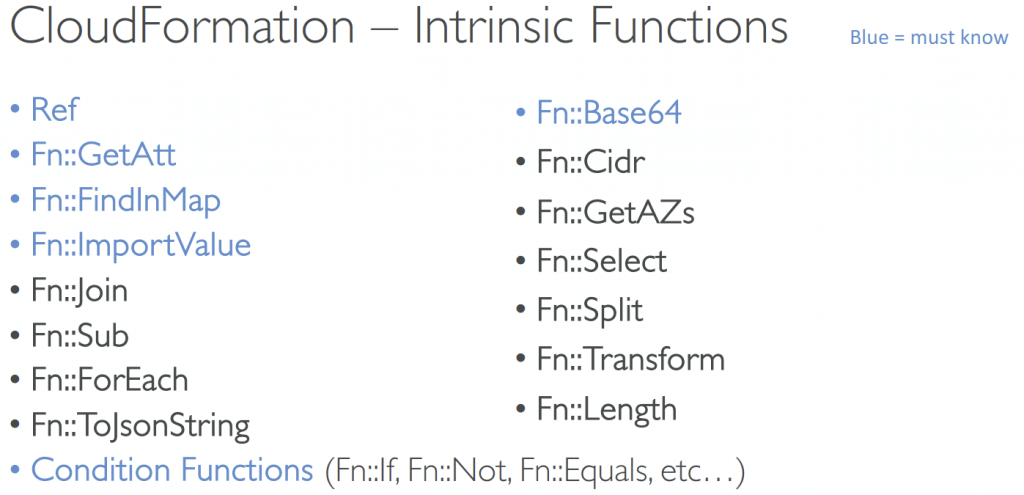
- Intrinsic Functions
- Fn::Ref (!Ref)
- Parameters – returns the value of the parameter
- Resources – returns the physical ID of the underlying resource (e.g., EC2 ID)
- Fn::GetAtt (!GetAtt)
- Attributes are attached to any resources you create
- Fn::FindInMap (!FindInMap) [MapName, TopLevelKey, SecondLevelKey]
- Fn::ImportValue (!ImportValue)
- Import values that are expor ted in other stacks
- Fn::Base64 (!Base64)
- convert string to Base64; heavily used in EC2 instance’s UserData property
- user data script log is in /var/log/cloud-init-output.log
- Conditions (Fn::If, Fn::Not, Fn::Equal, Fn::And, Fn::Or, etc)
- Fn::Ref (!Ref)
- Rollbacks
- Stack Creation Fails:
- Default: ever ything rolls back (gets deleted). We can look at the log
- Option to disable rollback and troubleshoot what happened
- Stack Update Fails:
- The stack automatically rolls back to the previous known working state
- Ability to see in the log what happened and error messages
- Rollback Failure? Fix resources manually then issue ContinueUpdateRollback API from Console
- Or from the CLI using continue-update-rollback API call
- Stack Creation Fails:
- Service Role
- IAM role that allows CloudFormation to create/update/delete stack resources on your behalf
- User must have iam:PassRole permissions
- Capabilities
- CAPABILITY_(Resource Named)_IAM & CAPABILITY_IAM
- Necessary to enable when you CloudFormation template is creating or updating IAM resources (IAM User, Role, Group, Policy, Access Keys, Instance Profile…)
- CAPABILITY_AUTO_EXPAND, for Macro and Nested stakes
- Necessar y when your CloudFormation template includes Macros or Nested Stacks (stacks within stacks) to perform dynamic transformations
- InsufficientCapabiltiesException
- Exception that will be thrown by CloudFormation if the capabilities haven’t been acknowledged when deploying a template (security measure)
- CAPABILITY_(Resource Named)_IAM & CAPABILITY_IAM
- DeletionPolicy
- Default: Delete (wont work in S3 if the bucket is not empty)
- Retain
- Snapshot: create a final snapshot before deleted
- works with storage related (EBS, ElastiCache, RDS, Redshift, Neptune, etc)
- Stack policy is a JSON to tell which resource(s) should be protected as not touched during update; so an explicit ALLOW for the desired resources for update is needed
- Termination Protection is to prevent accidental delete
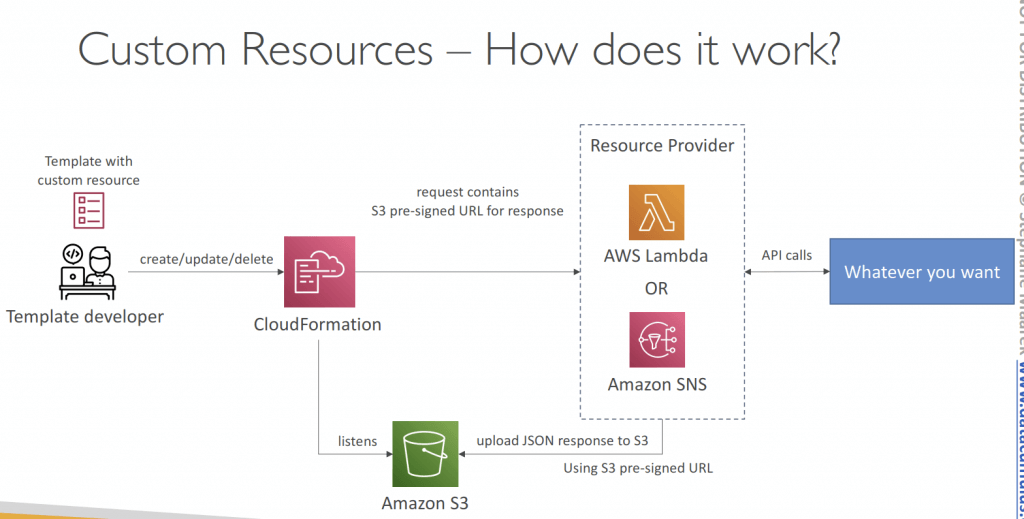
- Custom Resources
- custom functions running via Lambda, for example, empty a S3 bucket
- AWS::CloudFormation::CustomResource or Custom::MyCustomResourceTypeName
- Properties with Service Token (Lambda function or SNS topic, in the sam region) and optional Input data
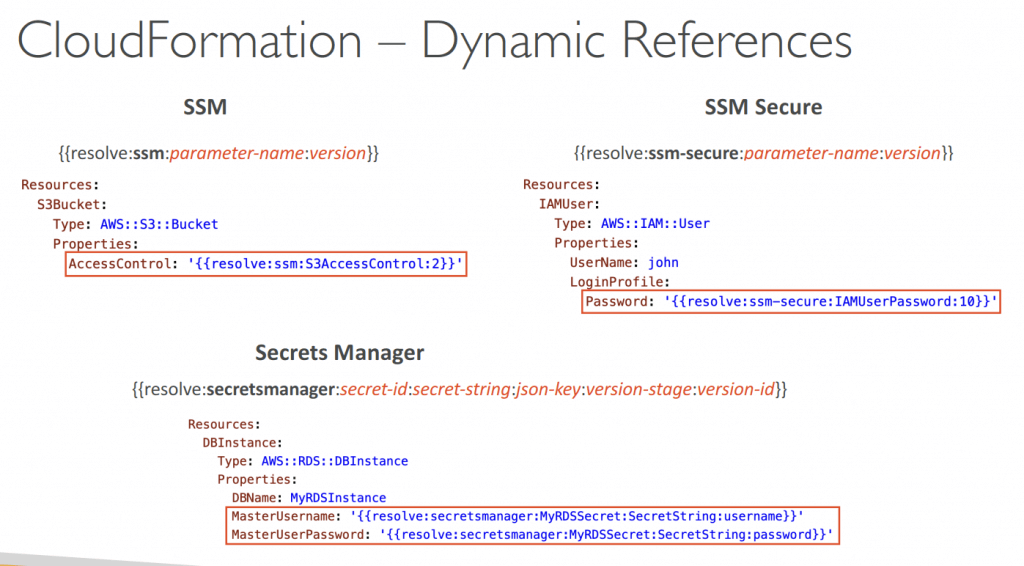
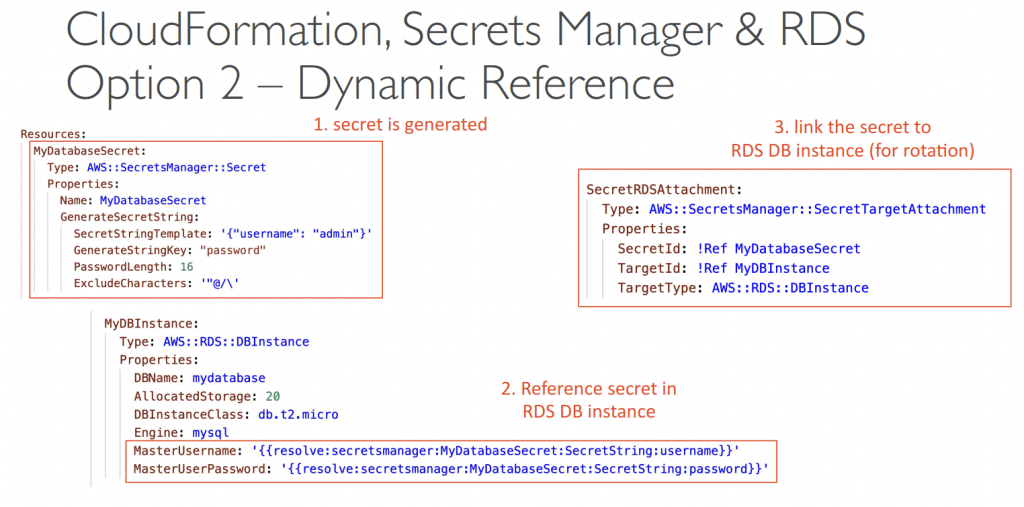
- Dynamic References
- Reference external values stored in Systems Manager Parameter Store and Secrets Manager within CloudFormation templates
- CloudFormation retrieves the value of the specified reference during create/update/delete operations
- Using ‘{{resolve:service-name:reference-key}}’
- ssm – for plaintext values stored in SSM Parameter Store
- ssm-secure – for secure strings stored in SSM Parameter Store
- secretsmanager – for secret values stored in Secrets Manager
- (Python) Helper scripts
- cfn-init – Use to retrieve and interpret resource metadata, install packages, create files, and start services.
- AWS::CloudFormation::Init
- A config contains the following and is executed in that order
- Packages: used to download and install pre-packaged apps and components on Linux/Windows (ex. MySQL, PHP, etc…)
- Groups: define user groups
- Users: define users, and which group they belong to
- Sources: download files and archives and place them on the EC2 instance
- Files: create files on the EC2 instance, using inline or can be pulled from a URL
- Commands: run a series of commands
- Services: launch a list of sysvinit
- AWS::CloudFormation::Init
- cfn-signal – Use to signal with a WaitCondition, so you can synchronize other resources in the stack when the prerequisite resource or application is ready
- WaitCondition
- Block the template until it receives a signal from cfn-signal
- We attach a CreationPolicy (also works on EC2, ASG)
- We can define a Count > 1 (in case you need more than 1 signal)
- Troubleshooting: Verify that the instance has a connection to the Internet.
- WaitCondition
- cfn-get-metadata – Use to retrieve metadata for a resource or path to a specific key.
- cfn-hup – Use to check for updates to metadata every 15(default) minutes and execute custom hooks when changes are detected.
- cfn-init – Use to retrieve and interpret resource metadata, install packages, create files, and start services.
- Troubleshooting
- DELETE_FAILED
- Some resources must be emptied before deleting, such as S3 buckets
- Use Custom Resources with Lambda functions to automate some actions
- Security Groups cannot be deleted until all EC2 instances in the group are gone
- Think about using DeletionPolicy=Retain to skip deletions
- UPDATE_ROLLBACK_FAILED
- Can be caused by resources changed outside of CloudFormation, insufficient permissions, Auto Scaling Group that doesn’t receive enough signals…
- Manually fix the error and then ContinueUpdateRollback
- DELETE_FAILED
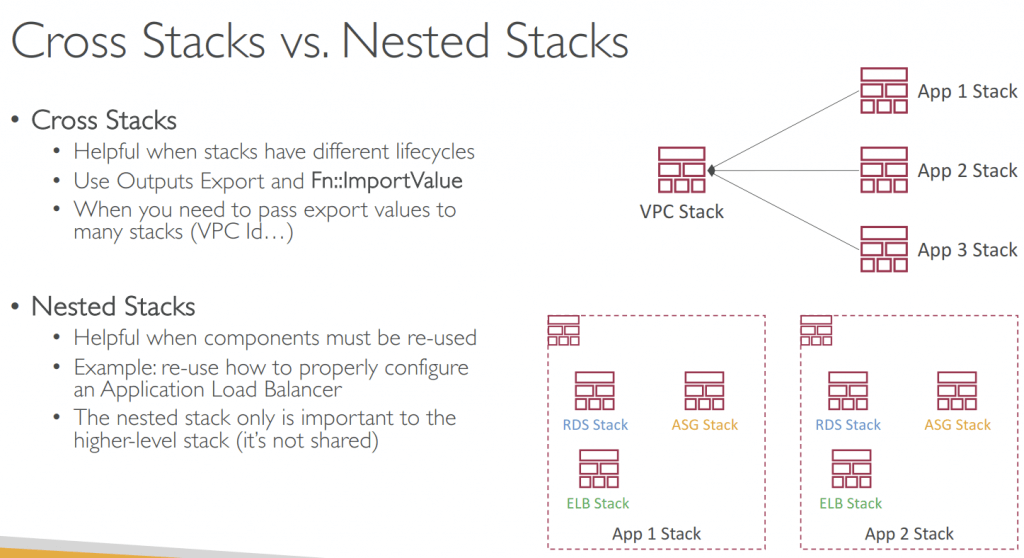
- Nested Stacks
- Nested stacks are stacks as par t of other stacks
- Nested stacks are considered best practice
- To update a nested stack, always update the parent (root stack)
- Nested stacks can have nested stacks themselves!
- DependsOn
- Specify that the creation of a specific resource follows another
- When added to a resource, that resource is created only after the creation of the resource
specified in the DependsOn attribute - Applied automatically when using !Ref and !GetAtt
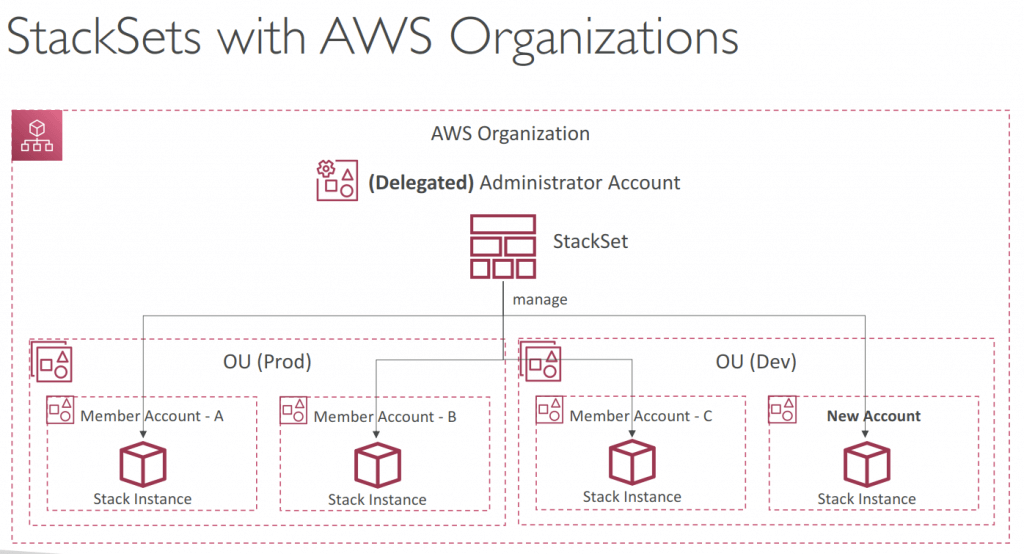
- Stackset is used for cross accounts/regions stacks management, with a single CloudFormation template.
- A stack instance is simply a reference to a stack in a target account within a region.
- When you update a stackset, all associated stack instances are updated throughout all accounts and regions
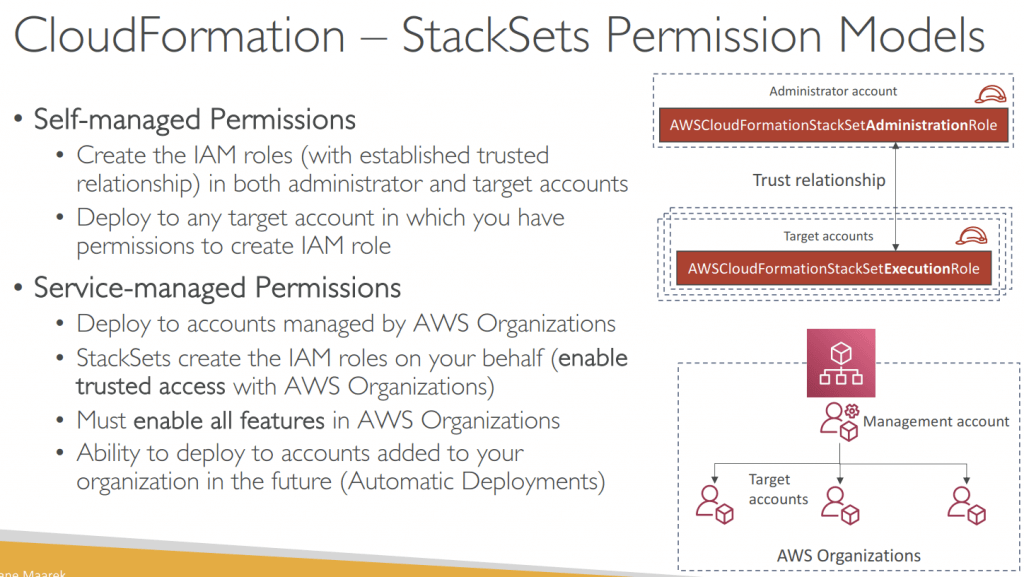
- Permission Models
- Self-managed Permissions
- Create the IAM roles (with established trusted relationship) in both administrator and target accounts
- Deploy to any target account in which you have permissions to create IAM role
- Service-managed Permissions
- Deploy to accounts managed by AWS Organizations
- StackSets create the IAM roles on your behalf (enable trusted access with AWS Organizations)
- Must enable all features in AWS Organizations
- Ability to deploy to accounts added to your organization in the future (Automatic Deployments)
- Self-managed Permissions
- Troubleshooting
- A stack operation failed, and the stack instance status is OUTDATED.
- Insufficient permissions in a target account for creating resources that are specified in your template.
- The template could be trying to create global resources that must be unique but aren’t, such as S3 buckets
- The administrator account does not have a trust relationship with the target account
- Reached a limit or a quota in the target account (too many resources)
- A stack operation failed, and the stack instance status is OUTDATED.
- Drift
- Performs drift detection on the stack associated with each stack instance in the StackSet
- If the current state of a resource in a stack varies from the expected state:
- The stack considered drifted
- And the stack instance that the stack associated with considered drifted
- And the StackSet is considered drifted
- Drift detection identifies unmanaged changes (outside CloudFormation)
- Changes made through CloudFormation to a stack directly (not at the StackSet level), aren’t considered drifted
- You can stop drift detection on a StackSet
- ChangeSets
- When you update a stack, you need to know what changes will happen before it applying them for greater confidence
- ChangeSets won’t say if the update will be successful
- For Nested Stacks, you see the changes across all stacks
- Local artifacts declared in CodeUri property
- The aws cloudformation package command packages the local artifacts (local paths) that your AWS CloudFormation template references.
- After you package your template’s artifacts, run the aws cloudformation deploy command to deploy the returned template.
AWS Serverless Application Model (SAM)
- configure via JSON/YAML, complied to CloudFormation stack
- use CodeDeploy for Lambda function
- Traffic Shifting (from OLD ver to New ver)
- Linear: grow traffic every N minutes until 100%
- Canary: try X percent then 100%
- AllAtOnce: immediate
- Pre- and Pro- for testing on traffic shifting
- rollback by AWS CloudWatch Alarm
- AppSpec.yml
- Name
- Alias
- CurrentVersion
- TargetVersion
- Traffic Shifting (from OLD ver to New ver)
- run Lambda, API Gateway, DynamoDB locally
- Lambda start/invoke
- API Gateway
- AWS Events (sample payloads for event resources)
- SAM Recipe
- Transform Header – template
- Write Code
- Package and Deploy – into S3 Bucket
- SAM commands
- sam init – creating a new SAM project
- sam build – resolve dependencies and construct deployment artifacts for all functions and layers in the SAM template.
- sam package – prepares the serverless application for deployment by zipping artifacts, uploading them to S3, and generating a CloudFormation template with references to the uploaded artifacts in S3. But, it doesn’t deploy the application.
- sam deploy – zips your code artifacts, uploads them to Amazon S3, and produces a packaged AWS SAM template file that it uses to deploy your application
- for nested applications, need “
CAPABILITY_AUTO_EXPAND” option - Compared with “aws cloudformation deploy” – deploy a CloudFormation stack, it expects that your artifacts are already packaged and uploaded to S3.
- for nested applications, need “
- sam publish – publishes an AWS SAM application to the AWS Serverless Application Repository
- sam sync – update existing SAM template
- as Accelerate, reduce latency on deployments for rapid development testing
- using “–code” option, without updating infrastructure (service APIs and bypass CloudFormation)
- sam local
- can specify a named profile from your AWS CLI configuration using the –profile parameter with the sam local invoke command
- run the aws configure with the –profile option to set the credentials for a named profile
- AWS SAM template file
- AWS::Serverless::Application – for nested application
- AWS::Serverless::Function – configuration information for creating a Lambda function
- AWS::Serverless::LayerVersion – creates a Lambda layer version (LayerVersion) that contains library or runtime code that’s needed by a Lambda function
- AWS::Serverless::Api – describes an API Gateway resource. It’s useful for advanced use cases where you want full control and flexibility when you configure your APIs. Mostly as part of event sources of “AWS::Serverless::Function”
- SAM Policy Templates
- apply permissions to Lambda Functions
- SAM Multiple Environments, using “samconfig.toml”
AWS Elastic Beanstalk
- provision infrastructure using a text-based template that describes exactly what resources are provisioned and their settings
- Amazon EC2 Instance
- Amazon CloudWatch
- ELB & ASG
- AWS S3
- RDS, DynamoDB
- Amazon SNS
- complied to CloudFormation stack
- Components
- Application
- Application Version
- Environment
- Web Server Tier and Worker Tier
- Deployment Method
- All at once, has downtime
- Rolling: running under capacity, no additional costs
- Rolling with additional batches: compared to Rolling, this let application running at capacity (ie temporary create more instances)
- Immutable: create new instances in a new ASG, then swap; zero downtime
- (Blue Green: new environment then swap, using Route53 with weighted policies)
- Traffic Splitting: canary testing

- Lifecycle
- max most Application versions: 1000, use LifeCycle Policy to phase out, based on Time or Space
- has option to retain source bundles on S3
- EB Extensions
- YAML/JSON, with “.config” extension as file name
- update defaults with “option_settings”
- place under the “.ebextensions/” folder under root of source code
- resources managed by .ebextensions would be deleted if the environment goes away
- EB Clone, can help to setup exact same “configuration” environment
- Load Balancer type and configure
- RDS configure, but no data
- Environment variables
- EB Migration
- Once EB created, the Elastic Load Balancer (ELB) type cannot change
- Create another environment with new ELB, then using Route53 update or CNAME swap
- Decouple RDS with EB, for PROD
- Once EB created, the Elastic Load Balancer (ELB) type cannot change
- extra Configuration file could be able to add to the source bundle
- cron.yaml – schedule tasks
- env.yaml – configure the environment name, solution stack, and environment links
- Dockerrun.aws.json – multi-container Docker environments that are hosted in Elastic Beanstalk
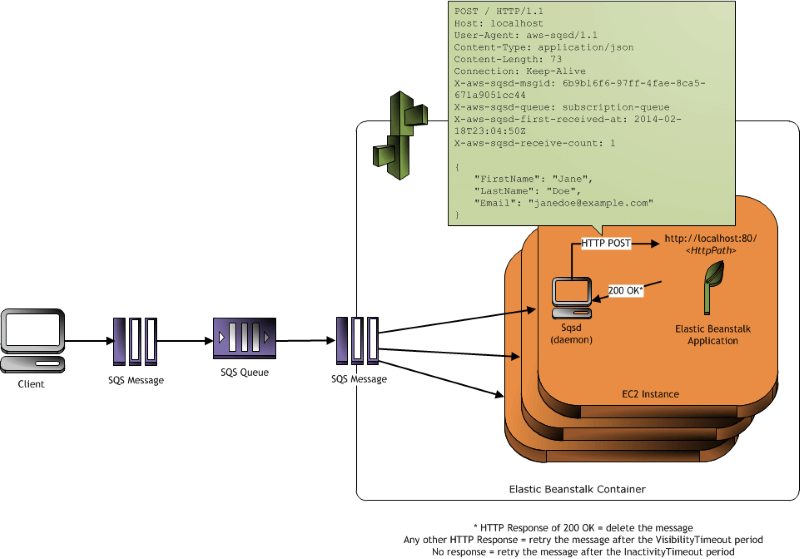
- Elastic Beanstalk worker environments simplify the process by managing the Amazon SQS queue (with support of DLQ) and running a daemon process on each instance that reads from the queue
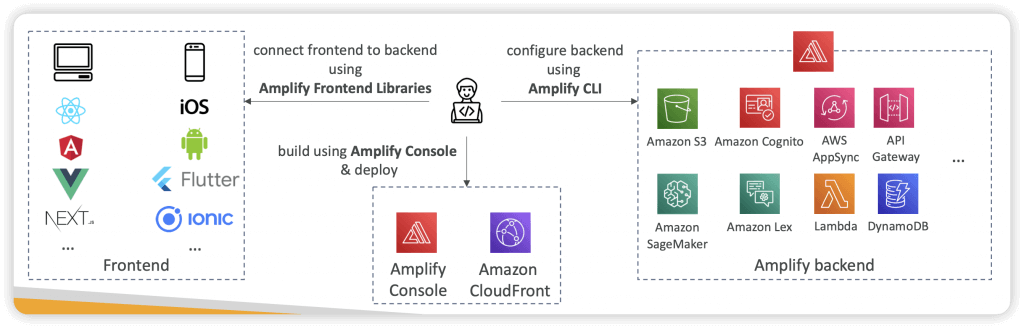
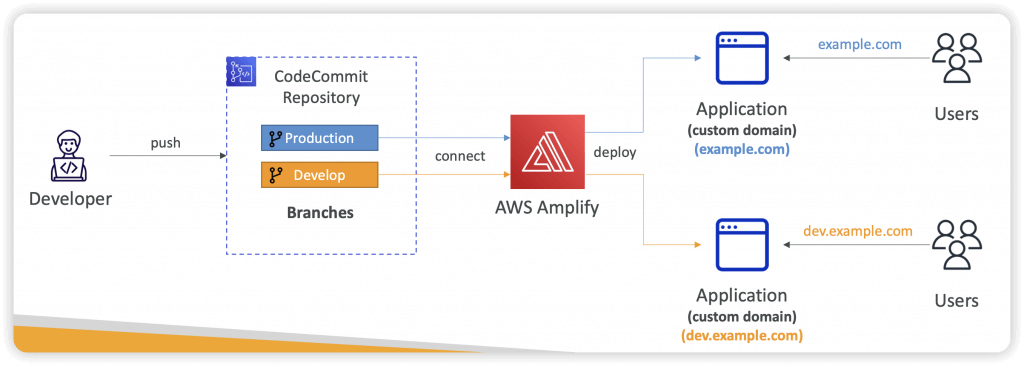
AWS Amplify
- create mobile and web applications (aka. ElasticBeans for mobile and web application)
- Authentication (Cognito), Storage (AppSync + DynamoDB), API (REST, GraphQL), CI/CD, PubSub, Analytics, AI/ML Predictions, Monitoring…
- Connect your source code from GitHub, AWS CodeCommit, Bitbucket, GitLab, or upload directly
- End-to-End (E2E) test, using Cypress
AWS AppConfig
- deploy dynamic configuration change without code deployment; validate with JSON Schema or Lambda Function
- provides the functionality to manage feature flags, a powerful technique that allows developers to test and control new features in live environments
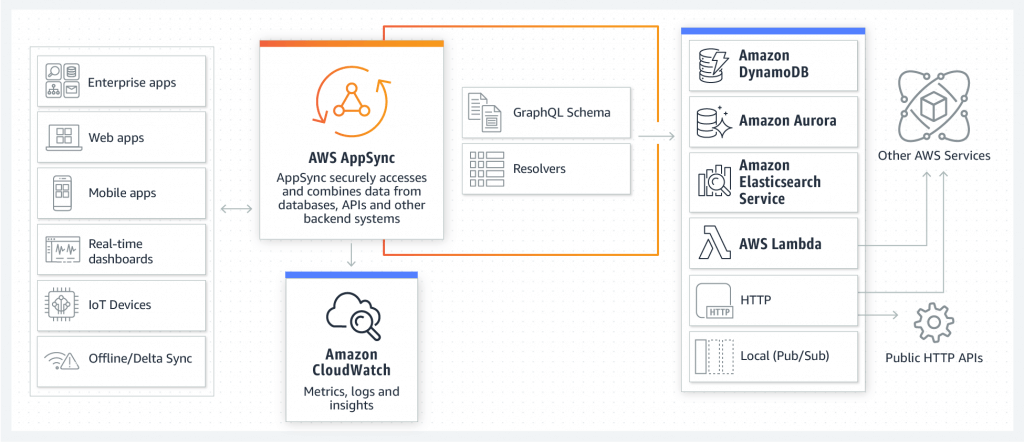
AWS AppSync
- extend Cognito Sync (user data, like app preferences or game state), and also allowing multiple users to synchronize and collaborate in real time on shared data.
- managed service of GraphQL, combining multiples data sources
- retrieve data in “realtime” or “MQTT” of WebSocket
- for mobile apps: local data access and data sync
- Security: API_KEY, AWS_IAM, OPENID_CONNECT, AMAZON_COGNITO_USER_POOLS
AWS Systems Manager
- focused on management and operations of AWS resources (EC2 and On-Premise), such as automation, patching, and configuration
- with SSM Agent installed on nodes
== CONTAINERS ==
Amazon Elastic Container Service (ECS)
- Container management service for Docker containers (ECS Task)
- Highly scalable / high performance, lets you run applications on an EC2 cluster
- Amazon Elastic Container Registry (ECR) is private repository for Docker images, the public version is Amazon ECR Public Gallery; backed by Amazon S3, access controlled through IAM
- ECS Launch Types
- Fargate Launch Type is serverless, managed by AWS
- EC2 Launch Type gives you direct access to the instances, but you have to manage them, with ECS Agent
- ECS Agent would use EC2 Instance Profile
- ESC Tasks use each individual ESC Task Role, which is defined in the task definition
- Mount EFS for ECS tasks, which can ensure all tasks in any AZ will share the same data; in comparison, S3 cannot be mounted as File System
- ECS Task definition is metadata in JSON, up to 10 containers in one file
- Image name
- Port Binding for Container and Host
- on EC2 Launch type, if only define container port, then the ALB would use Dynamic Host Port Mapping, then on EC2 instance’s Security Group should set allow on any port from ALB security group
- each task has its unique private IP on Fargate Launch, so only define the container port
- Memory and CPU required
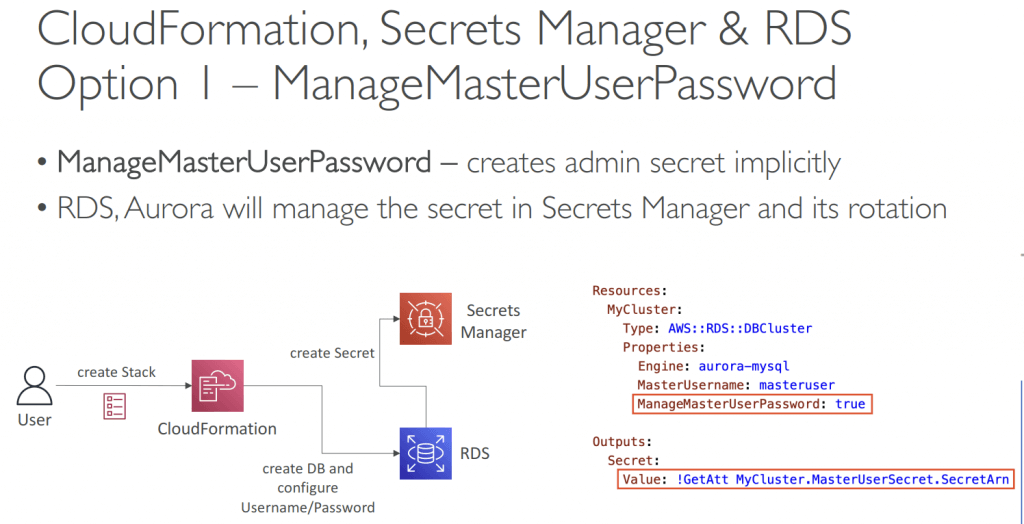
- Environment variables (Hardcoded ,SSM Parameter Store, Secrets Manager, or files stored in S3)
- Networking
- IAM Role (One IAM Role per Task Definition)
- Logging configuration (CloudWatch)
- Data Volume to share data among multiple containers (Applications and Metrics/Logs, aka sidecar)
- EC2 Launch Type – using EC2 instance storage
- Fargate Launch Type – using ephemeral storage (20-200 GB), data deleted when containers demolished
- ECS Task Placement strategy & Task Placement constraints – Only for EC2 Launch Type
- find instances meet CPU/Memory/Port requirements
- find those satisfy task placement constraints
- distinctInstance – place each task on different container instance
- memberOf – using Cluster Query Language, placing on certain instances (like t2.*)
- find those satisfy task placement strategies
- Binpack – cost-saving by using least available amount of CPU or Memory as minimum instances
- Random
- Spread (can be AZ or instance ID)
- ECS does not use EC2 Auto Scaling, instead, uses the AWS Application Auto Scaling based on
- Average CPU Utilization
- Average Memory Utilization – Scale on RAM
- ALB Request Count Per Target
- AWS Application Auto Scaling policy can be
- Target Tracking – scale based on the target specific CloudWatch metric
- Step Scaling – based on a specified CloudWatch Alarm
- Scheduled Scaling
- Under EC2 Launch Type, the way to auto-scaling EC2 instances by
- Auto Scaling Group Scaling – use EC2 ASG to check instance loadings (CPU, Memory, etc.)
- ECS Cluster Capacity Provider, paired with ASG
- AWS Coplit is the CLI tool, running apps on AppRunner, ECS and Fargate; with CodePipeline for deployment
Amazon Elastic Kubernetes Service (EKS)
- EC2 Launch for deploy worker node; Fargate for serverless
- Kubernetes is cloud-agnostic
- Node Types
- Managed Node Groups
- AWS handles EC2 instances with ASG managed by EKS
- On-Demand or Spot instances
- Self-Managed Nodes
- Self create and manage EC2 instance with self-define ASG
- On-Demand or Spot instances
- AWS Fargate
- Managed Node Groups
- Can specify StorageClass manifest on EKS cluster, leverage a Container Storage Interface (CSI) compliant driver
- Amazon EBS (EC2)
- Amazon EFS (EC2, Fargate)
- Amazon FSx for Lustre (EC2)
- Amazon FSx for NetApp ONTAP (EC2)
== MONITORING ==
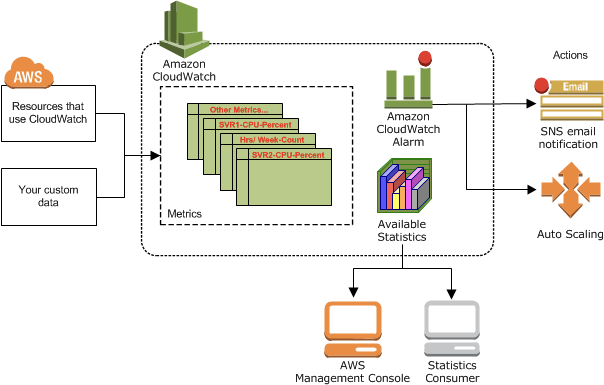
AWS CloudWatch
- Metrics: Collect and track key metrics for every AWS services
- namespace (specify a namespace for each data point, as new metric)
- dimension is an attributes (instance id, environment, …)
- timestamps
- for EC2 memory
- CloudWatch does not monitor the memory, swap, and disk space utilization of your instances. If you need to track these metrics, you can install a CloudWatch agent in your EC2 instances.
- (EC2) Memory usage is a custom metric, using API PutMetricData
- for Lambda function
- The ConcurrentExecutions metric in Amazon CloudWatch explicitly measures the number of instances of a Lambda function that are running at the same time.
- StorageResolution can be 1min (Standard) or 1/5/10/30 sec(High Resolution)
- Data point range of custom metric would be 2 weeks for past history and 2 hours in future
- detailed monitoring, just shorten the period to 1-minute; no extra fields
- Logs: Collect, monitor, analyze and store log files
- Group – application (to encrpyt with KMS keys, need to use CloudWatch Logs API)
- stream – instances / log files / containers
- export
- Amazon S3, may take up to 12 hour, with API CreateExportTask
- Using Logs Subscripton to export real-time events to Kinesis Data Streams, Kinesis Data Firehose, AWS Lambda, with Subscription Filter
- Cross-Account Subscription (Subscription Filter -> Subscription Destination)
- Live Tail – for realtime tail watch
- By default, no logs from EC2 machine to CloudWatch
- CloudWatch Logs Agent – only push logs
- CloudWatch Unified Agent – push logs + collect metrics (extra RAM, Process, Swap) + centralized by SSM Parameter Store
- Metric Filters to trigger alarms; not traceback of history
- With “aws logs associate-kms-key“, enable (AWS KMS) encryption for an existing log group, eliminating the need to recreate the log group or manually encrypt logs before submission
- Log Insight
- facilitate in-depth analysis of log data
- enables users to run queries on log data collected from various AWS services and applications in real-time
- Alarms: Re-act in real-time to metrics / events
- based on a single metric; Composite Alarms are monitoring on multiple other alarms
- Targets
- EC2
- EC2 ASG
- Amazon SNS
- Settings
- Period is the length of time to evaluate the metric or expression to create each individual data point for an alarm. It is expressed in seconds. If you choose one minute as the period, there is one datapoint every minute.
- Evaluation Period is the number of the most recent periods, or data points, to evaluate when determining alarm state.
- Datapoints to Alarm is the number of data points within the evaluation period that must be breaching to cause the alarm to go to the ALARM state. The breaching data points do not have to be consecutive, they just must all be within the last number of data points equal to Evaluation Period.
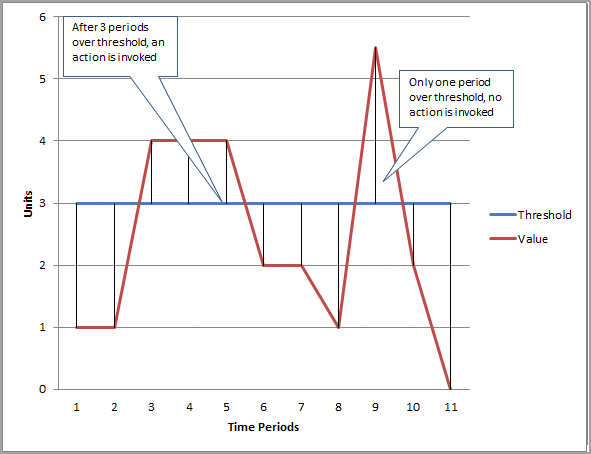
- Synthetics Canary: monitor your APIs, URLs, Websites, …
- Events, now called Amazon EventBridge
- Schedule – cron job
- Event Pattern – rules to react/trigger services
- Event Bus,a router that receives events and delivers them to zero or more destinations, or targets.
- (AWS) default, Partner, Custom
- Schema – the structure template for event (json)
- CloudWatch Evidently
- validate/serve new features to specified % of users only
- Launches (= feature flags) and Experiments (= A/B testing), and Overrides (specific variants assigned to specific user-id)
- evaluation events stored in CloudWatch Logs or S3
AWS X-Ray
- Troubleshooting (not monitoring) application performance and errors as “centralized service map visualization”
- Request tracking across distributed systems
- Focus on Latency, Errors and Fault analysis
- Compatible
- AWS Lambda
- Elastic Beanstalk
- ECS
- ELB
- API Gateway
- EC2 Instances or any application server (even on premise)
- But X-Ray cannot track the memory and swap usage of the instance; only CloudWatch Agents can do.
- Enable by
- AWS X-Ray SDK (on applications)
- Install X-Ray daemon (low lv UDP packet interceptor on OS) (on EC2 or ECS)
- a software application that listens for traffic on UDP port 2000, gathers raw segment data, and relays it to the AWS X-Ray API.
- for EC2, X-Ray daemon can be installed via user-data script
- for ECS, create a Docker image that runs the X-Ray daemon, upload it to a Docker image repository, and then deploy it to your Amazon ECS cluster
- Lambda runs the daemon automatically any time a function is invoked for a sampled request
- Enable X-Ray AWS Integration (IAM Role with proper permission) (on AWS services)
- for ElasticBeanstalk: to enable the X-Ray daemon by including the xray-daemon.config configuration file in the .ebextensions directory of your source code.
- Instrumentation means the measure of product’s performance, diagnose errors, and to write trace information
- AWS X-Ray receives data from services as segments. X-Ray then groups segments that have a common request into traces. X-Ray processes the traces to generate a service graph that provides a visual representation of your application.
- segments/subsegments -> traces -> service graph
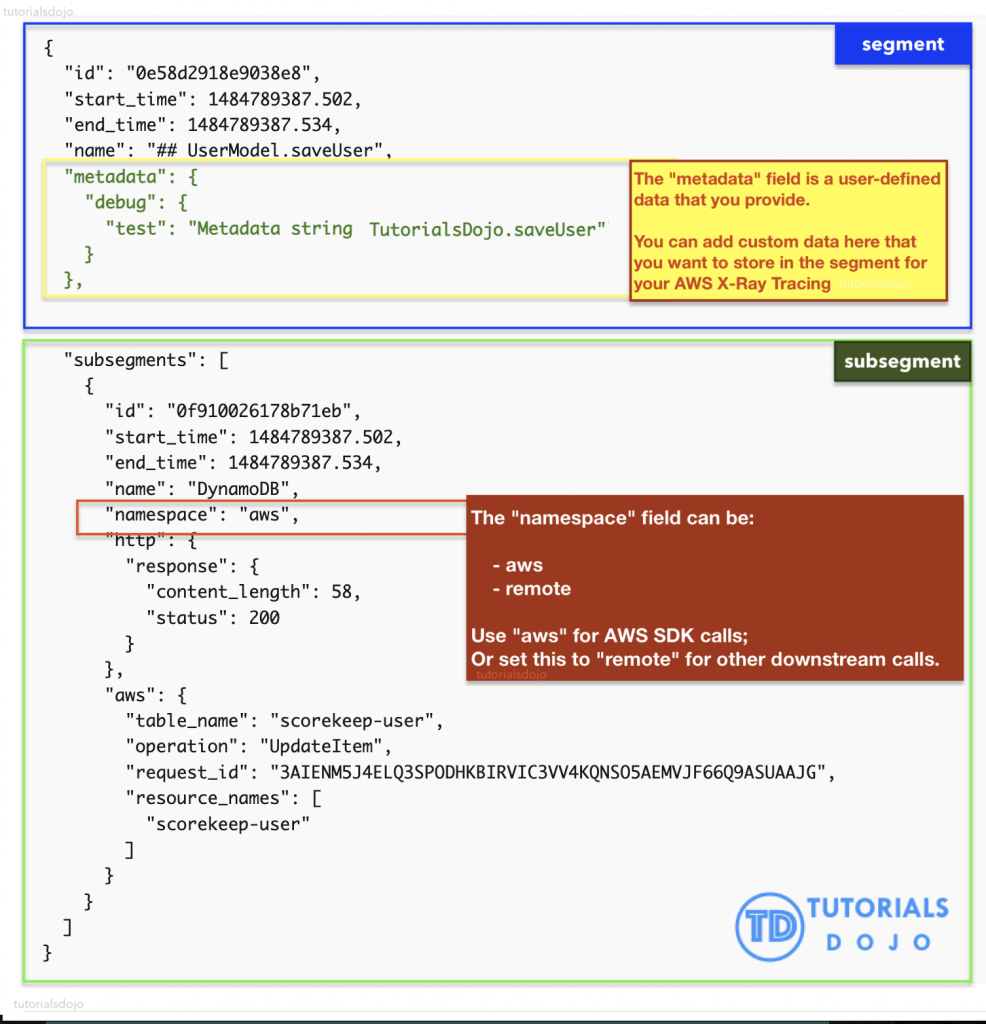
- Segments: each application / service will send them
- Subsegments: if you need more details in your segment, especially for DynanmoDB.
- Trace: segments collected together to form an end-to-end trace
- A trace segment is just a JSON representation of a request that your application serves.
- Sampling: decrease the amount of requests sent to X-Ray, reduce cost
- (default) 1st request each second (aka reservoir: 1), and then 5% of additional requests (aka rate: 0.05)
- Annotations: Key Value pairs used to index traces (for search) and use with filters
- Metadata: “EXTRA” Key Value pairs, not indexed, not used for searching
- AWS X-Ray receives data from services as segments. X-Ray then groups segments that have a common request into traces. X-Ray processes the traces to generate a service graph that provides a visual representation of your application.
- A subset of segment fields are indexed by X-Ray for use with filter expressions. You can search for segments associated with specific information in the X-Ray console or by using the GetTraceSummaries API.
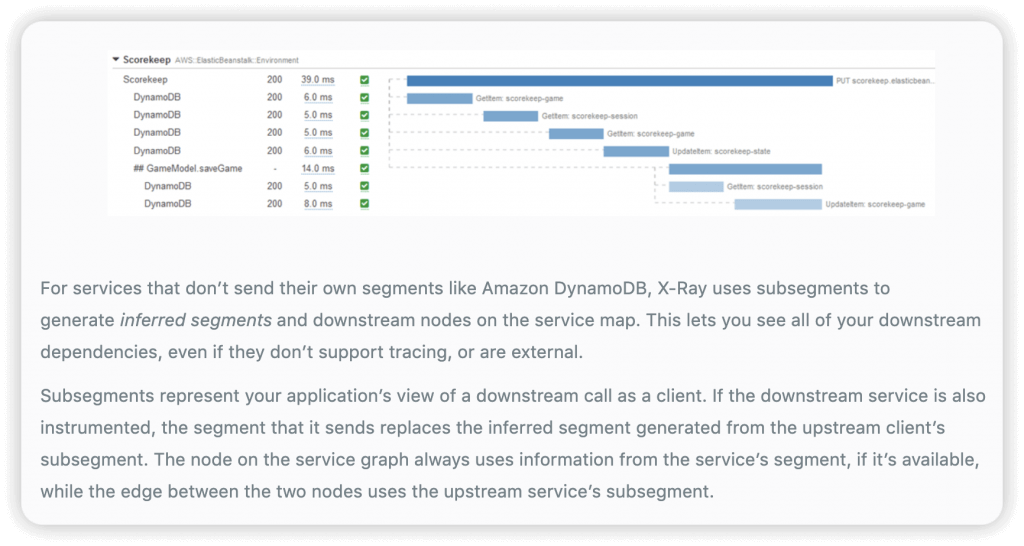
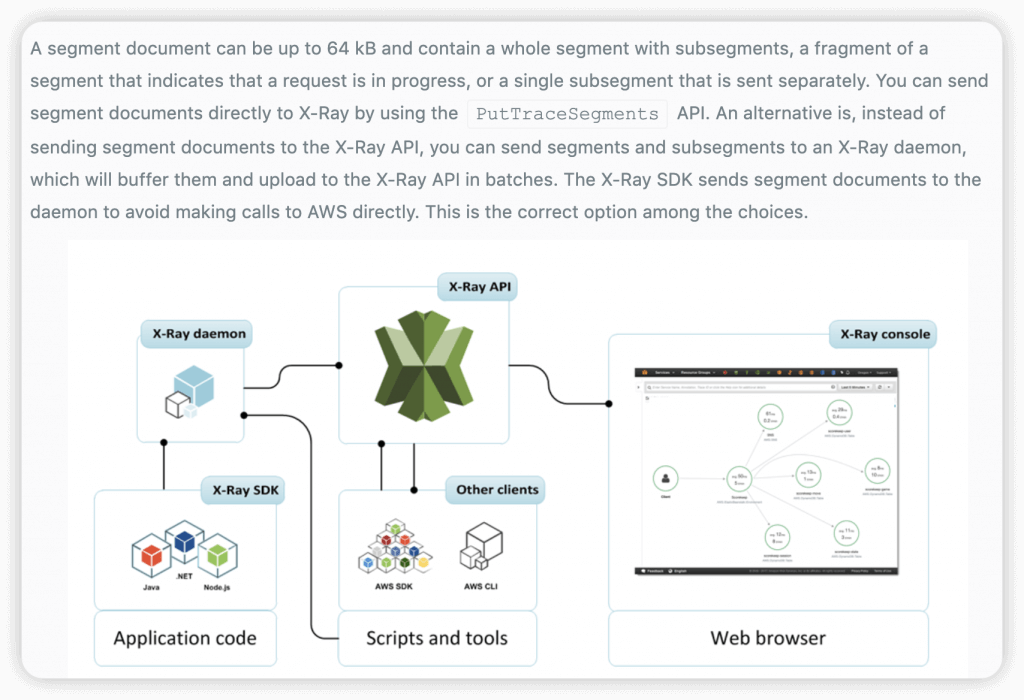
- X-Ray APIs Policy
- AWSXrayWriteOnlyAccess
- PutTraceSegments
- PutTelemetryRecords
- GetSamplingRules
- GetSamplingTargets
- GetSamplingStatisticSummaries
- AWSXrayReadOnlyAccess – grant console access
- GetServiceGraph
- BatchGetTraces
- GetTraceSummaries
- GetTraceGraph
- AWSXRayDaemonWriteAccess
- AWSXrayFullAccess – Read + Write + configure encryption key settings and sampling rules
- AWSXrayWriteOnlyAccess
- APIs
- GetTraceSummaries – trace summaries, as a list of trace IDs of the application (also with annotations)
- BatchGetTraces – full traces, retrieve the list of traces (ie activity events)
- GetGroup – retrieves the group resource details.
- GetServiceGraph – shows which services process the incoming requests, including the downstream services that they call as a result.
- If a load balancer or other intermediary forwards a request to your application, X-Ray takes the client IP from the X-Forwarded-For header in the request instead of from the source IP in the IP packet.
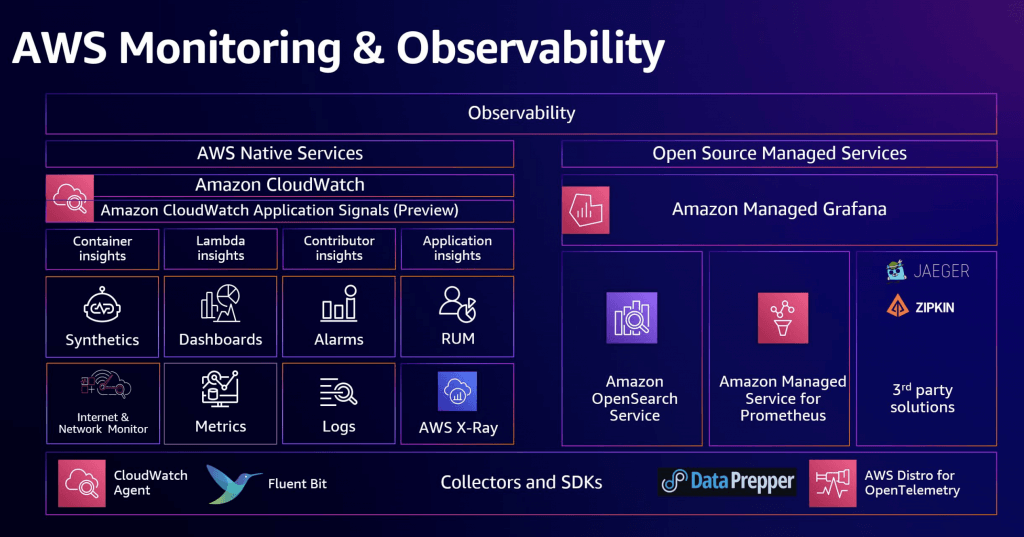
Amazon Managed Grafana
- a fully managed and secure data visualization service that you can use to instantly query, correlate, and visualize operational metrics, logs, and traces
| Use case | What is it optimized for? | Monitoring and observability services |
|---|---|---|
| Monitoring and alerting | These services are optimized to provide real-time visibility, proactive issue detection, resource optimization, and efficient incident response, contributing to overall application and infrastructure health. | – Amazon CloudWatch – Amazon CloudWatch Logs – Amazon EventBridge |
| Application performance monitoring | These services provide comprehensive insights into application behavior, offer tools for identifying and resolving performance bottlenecks, aid in efficient troubleshooting, and contribute to delivering modern user experiences across distributed and web applications. | – Amazon CloudWatch Application Signals – Amazon Managed Service for Prometheus – AWS X-Ray – Amazon CloudWatch Synthetics |
| Infrastructure observability | These services provide a holistic view of your cloud resources, helping you make more informed decisions about resource utilization, performance optimization, and cost-efficiency. | – Amazon CloudWatch Metrics – Amazon CloudWatch Container Insights |
| Logging and analysis | These services help you efficiently manage and analyze log data, troubleshoot, detect anomalies, support security, meeting compliance requirements, and get actionable insights into your applications and infrastructure. | – Amazon Cloudwatch Logs Insights – Amazon CloudWatch Logs Anomaly Detection – Amazon Managed Grafana – Amazon OpenSearch Service – Amazon Kinesis Data Streams |
| Security and compliance monitoring | Optimized to provide a robust security framework, enabling proactive threat detection, continuous monitoring, compliance tracking, and audit capabilities to help safeguard your AWS resources and maintain a secure and compliant environment. | – Amazon GuardDuty – AWS Config – AWS CloudTrail |
| Network monitoring | These services provide visibility into network traffic, enhance security by detecting and preventing threats, enable efficient network traffic management, and support incident response activities. | – Amazon CloudWatch – Network Monitor – Amazon CloudWatch Internet Monitor – Amazon VPC Flow Logs – AWS Network Firewall |
| Distributed tracing | These services provide a comprehensive view of the interactions and dependencies within your distributed applications. They enable you to diagnose performance bottlenecks, optimize application performance, and support the smooth functioning of complex systems by offering insights into how different parts of your application communicate and interact. | – AWS Distro for OpenTelemetry – AWS X-Ray – Amazon CloudWatch Application Signals (Preview) |
| Hybrid and multicloud observability | Maintain reliable operations, provide modern digital experiences for your customers, and get help to meet service level objectives and performance commitments. | – Amazon CloudWatch (hybrid and multicloud support) |
== CICD ==
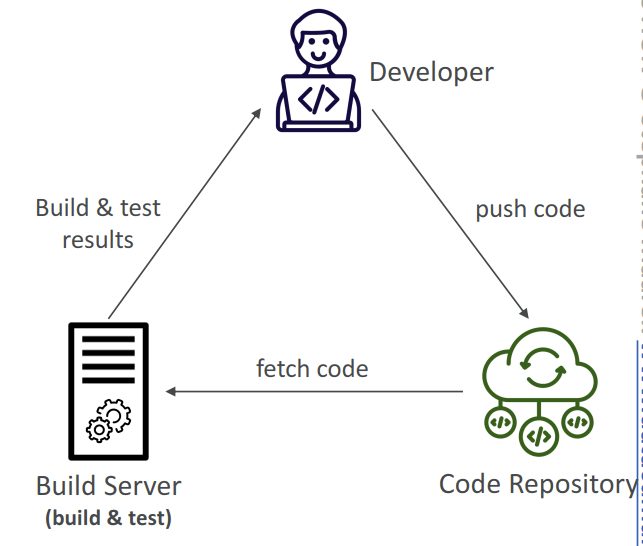
Continuous Integration (CI)
- Developers push the code to a code repository often (e.g., GitHub, CodeCommit, Bitbucket…)
- A testing / build server checks the code as soon as it’s pushed (CodeBuild, Jenkins CI…)
- The developer gets feedback about the tests and checks that have passed / failed
- Find bugs early, then fix bugs
- Deliver faster as the code is tested
- Deploy often
- Happier developers, as they’re unblocked
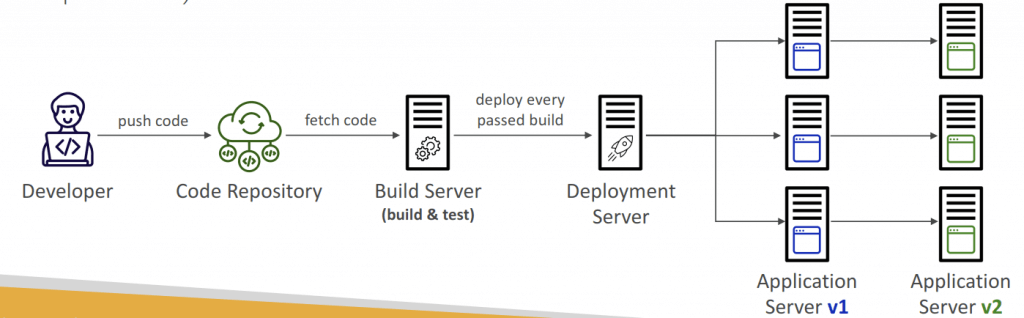
Continuous Delivery (CD)
- Ensures that the software can be released reliably whenever needed
- Ensures deployments happen often and are quick
- Shift away from “one release every 3 months” to ”5 releases a day”
- That usually means automated deployment (e.g., CodeDeploy, Jenkins CD, Spinnaker…)
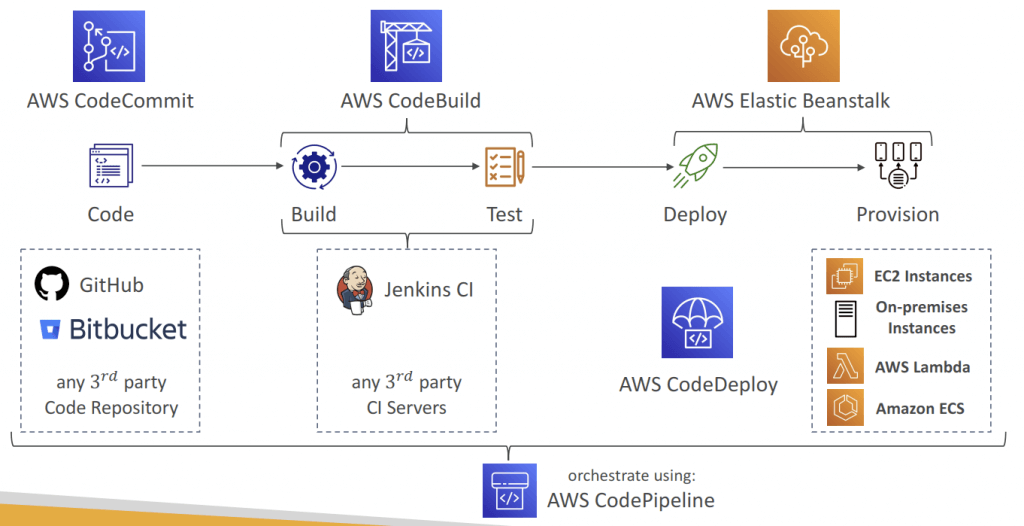
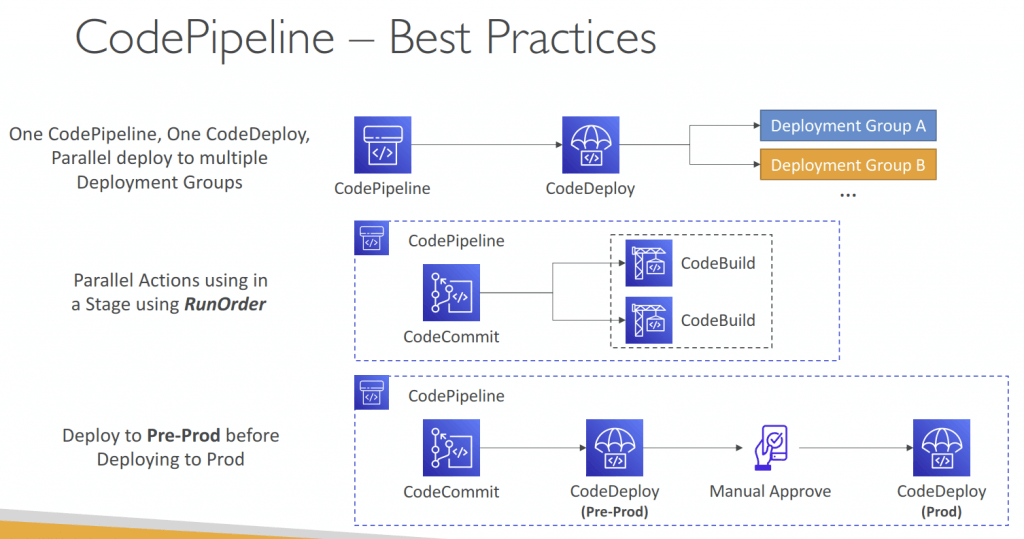
AWS CodePipeline
- [Machine Learning] Automate the entire process of training, testing, and deploying the models
- automating pipeline from code to deployments, as visual workflow
- Source – CodeCommit, ECR, S3, Bitbucket, GitHub
- Build – CodeBuild, Jenkins, CloudBees, TeamCity
- Test – CodeBuild, AWS Device Farm, 3rd party tools…
- Deploy – CodeDeploy, Elastic Beanstalk, CloudFormation, ECS, S3…
- Invoke – Lambda (invokes a Lambda function within a Pipeline), Step Functions (star ts a State Machine within a Pipeline)
- Consists of stages:
- Each stage can have sequential actions and/or parallel actions
- Manual approval can be defined at any stage
- each stage can create artifacts, stored in S3 bucket
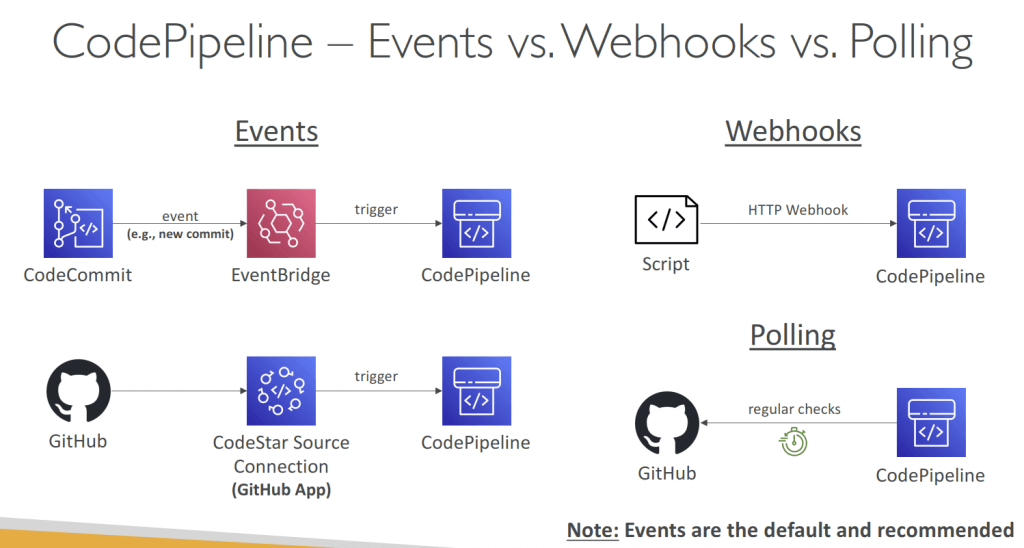
- Use AWS EventBridge for troubleshooting; with CloudTrail for audit AWS API calls
- If pipeline can’t perform an action, make sure the “IAM ServiceRole” attached does have enough IAM permissions (IAM Policy)
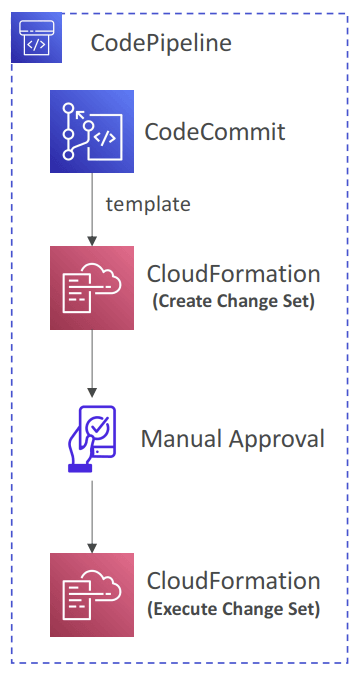
- CloudFormation as a Target
- CloudFormation Deploy Action can be used to deploy AWS resources
- Example: deploy Lambda functions using CDK or SAM (alternative to CodeDeploy)
- Works with CloudFormation StackSets to deploy across multiple AWS accounts and AWS Regions
- Configure different settings:
- Stack name, Change Set name, template, parameters, IAM Role, Action Mode…
- CREATE_UPDATE – create or update an existing stack
- DELETE_ONLY – delete a stack if it exists
- Action Modes
- Create or Replace a Change Set, Execute a Change Set
- Create or Update a Stack, Delete a Stack, Replace a Failed Stack
- Template Parameter Overrides
- Specify a JSON object to override parameter values
- Retrives the parameter value from CodePipeline Input Artifact
- All parameter names must be present in the template
- Static – use template configuration file (recommended)
- Dynamic – use parameter overrides
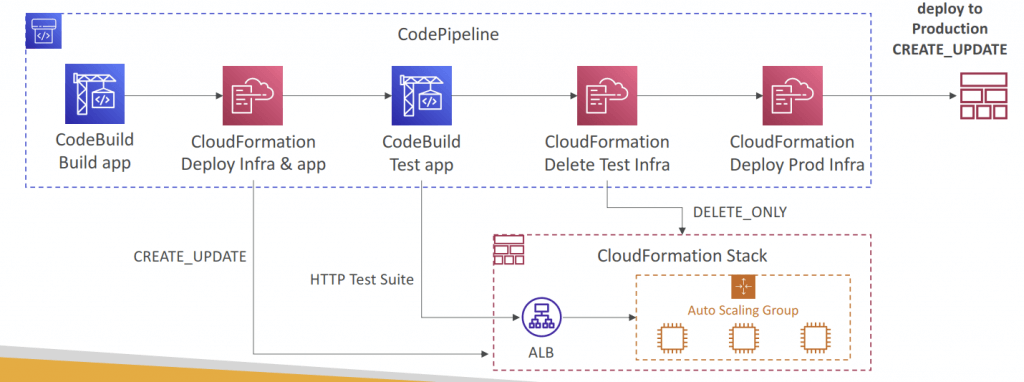
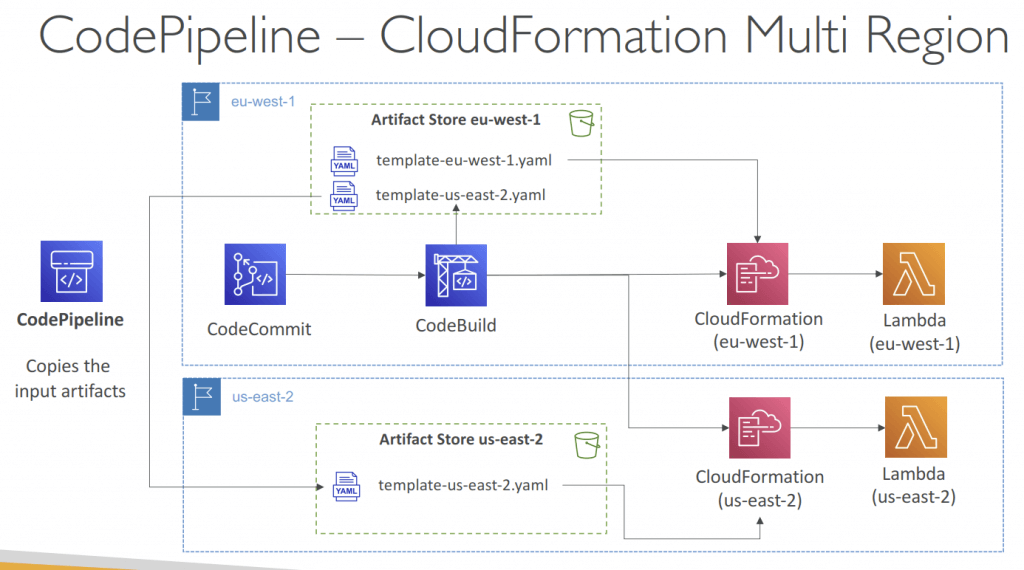
- Multi Region
- Actions in your pipeline can be in different regions
- Example: deploy a Lambda function through CloudFormation into multiple regions
- S3 Artifact Stores must be defined in each region where you have actions
- CodePipeline must have read/write access into every artifact buckets
- If you use the console default artifact buckets are configured, else you must create them
- CodePipeline handles the copying of input artifacts from one AWS Region
to the other Regions when performing cross-region actions- In your cross-region actions, only reference the name of the input artifacts
- Actions in your pipeline can be in different regions
| Owner | Type of action | Provider | Valid number of input artifacts | Valid number of output artifacts |
|---|---|---|---|---|
AWS | Source | S3 | 0 | 1 |
AWS | Source | CodeCommit | 0 | 1 |
AWS | Source | ECR | 0 | 1 |
ThirdParty | Source | CodeStarSourceConnection | 0 | 1 |
AWS | Build | CodeBuild | 1 to 5 | 0 to 5 |
AWS | Test | CodeBuild | 1 to 5 | 0 to 5 |
AWS | Test | DeviceFarm | 1 | 0 |
AWS | Approval | ThirdParty | 0 | 0 |
AWS | Deploy | S3 | 1 | 0 |
AWS | Deploy | CloudFormation | 0 to 10 | 0 to 1 |
AWS | Deploy | CodeDeploy | 1 | 0 |
AWS | Deploy | ElasticBeanstalk | 1 | 0 |
AWS | Deploy | OpsWorks | 1 | 0 |
AWS | Deploy | ECS | 1 | 0 |
AWS | Deploy | ServiceCatalog | 1 | 0 |
AWS | Invoke | Lambda | 0 to 5 | 0 to 5 |
ThirdParty | Deploy | AlexaSkillsKit | 1 to 2 | 0 |
Custom | Build | Jenkins | 0 to 5 | 0 to 5 |
Custom | Test | Jenkins | 0 to 5 | 0 to 5 |
Custom | Any supported category | As specified in the custom action | 0 to 5 | 0 to 5 |
AWS CodeBuild
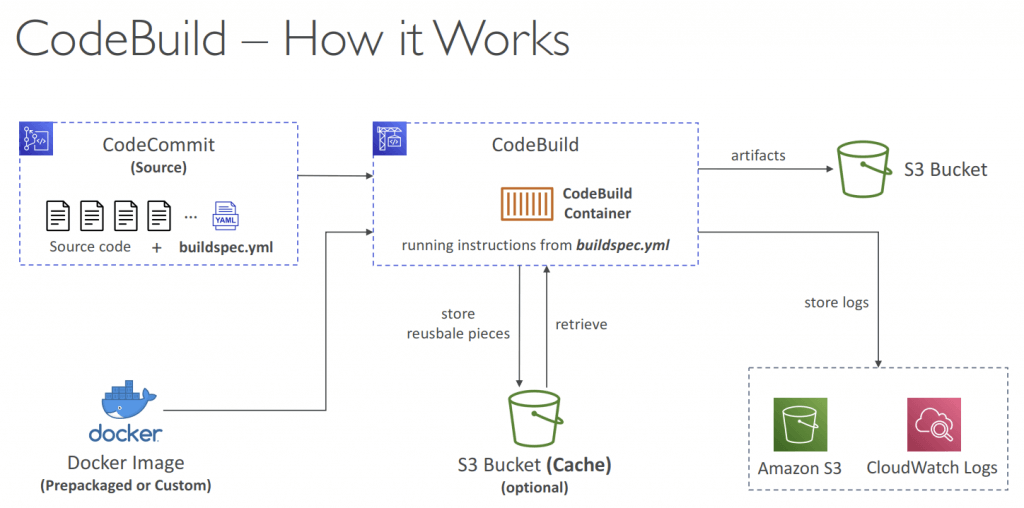
- A fully managed continuous integration (CI) service
- Compile the code, execute unit tests, and build the necessary artifacts
- Continuous scaling (no servers to manage or provision – no build queue)
- Alternative to other build tools (e.g., Jenkins)
- Charged per minute for compute resources (time it takes to complete the builds)
- Leverages Docker under the hood for reproducible builds
- Use prepackaged Docker images or create your own custom Docker image
- Security:
- Integration with KMS for encryption of build artifacts
- IAM for CodeBuild permissions, and VPC for network security
- AWS CloudTrail for API calls logging
- CodeBuild Service Role allows CodeBuild to access AWS resources on your behalf (assign the required permissions)
- Use cases:
- Download code from CodeCommit repositor y
- Fetch parameters from SSM Parameter Store
- Upload build ar tifacts to S3 bucket
- Fetch secrets from Secrets Manager
- Store logs in CloudWatch Logs
- Use cases:
- In-transit and at-rest data encryption (cache, logs…)
- Source – CodeCommit, S3, Bitbucket, GitHub
- Build instructions: on buildspec.yml, stored at the root of codes; or insert manually in Console
- env
- variables – plaintext variables
- parameter-store – variables stored in SSM Parameter Store
- secrets-manager – variables stored in AWS Secrets Manager
- phases
- install – install dependencies you may need for your build
- pre_build – final commands to execute before build
- Build – actual build commands
- post_build – finishing touches (e.g., zip output)
- artifacts – what to upload to S3 (encrypted with KMS)
- cache – files to cache (usually dependencies) to S3 for future build speedup
- env
- Output logs can be stored in Amazon S3 & CloudWatch Logs
- Use CloudWatch Metrics to monitor build statistics
- Use EventBridge to detect failed builds and trigger notifications
- Use CloudWatch Alarms to notify if you need “thresholds” for failures
- Build Projects can be defined within CodePipeline or CodeBuild
- You can run CodeBuild locally on your desktop (after installing Docker)
- Inside VPC
- By default, your CodeBuild containers are launched outside your VPC
- It cannot access resources in a VPC
- You can specify a VPC configuration:
- VPC ID
- Subnet IDs
- Security Group IDs
- Then your build can access resources in your VPC (e.g., RDS, ElastiCache, EC2, ALB…)
- Use cases: integration tests, data query, internal load balancers…
- By default, your CodeBuild containers are launched outside your VPC
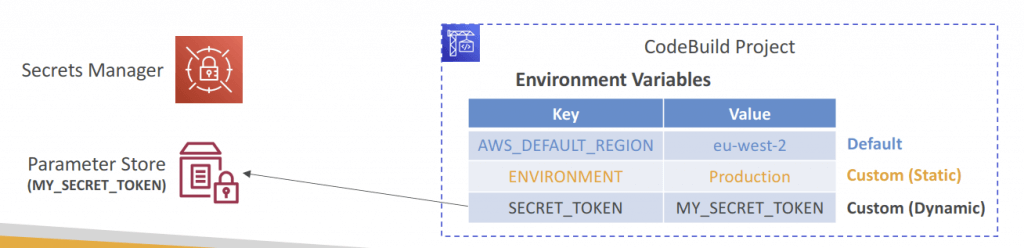
- Environment Variables
- Default Environment Variables
- Defined and provided by AWS
- AWS_DEFAULT_REGION, CODEBUILD_BUILD_ARN, CODEBUILD_BUILD_ID, CODEBUILD_BUILD_IMAGE…
- Custom Environment Variables
- Static – defined at build time (override using start-build API call)
- Dynamic – using SSM Parameter Store and Secrets Manager
- Default Environment Variables
- Build Badges
- Suppor ted for CodeCommit, GitHub, and BitBucket
- Note: Badges are available at the branch level
- Validate Pull Requests
- Validate proposed code changes in PRs before they get merged
- Ensure high level of code quality and avoid code conflicts
- Test Reports
- Contains details about tests that are run during builds
- Unit tests, configuration tests, functional tests
- Create your test cases with any test framework that can create repor t files in the following format:
- JUnit XML, NUnit XML, NUnit3 XML
- Cucumber JSON, TestNG XML, Visual Studio TRX
- Create a test report and add a Report Group name in buildspec.yml file with information about your tests
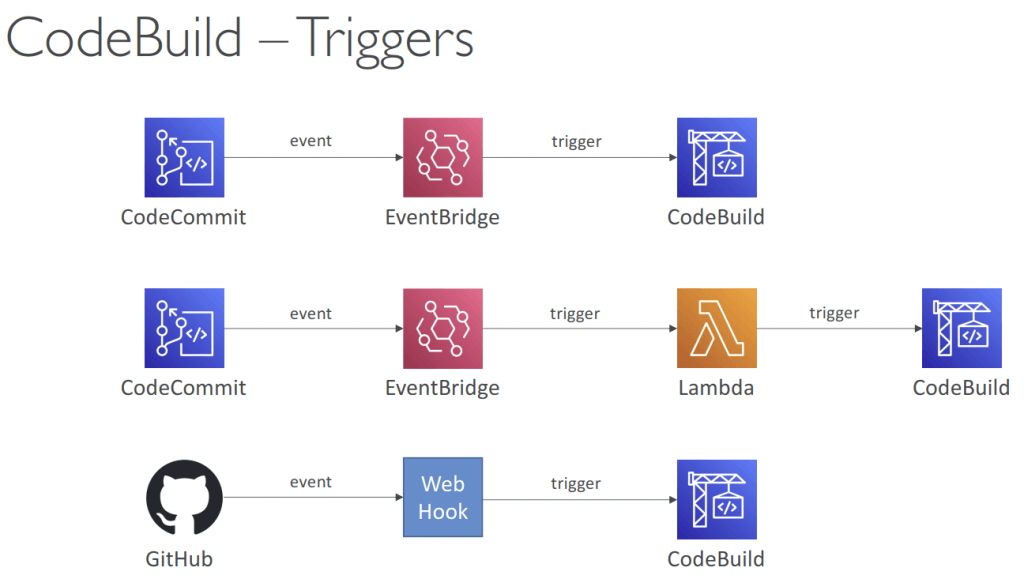
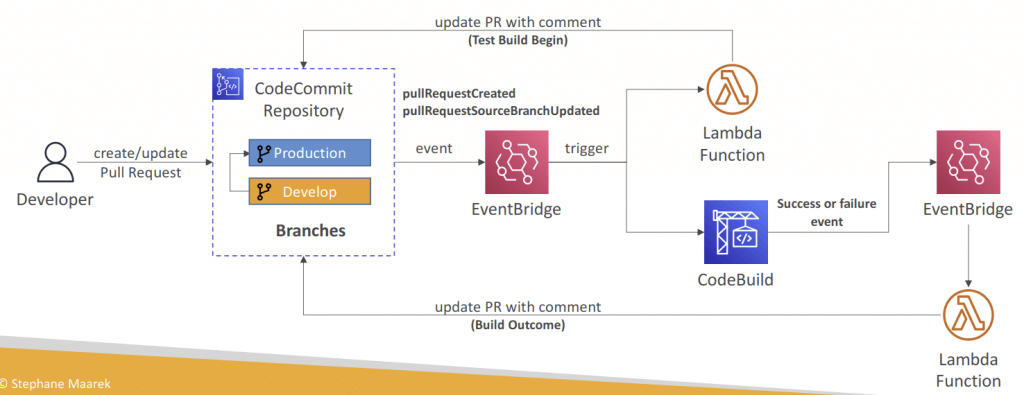

AWS CodeDeploy
- [Machine Learning] Automatically release new versions of the models to various environments while avoiding downtime and handling the complexity of updating them
- Deploy new applications versions
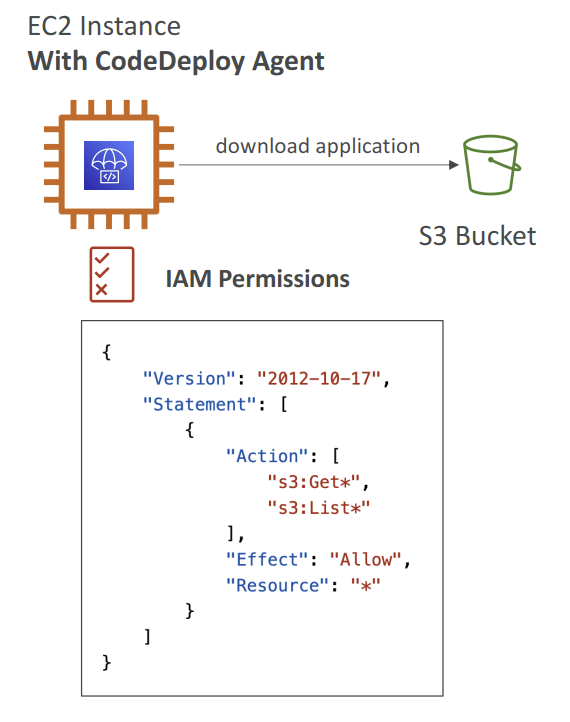
- EC2 Instances, On-premises servers
- need CodeDeployAgent on the target instance, with S3 access permit
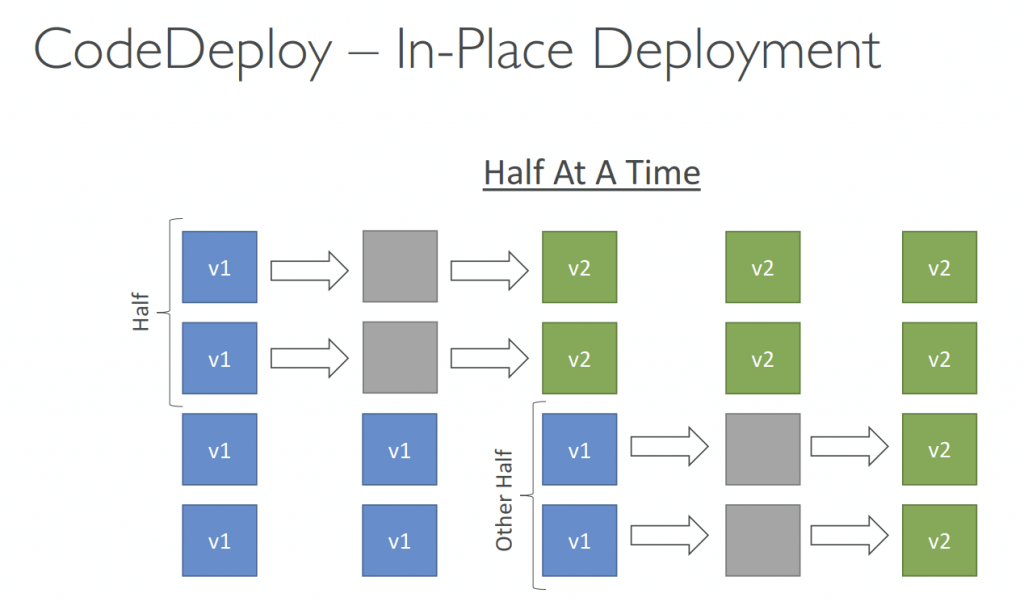
- In-place Deployment (compatible with existing ASG)
- AllAtOnce: most downtime
- HalfAtATime: reduced capacity by 50%
- OneAtATime: slowest, lowest availability impact (health-check on every new instance deployed)
- Custom: define your %
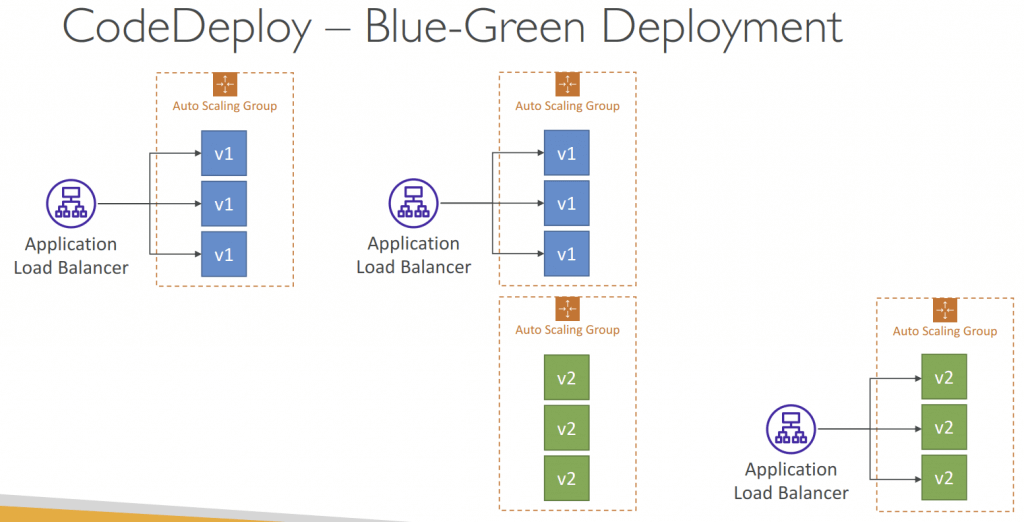
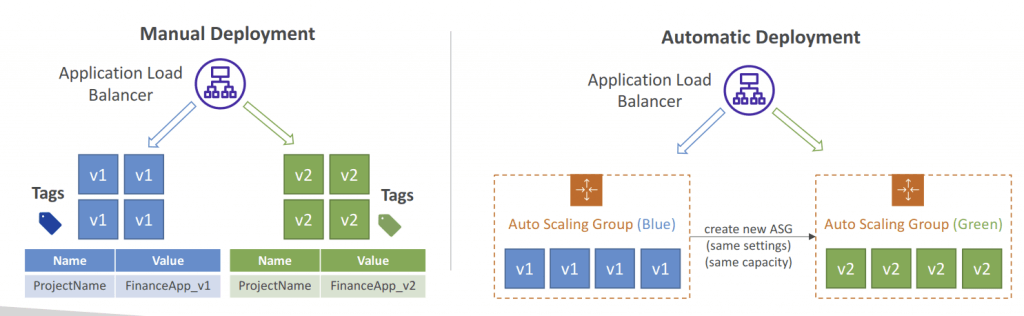
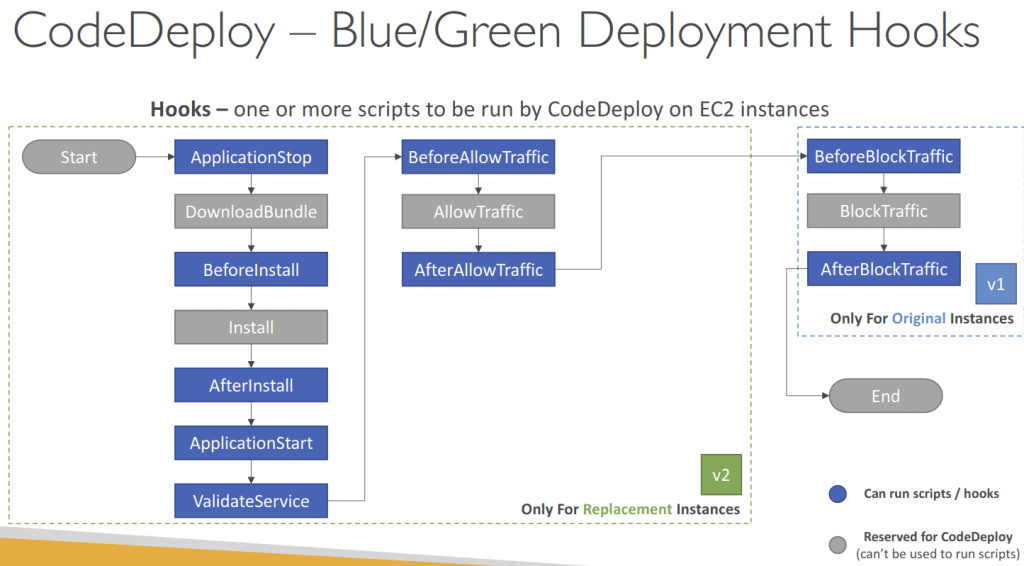
- or Blue/Green Deployment (new ASG created) (also as one deployment attempt)
- must be using an ELB
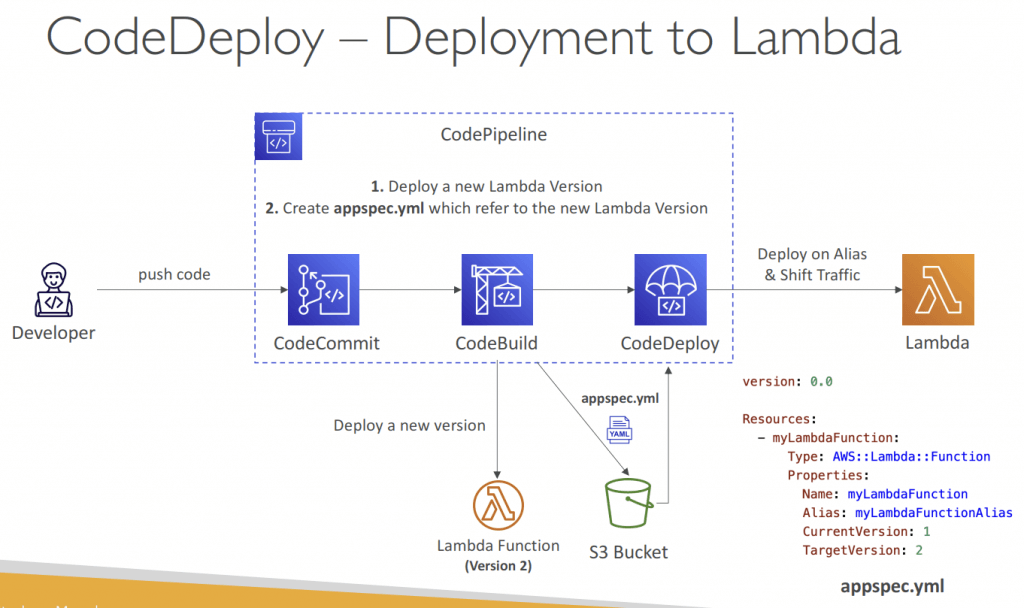
- Lambda functions (integrated into SAM)
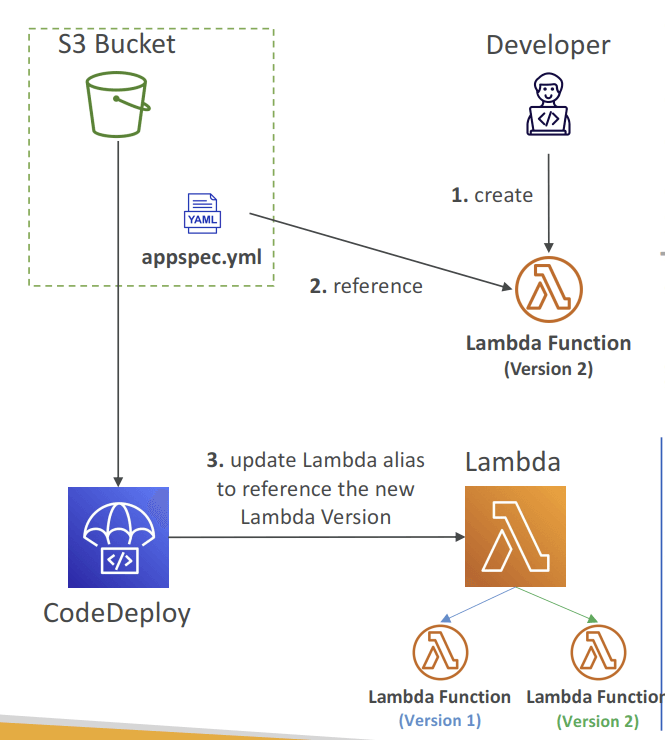
- create a new Lambda function Version; ie, only Blue-Green Deployment supported
- Specify the Version info in the appspec.yml file
- Name (required) – the name of the Lambda function to deploy
- Alias (required) – the name of the alias to the Lambda function
- CurrentVersion (required) – the version of the Lambda function traffic currently points to
- TargetVersion (required) – the version of the Lambda function traffic is shifted to
- Specify the Version info in the appspec.yml file
- traffic would be redirected by
- Linear: grow traffic every N minutes until 100%
- LambdaLinear10PercentEvery3Minutes
- LambdaLinear10PercentEvery10Minutes
- Canary (two deployment attempts only): try X percent then 100%
- LambdaCanary10Percent5Minutes
- LambdaCanary10Percent30Minutes
- AllAtOnce (one deployment attempt): immediate
- Linear: grow traffic every N minutes until 100%
- For Lambda Deployment, the hook would be “a Lambda function”
- BeforeAllowTraffic and AfterAllowTraffic hooks can be used to check the health of the Lambda function
- create a new Lambda function Version; ie, only Blue-Green Deployment supported
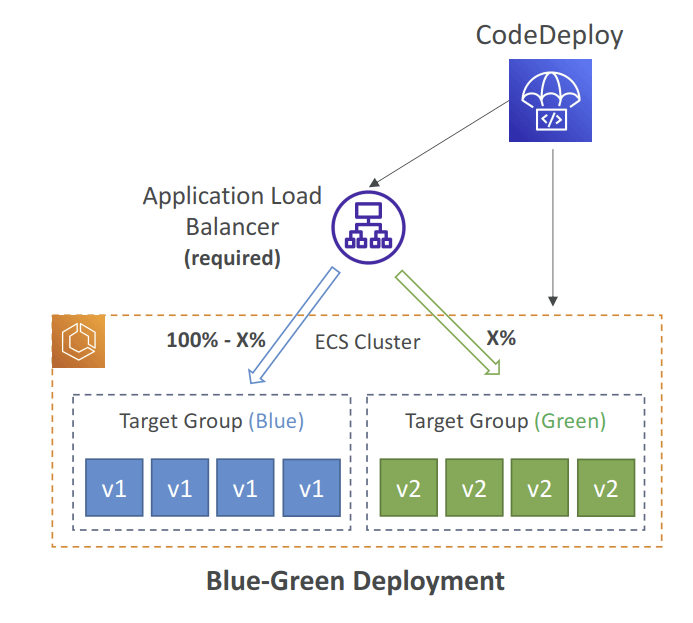
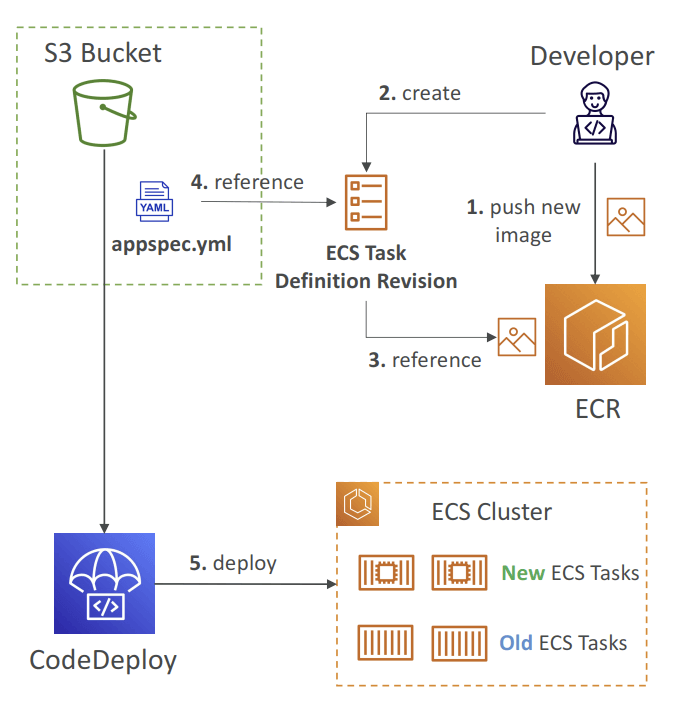
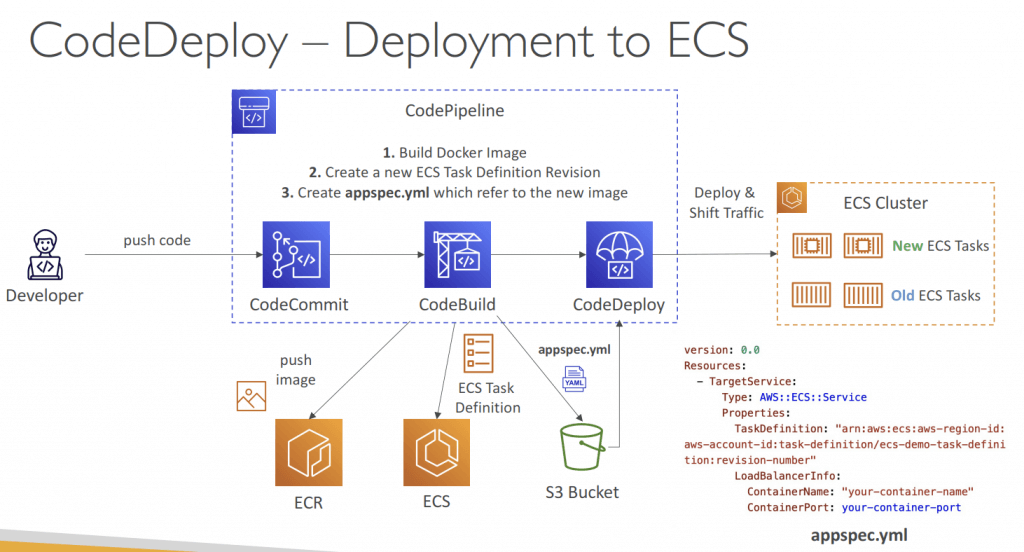
- ECS Services
- with only Blue/Green deployment
- needs Application Load Balancer (ALB) to control traffic
- Linear: grow traffic every N minutes until 100%
- Canary (two deployment attempts only): try X percent then 100%
- LambdaCanary10Percent5Minutes
- LambdaCanary10Percent30Minutes
- AllAtOnce (one deployment attempt): immediate
- not Elastic Beanstalk
- The ECS Task Definition and new Container Images must be already created
- A reference to the new ECS Task Revision (TaskDefinition) and load balancer
- information (LoadBalancerInfo) are specified in the appspec.yml file
- Can define a second ELB Test Listener to test the Replacement (Green) version before traffic is rebalanced
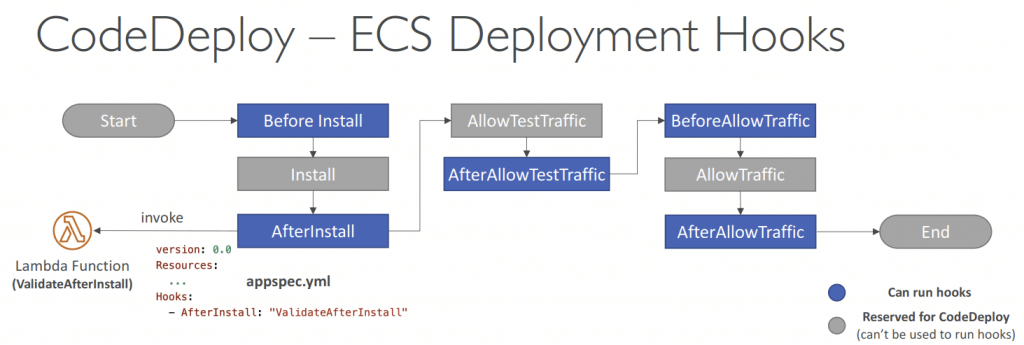
- For ECS Deployment, the hook would be “a Lambda function”
- For example, AfterAllowTestTraffic – run AWS Lambda function after the test ELB Listener serves traffic to the Replacement ECS Task Set
- EC2 Instances, On-premises servers
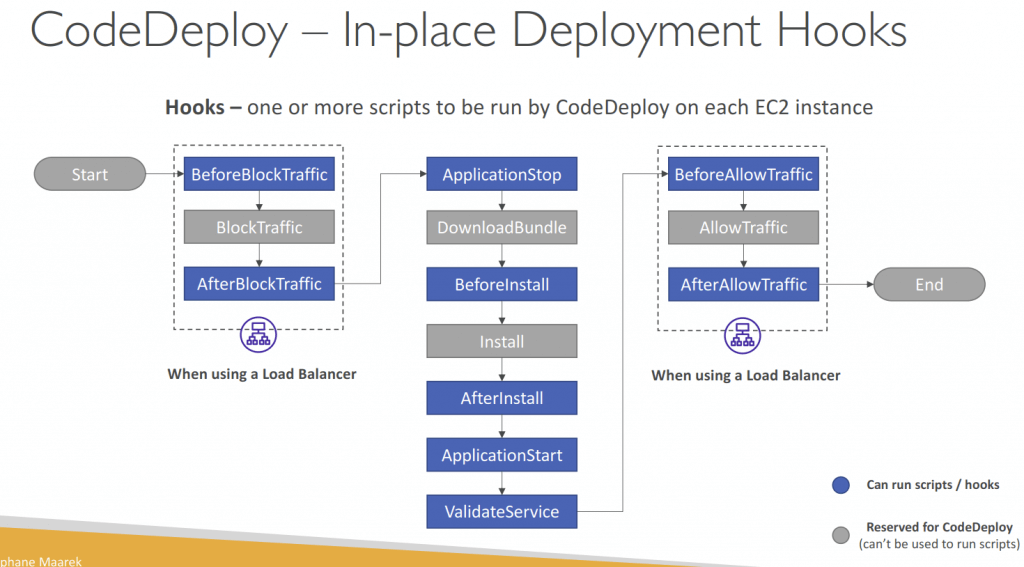
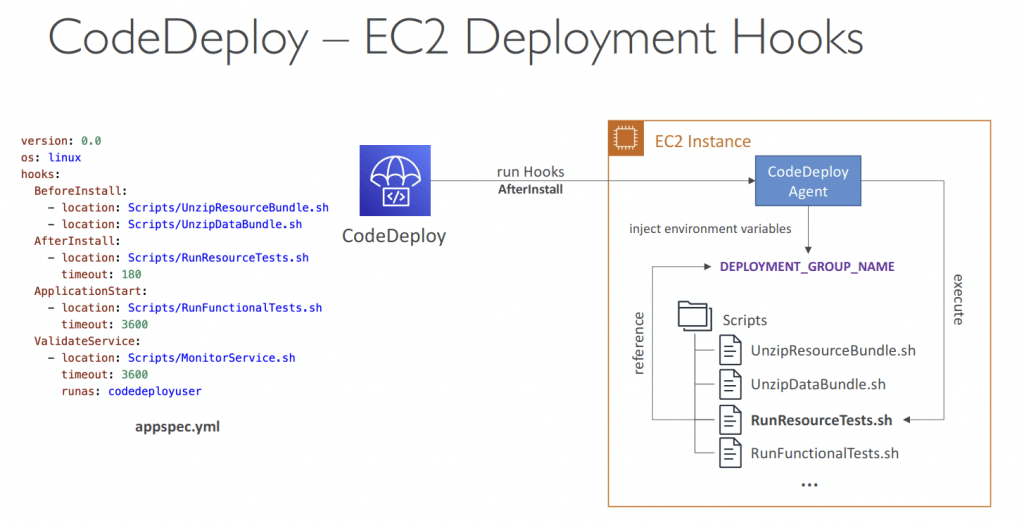
- Use appspec.yml to define actions (manage each application deployment as a series of lifecycle event hooks in CodeDeploy)
- For “In-place Deployments”
- Use EC2 Tags or ASG to identify instances you want to deploy to
- With a Load Balancer: traffic is stopped before instance is updated, and started again after the instance is updated
- For “Blue/Green Deployments”
- Manually mode: provision EC2 Instances for Blue and Green and identify by Tags
- Automatic mode: new ASG is provisioned by CodeDeploy (settings are copied)
- Using a Load Balancer is necessary for Blue/Green
- BlueInstanceTerminationOption – specify whether to terminate the original (Blue) EC2 instances after a successfully Blue-Green deployment
- Action Terminate – Specify Wait Time, default 1 hour, max 2 days
- Action Keep Alive – Instances are kept running but deregistered from ELB and deployment group
- Deployment Hooks Examples
- BeforeInstall – used for preinstall tasks, such as decrypting files and creating a backup of the current version
- AfterInstall – used for tasks such as configuring your application or changing file permissions
- ApplicationStart – used to start services that stopped during ApplicationStop
- ValidateService – used to verify the deployment was completed successfully
- BeforeAllowTraffic – run tasks on EC2 instances before registered to the load balancer
- Example: perform health checks on the application and fail the deployment if the health
checks are not successful
- Example: perform health checks on the application and fail the deployment if the health
- Deployment Configurations
- Specifies the number of instances that must remain available at any time during the deployment
- Use Pre-defined Deployment Configurations
- CodeDeployDefault.AllAtOnce – deploy to as many instances as possible at once
- CodeDeployDefault.HalfAtATime – deploy to up to half of the instances at a time
- CodeDeployDefault.OneAtATime – deploy to only one instance at a time
- Can create your own custom Deployment Configurations
- Triggers: Publish Deployment or EC2 instance events to SNS topic
- Examples: DeploymentSuccess, DeploymentFailure, InstanceFailure
- Rollback = redeploy a previously the last known good revision as a new deployment (with new deployment ID), not a restored version
- Deployments can be rolled back:
- Automatically – rollback when a deployment fails or rollback when a CloudWatch Alarm thresholds are met
- Manually
- Disable Rollbacks — do not perform rollbacks for this deployment
- Deployments can be rolled back:
- TroubleShooting
- CASE ONE – Deployment Error: “InvalidSignatureException – Signature expired: [time] is now earlier than [time]”
- For CodeDeploy to perform its operations, it requires accurate time references
- If the date and time on your EC2 instance are not set correctly, they might not match the signature date of your deployment request, which CodeDeploy rejects
- CASE TWO – When the Deployment or all Lifecycle Events are skipped (EC2/On-Premises), you get one of the following errors:
- “The overall deployment failed because too many individual instances failed deployment”
- “Too few healthy instances are available for deployment”
- “Some instances in your deployment group are experiencing problems. (Error code: HEALTH_CONSTRAINTS)”
- Reasons:
- CodeDeploy Agent might not be installed, running, or it can’t reach CodeDeploy
- CodeDeploy Service Role or IAM instance profile might not have the required permissions
- You’re using an HTTP Proxy, configure CodeDeploy Agent with :proxy_uri: parameter
- Date and Time mismatch between CodeDeploy and Agent
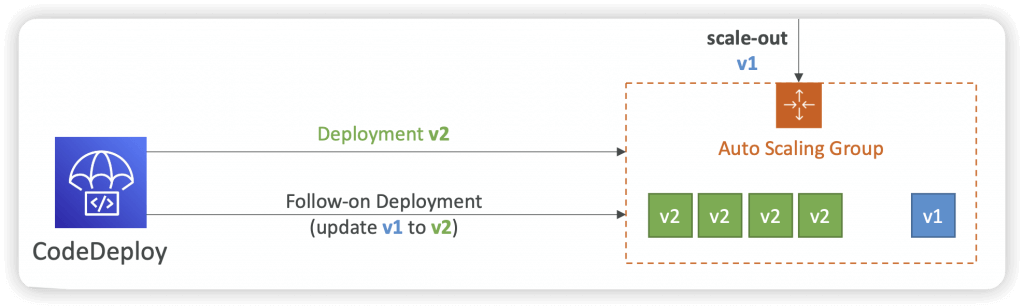
- CASE THREE – If a CodeDeploy deployment to ASG is underway and a scale-out event occurs, the new instances will be updated with the application revision that was most recently deployed (not the application revision that is currently being deployed)
- ASG will have EC2 instances hosting different versions of the application
- By default, CodeDeploy automatically starts a follow-on deployment to update any outdated EC2 instances
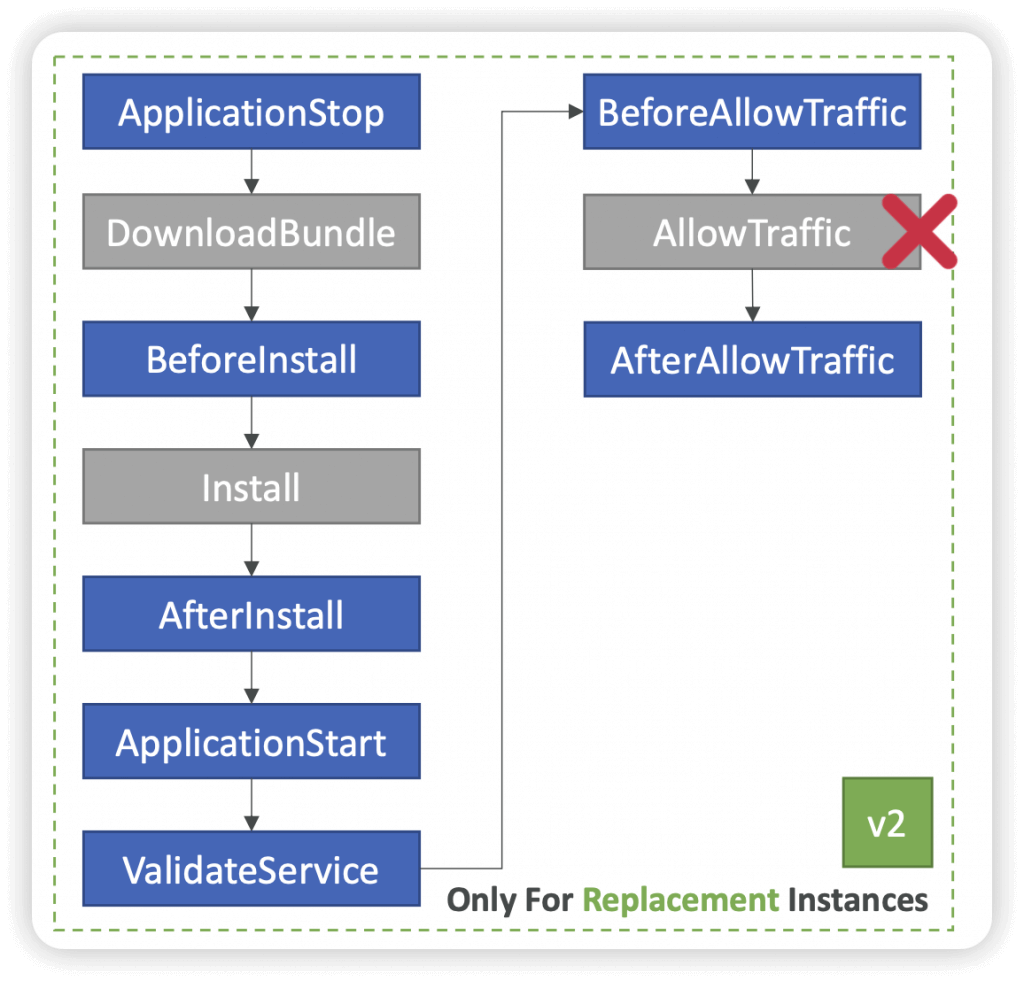
- CASE FOUR – failed AllowTraffic lifecycle event in Blue/Green Deployments with no error reported in the Deployment Logs
- Reason: incorrectly configured health checks in ELB
- Resolution: review and correct any errors in ELB health checks configuration
- CASE ONE – Deployment Error: “InvalidSignatureException – Signature expired: [time] is now earlier than [time]”
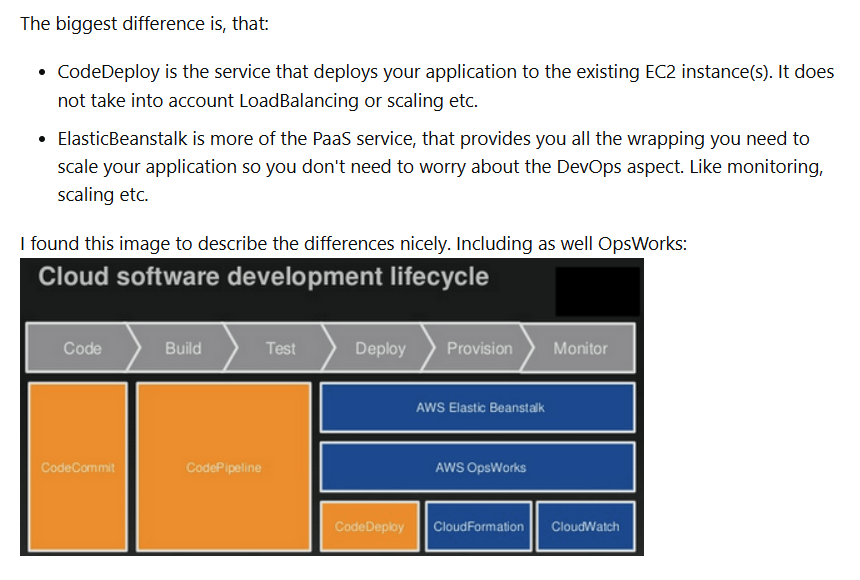

AWS CodeArtifact
- store, publish, and share software packages (aka code dependencies)
- Software packages depend on each other to be built (also called code dependencies), and new ones are created
- Storing and retrieving these dependencies is called artifact management
- Works with common dependency management tools such as Maven, Gradle, npm, yarn, twine, pip, and NuGet
- Developers and CodeBuild can then retrieve dependencies straight from CodeArtifact
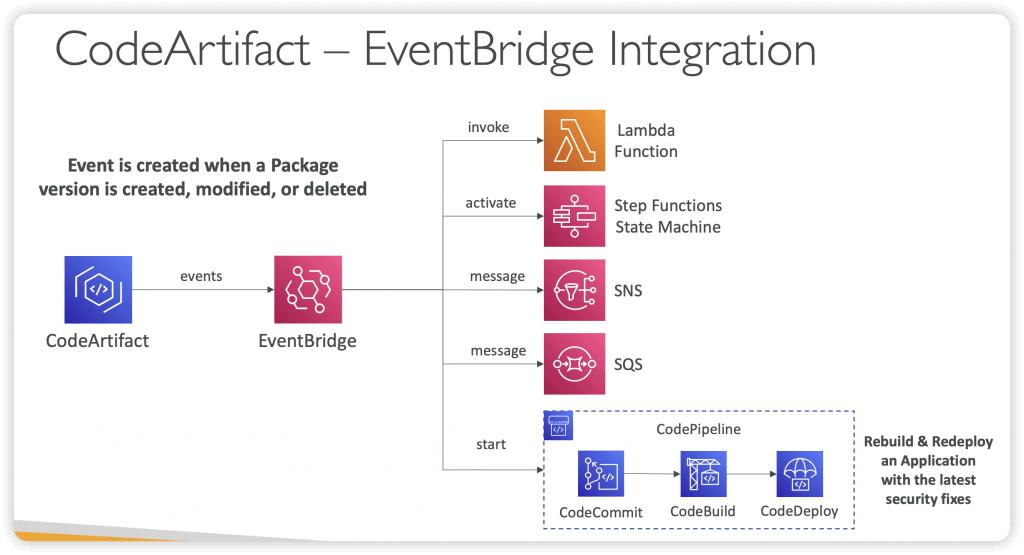
- CodeArtifact seamlessly integrates with Amazon EventBridge, a service that automates actions responding to specific events, including any activity within a CodeArtifact repository. This integration allows you to establish rules that dictate the actions to be taken when a particular event occurs.
- Resource Policy
- Can be used to authorize another account to access CodeArtifact
- A given principal can either read all the packages in a repository or none of them
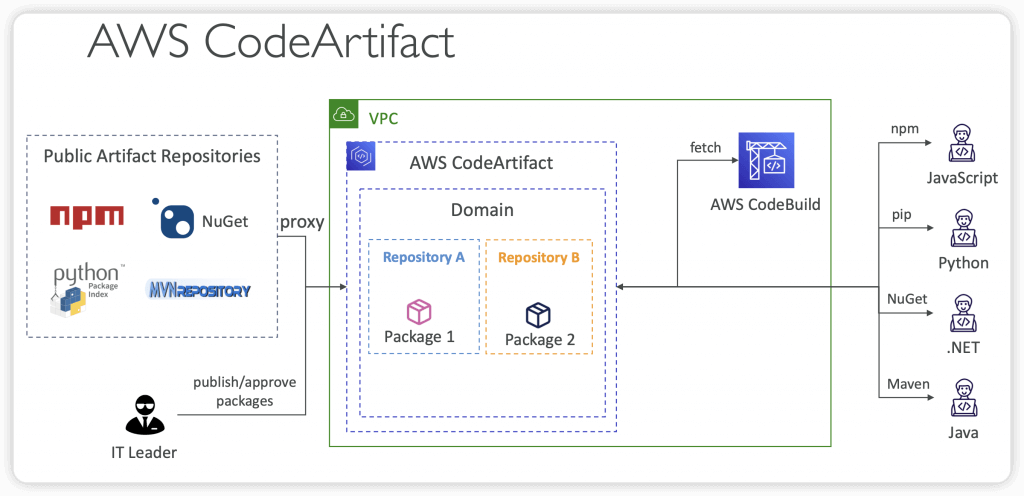
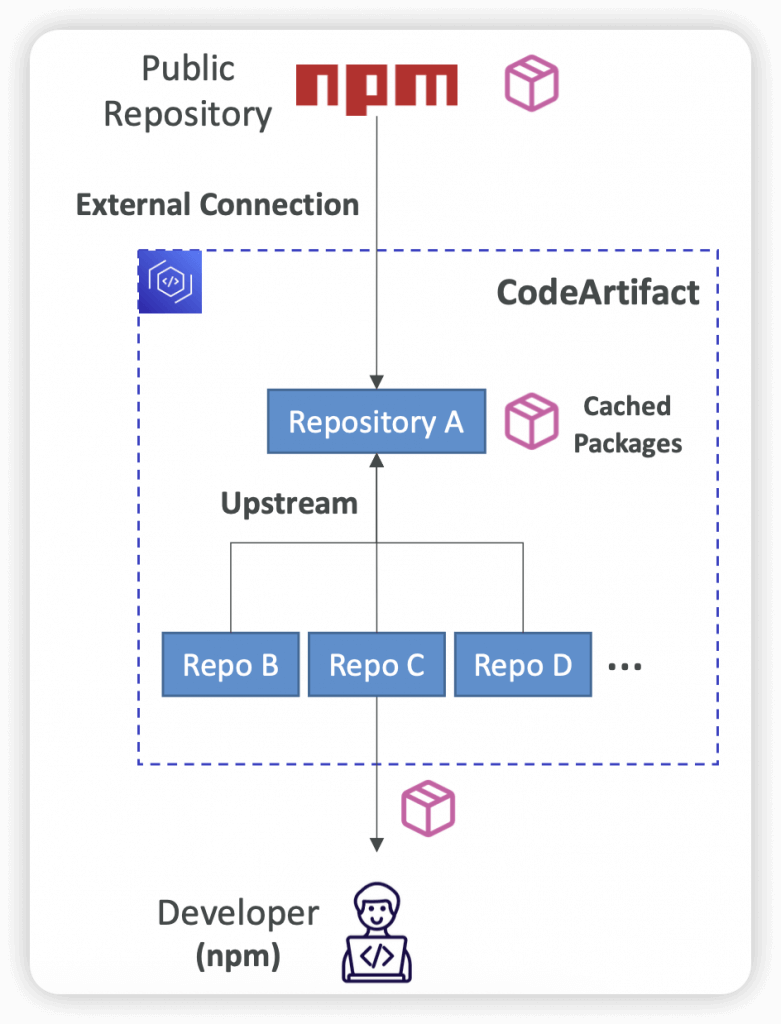
- Upstream Repositories
- A CodeArtifact repository can have other CodeArtifact repositories as Upstream Repositories
- So it works as a proxy, to keep the “depedencies” cached
- Allows a package manager client to access the packages that are contained in more than one repository using a single repository endpoint
- Up to 10 Upstream Repositories
- Only one external connection
- A CodeArtifact repository can have other CodeArtifact repositories as Upstream Repositories
- External Connection
- An External Connection is a connection between a CodeArtifact Repository and an external/public repository (e.g., Maven, npm, PyPI, NuGet…)
- A repository has a maximum of 1 external connection
- Create many repositories for many external connections
- Example – Connect to npmjs.com
- Configure one CodeArtifact Repository in your domain with an external connection to npmjs.com
- Configure all the other repositories with an upstream to it
- Packages fetched from npmjs.com are cached in the Upstream
- Example – Connect to npmjs.com
- Retention
- If a requested package version is found in an Upstream Repository, a reference to it is retained and is always available from the Downstream Repository
- The retained package version is not affected by changes to the Upstream Repository (deleting it, updating the package…)
- Intermediate repositories do not keep the package
- Example – Fetching Package from npmjs.com
- Package Manager connected to Repository A requests the package Lodash v4.17.20
- The package version is not present in any of the three repositories
- The package version will be fetched from npmjs.com
- When Lodash 4.17.20 is fetched, it will be retained in:
- Repository A – the most-downstream repository
- Repository C – has the external connection to npmjs.com
- The Package version will not be retained in Repository B as that is an intermediate Repository
- Example – Fetching Package from npmjs.com
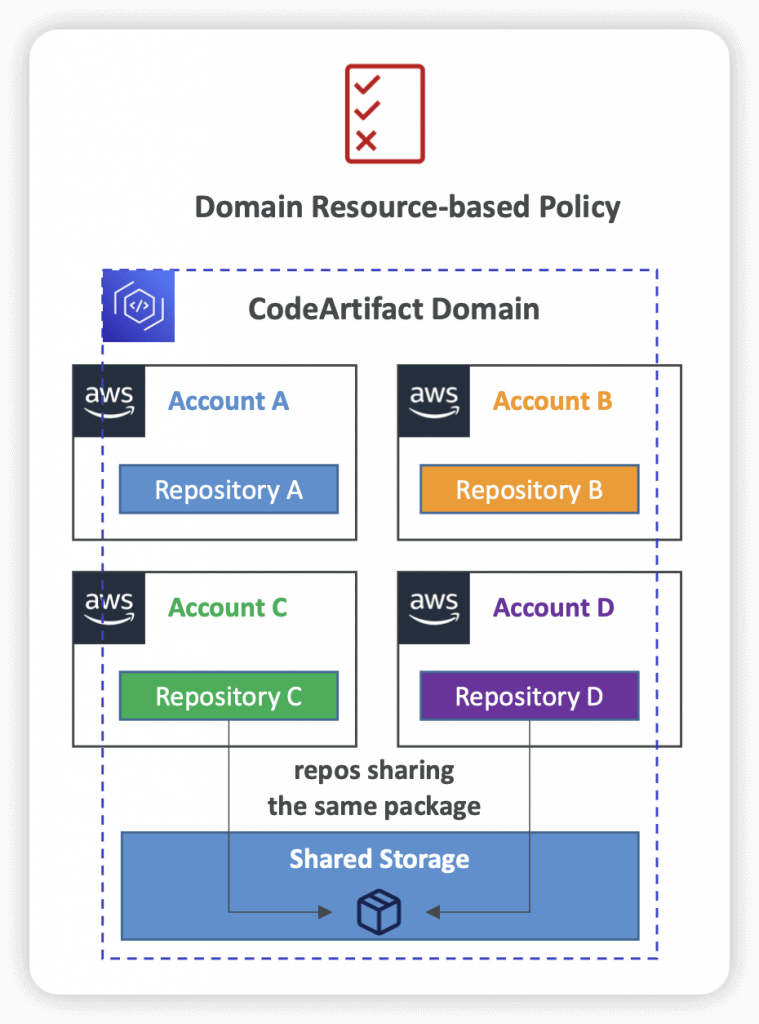
- Domains
- Deduplicated Storage – asset only needs to be stored once in a domain, even if it’s available in many repositories (only pay once for storage)
- Fast Copying – only metadata record are updated when you pull packages from an Upstream CodeArtifact Repository into a Downstream
- Easy Sharing Across Repositories and Teams – all the assets and metadata in a domain are encrypted with a single AWS KMS Key
- Apply Policy Across Multiple Repositories – domain administrator can apply policy across the domain such as:
- Restricting which accounts have access to repositories in the domain
- Who can configure connections to public repositories to use as sources of packages
AWS CodeGuru
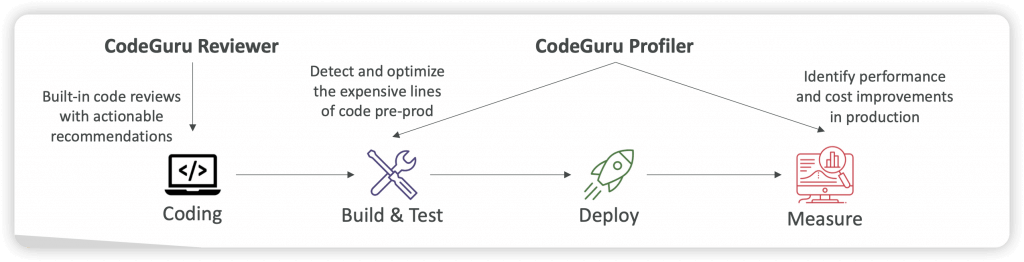
- a developer tool that provides intelligent recommendations to improve the quality of your codebase and for identifying an application’s most “expensive” lines of code in terms of resource intensiveness, CPU performance, and code efficiency
- using Machine Learning for automated code reviews and application performance recommends
- CodeGuru Reviewer – identify critical issues, security vulnerabilities, and hard-to-find bugs
- automated code reviews for static code analysis (development)
- Example: common coding best practices, resource leaks, security detection, input validation
- Uses Machine Learning and automated reasoning
- CodeGuru Reviewer Secrets Detector
- Uses ML to identify hardcoded secrets embedded in your code (e.g., passwords, API keys, credentials, SSH keys…)
- Besides scanning code, it scans configuration and documentation files
- Suggests remediation to automatically protect your secrets with Secrets Manager
- CodeGuru Profiler
- visibility/recommendations about application performance during runtime (production)
- Example: identify if your application is consuming excessive CPU capacity on a logging routine
- Features:
- Identify and remove code inefficiencies
- Improve application performance (e.g., reduce CPU utilization)
- Decrease compute costs
- Provides heap summary (identify which objects using up memory)
- Anomaly Detection
- Support applications running on AWS or on-premise
- Minimal overhead on application
- Integrate and apply CodeGuru Profiler to Lambda functions either using:
- Function Decorator @with_lambda_profiler
- Add codeguru_profiler_agent dependency to your Lambda function .zip file oruse Lambda Layers
- Enable Profiling in the Lambda function configuration
- Function Decorator @with_lambda_profiler
- CodeGuru Reviewer – identify critical issues, security vulnerabilities, and hard-to-find bugs
- Supports Java and Python
- CodeGuru Agent
- MaxStackDepth – the max depth of chain on method call
- MemoryUsageLimitPercent
- MinimumTimeForReportingInMilliseconds
- ReportingIntervalInMilliseconds
- SamplingIntervalInMilliseconds
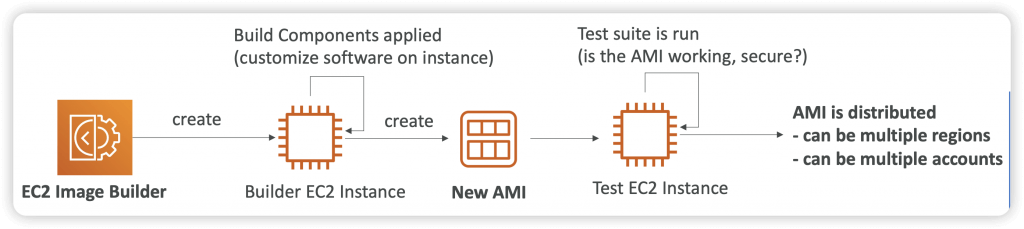
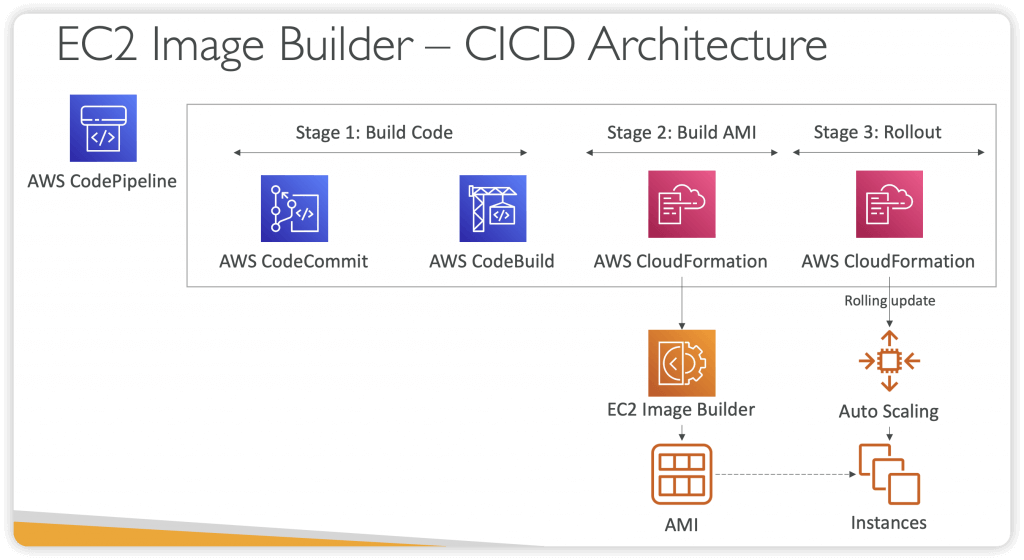
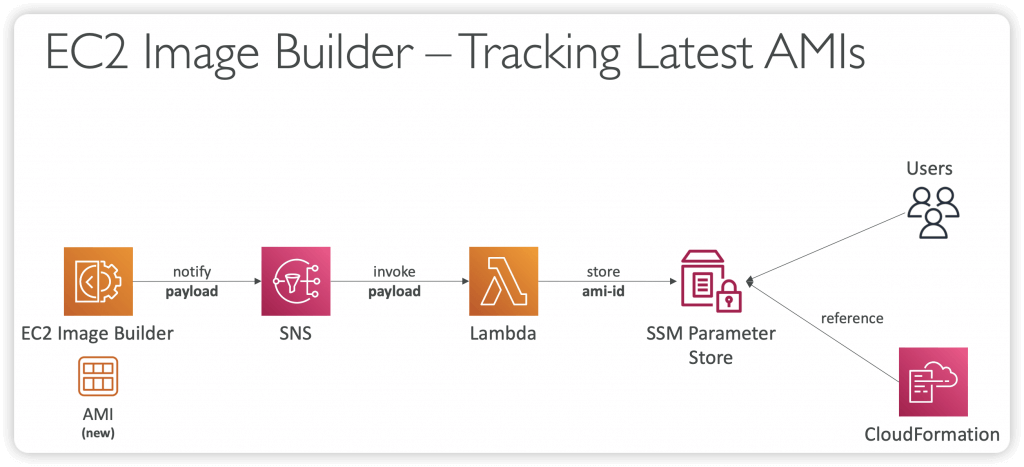
EC2 Image Builder
- Used to automate the creation of Virtual Machines or container images
- => Automate the creation, maintain, validate and test EC2 AMIs
- Can be run on a schedule (weekly, whenever packages are updated, etc…)
- Free service (only pay for the underlying resources)
- Can publish AMI to multiple regions and multiple accounts
- Use AWS Resource Access Manager (RAM) to share Images, Recipes, and Components across AWS accounts or through AWS Organization
| Parameters | AWS EC2 Image Builder | Packer |
|---|---|---|
| Tool Type | Fully managed service by AWS | Open-source tool by HashiCorp |
| Supported Platforms | Primarily for AWS (EC2 AMIs) with integration into AWS services | Multi-cloud (AWS, Azure, GCP), on-premise, and container platforms |
| Customization | Limited to AWS-managed pipelines, some customization possible | Fully customizable, supports a wide range of provisioners like Ansible, Chef, Shell |
| Ease of Use | User-friendly, integrated with AWS services, no manual server setup | Requires manual configuration, more complex setup but highly flexible |
| Cost | No additional cost beyond the AWS resources used | Free (open-source), but costs may arise from cloud usage during image builds |
| Automation | Fully automated AMI creation and distribution pipelines | Can be automated but requires more manual setup and scripting for pipelines |
| Testing & Validation | Integrated with AWS services like CloudWatch and Systems Manager for validation | Requires custom scripting or external tools for validation and testing |
| Version Control | Provides version control for image pipelines within the AWS ecosystem | Supports versioning of templates but requires manual version control of scripts |
| Multi-environment Support | Primarily focused on AWS environments | Supports multiple cloud environments, containers, and virtualization platforms |
| Parallel Builds | Limited to AWS resources; no built-in multi-cloud capability | Supports parallel image creation for multiple environments simultaneously |
| Security & Compliance | Built-in security updates and compliance checks via AWS services | Requires manual setup of security updates and compliance integration |
| Integration with IaC | Native integration with AWS services like CloudFormation | Integrates with Terraform, making it versatile across platforms |